What if the biggest threat to your organization isn’t an obvious breach, but a stealthy attack that blends in with normal user activity?
Cybercriminals are moving away from traditional methods, using devastatingly clever techniques to bypass defenses unnoticed.
In this context, cloud network security becomes a critical line of defense in protecting sensitive data and ensuring business continuity.
This article will explore the key components of cloud network security, the challenges ahead, and best practices to protect your cloud infrastructure.
- What is Cloud Network Security?
- Components of Cloud Network Security
- Importance of Cloud Network Security
- Challenges in Cloud Network Security
- Best Practices for Cloud Network Security
- Cloud Network Security vs Traditional Network Security
- Private Cloud vs Public Cloud Network Security
- Advanced Cloud Network Security Solutions
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Cloud Network Security?
Cloud network security is the practice of protecting your organization’s cloud-based data, applications, and infrastructure from unauthorized access, tampering, exposure, or misuse.
There are three core elements to it:
Data Protection
Employing encryption and strict access controls to protect sensitive information from threat actors.
Threat Prevention
Identifying vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors before they can be exploited, blocking malicious attempts in real-time.
Compliance
Ensuring that your security practices align with industry standards and legal requirements, protecting you from financial or reputational damage.
A resilient, secure infrastructure involves embracing cloud network security as a strategic priority, giving you the instruments you need to mitigate risks, maintain control, and thrive in an increasingly hostile environment.
Components of Cloud Network Security
Securing your cloud network relies on integrating key components that protect data, applications, and resources.
Each element plays a pivotal role in minimizing risks and ensuring the integrity of your infrastructure.
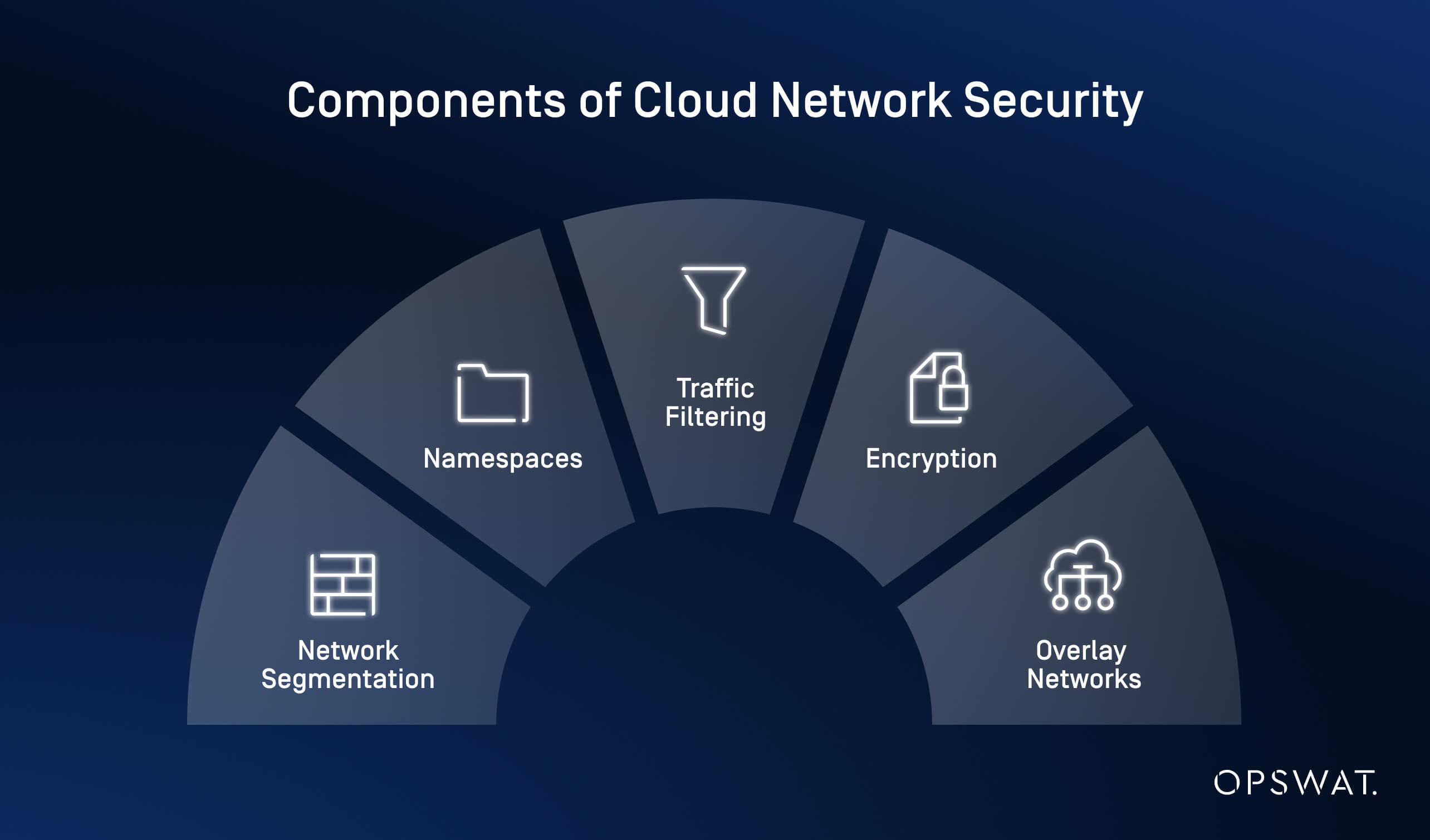
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides the cloud network into smaller, isolated sections.
This prevents attackers from easily spreading throughout the infrastructure if a breach occurs and limits access to sensitive data and high-risk areas.
Namespaces
Namespaces are logical divisions within your cloud environment that organize resources.
They separate services or workloads, reducing the risk of cross-contamination between environments like development, staging, and production.
Traffic Filtering
Using firewalls, Access Control Lists, and Intrusion Detection Systems, traffic filtering inspects incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Traffic filtering blocks unwanted activity before it reaches critical systems, acting as a defense against unauthorized access and attacks.
Encryption
Encryption turns data into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted with the right key.
It applies to both data in transit and at rest, making it harder for attackers to access sensitive information, even if they intercept it.
Overlay Networks
Overlay networks create a virtual layer on top of your cloud infrastructure, allowing secure communication between resources, regardless of the underlying network.
While they don’t directly enforce security policies, overlay networks help manage encryption, filtering, and segmentation more efficiently, providing a stronger security stance.
Keep in mind that, as you strengthen your defenses, cyberthreats will target your vulnerabilities, so it’s important to regularly update these components to maintain a resilient security stance.
Importance of Cloud Network Security
Cybercriminals exploit misconfigurations, weak access controls, and unprotected APIs to gain unauthorized entry.
Once inside, they can move across systems, steal sensitive information, or deploy ransomware that locks organizations out of their own data.
Security gaps can endanger business operations, lead to regulatory violations, fines, and harm a company's reputation.
Despite these challenges, strong security solutions exist to enforce policies, detect malicious activity, and secure communications in real-time.
These solutions go beyond just protection and compliance.

Improved Visibility and Centralized Management
Cloud network security solutions offer centralized monitoring, allowing teams to oversee network activity from a single interface. This simplifies threat detection, traffic analysis, and response efforts, reducing the need for juggling multiple tools.
Consistent Policy Enforcement Across Networks
Managing security policies across multiple cloud providers and hybrid environments can be complex.
Cloud network security solutions simplify this process by allowing organizations to define and enforce policies from a central platform. This ensures security controls are applied consistently, minimizing misconfigurations that attackers could exploit.
Enhanced Protection Against Cyberthreats
Cloud network security solutions defend against a variety of attacks, such as DDoS, unauthorized access, and malware distribution.
Advanced threat intelligence, powered by machine learning, detects suspicious activity and responds automatically to block threats before they cause harm.
Automated Network Security Management
Automation helps reduce human error, one of the leading causes of security breaches.
With automated traffic filtering, policy enforcement, and network segmentation, security teams can focus on more strategic tasks while the system handles routine maintenance.
Unified Security Across Distributed Networks
Organizations with a mix of cloud and on-premises infrastructure need a consistent security approach.
Cloud network security solutions ensure that the same security protocols apply across all environments, reducing weak points and simplifying security management as your network grows.
Risks and Benefits
Cloud network security often gets overlooked until a problem arises, but phishing, ransomware, and other attacks continue to rise.
This happens because cyber attackers are always on the hunt for cloud environments that lack strong defenses:
- Misconfigured storage buckets have led to large-scale data leaks.
- Unprotected APIs act as open doors for attackers.
- Weak authentication allows unauthorized access to critical resources.
To avoid these risks, treat cloud security as an ongoing process, not a one-time task.
Prioritizing cloud security better equips organizations to defend against threats, minimize financial losses, and maintain trust with customers and stakeholders.
Challenges in Cloud Network Security
Achieving full security in the cloud is challenging due to its flexibility, which introduces new concerns. For instance, when cloud infrastructure is shared, attacks targeting other tenants can cause service disruptions.
Another issue is “shadow IT,” where employees use unauthorized cloud services, bypassing the IT department's security measures and introducing potential entry points for attackers.
Cloud resources are dynamic, appearing and disappearing regularly, making traditional security monitoring more difficult.
Temporary systems might not undergo a security review, leaving them vulnerable.
Continuous monitoring and automated security tools are critical for detecting risks in such fluid environments.
Visibility and Misconfigurations
Cloud services give employees the flexibility to create and manage resources independently, but this also makes it harder for security teams to track all assets.
Limited visibility increases the risk of unauthorized access, misconfigurations, and undetected vulnerabilities.
For example, misconfigured cloud settings are one of the leading causes of data breaches.
A simple mistake – such as an open storage bucket or weak access controls – can expose critical data.
The issue becomes even more problematic when the organization is constantly scaling its cloud infrastructure, so security gaps may remain undetected for long periods.
Conducting regular audits and continuously monitoring resources is necessary to identify vulnerabilities quickly.
Best Practices for Cloud Network Security
With the flexibility and scalability that cloud infrastructure offers, avoiding it due to associated risks would be unwise.
Fortunately, proactive measures can help safeguard your cybersecurity.
While no system can be truly invulnerable, you can significantly reduce your risk and avoid becoming an easy target.
Key measures include implementing strict network policies, conducting regular security assessments and audits, and embracing the paradigm shift of a zero-trust security model.
Zero-Trust and Policy Enforcement
Zero-trust fundamentally changes how access control, trust, and security are managed within an organization.
In the traditional "castle-and-moat" approach, security focuses on defending the perimeter, trusting everything inside the network.
In zero-trust, everything – users, devices, and applications – is considered compromised.
This model comes with a “never trust, always verify” approach, in which every user, device, and application, whether inside or outside the network, is treated as potentially compromised.
The zero-trust model includes:
- Role-based access control.
- Multi-factor authentication.
- Continuous traffic filtering and DDoS protection.
Regular audits are also deployed to evaluate your organization's unique risks, and incident response protocols are created to adapt to evolving threats.
Cloud Network Security vs Traditional Network Security
Many organizations attempt to adjust traditional security models to fit the cloud, only to create blind spots, slow down operations, and struggle with scaling defenses against modern threats.
Traditional network security models differ from cloud-based ones in several key ways.
Deployment and Infrastructure
Cloud network security operates through software-defined security solutions, including cloud firewalls, security groups, and zero-trust architectures.
Security functions are integrated directly into cloud platforms, so there’s no need for physical hardware, as opposed to traditional network security, which relies on hardware-based security appliances such as Intrusion Prevention Systems and Network Access Control devices.
These require on-premises installation and physical maintenance.
Scalability and Adaptability
Traditional security solutions require manual configuration and planning for capacity, while cloud security adapts automatically to changes in demand.
Traffic Inspection and Threat Detection
Modern cloud network security solutions use AI-driven threat detection, behavior analytics, and deep packet inspection across distributed environments.
Security tools monitor east-west (internal cloud) and north-south (inbound/outbound) traffic at a granular level.
Traditional network security primarily focuses on perimeter defense with firewall rules, signature-based intrusion detection, and manual log analysis.
Monitoring internal network traffic is more challenging due to limited visibility.
Security Policy Enforcement
Compliance checks and remediations happen in real-time in cloud network security, while in traditional network security, they take time to implement and are prone to human error.
Control and Visibility
An important distinction between the two is your control over the network.
Traditional security assumes that critical assets stay within a controlled perimeter.
IT teams set up firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and monitoring tools based on predictable traffic and static infrastructure.
In cloud environments, resources launch and shut down frequently, often managed by teams outside of IT’s direct oversight. This creates opportunities for misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and shadow IT.
Cloud-native security solutions address these issues by integrating with cloud service provider APIs, allowing security teams to track assets, monitor network activity, and apply policies without deploying physical hardware.
Unlike perimeter-based logging, these tools analyze traffic in real-time, detect unauthorized changes, and flag anomalies before they escalate.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud Network Security
Many organizations might be tempted to migrate toward a private cloud network security, believing that public clouds carry higher risks due to shared infrastructure.
Though this is partly true, the real risk lies in how security responsibilities are managed, not necessarily the location.
Security Considerations
Organizations in regulated industries—such as healthcare, finance, and defense—often choose private clouds to control security configurations, data storage, and compliance requirements.
Customization options are extensive, but internal teams must manage all security operations, including patching and monitoring.
On the other hand, in the public cloud, providers handle all infrastructure security, allowing organizations to focus on securing applications, data, and access.
These providers invest heavily in cybersecurity, often surpassing what most businesses can achieve independently.
The greatest risks here usually come from misconfigurations—such as over-permissioned accounts, exposed storage, or unmonitored APIs—which attackers frequently exploit.
As for control, private clouds provide greater control but require strong security expertise. Public clouds simplify security operations but demand careful configuration to avoid exposure.
Hybrid Cloud: Combining Private and Public Security Strategies
A better solution, without all the drama, is using a mix of private and public cloud resources.
This approach brings flexibility but also creates new security challenges.
To address these challenges, organizations should implement:
- Unified (IAM) Identity and Access Management
- Consistent Encryption Standards
- Zero Trust Network Segmentation
Advanced Cloud Network Security Solutions
An industry as dynamic as cybersecurity is naturally impacted by Artificial Intelligence. But how exactly does AI enrich cybersecurity capabilities?
AI and Machine Learning
AI-driven threat detection uses (ML) machine learning and (DL) deep learning to monitor network activity and detect anomalies. AI helps detect threats earlier in the attack cycle, reducing damage and preventing breaches.
Machine learning also helps predict emerging threats based on historical data.
For critical financial transactions, organizations can deploy blockchain technologies and leverage a secure, transparent, and immutable environment, making it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter transaction data.
Conclusion
The threat to your organization is no longer just about breaches you can see.
Stealthy, sophisticated attacks are slipping past traditional defenses, making cloud network security an urgent priority.
It’s time to strengthen your defenses.
MetaDefender Cloud™ offers a powerful, zero-trust solution to secure your organization from file-borne malware and advanced cyberattacks.
Explore how our solution safeguards your sensitive data and ensures continuous protection for your cloud infrastructure.
FAQs
What is cloud network security?
Cloud network security is the practice of protecting cloud-based data, applications, and infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, tampering, or exposure. It includes data protection, threat prevention, and compliance with industry and legal standards to maintain security and business continuity.
What are the core components of cloud network security?
Key components of cloud network security include:
Network segmentation: Divides networks into isolated zones to limit attacker movement.
Namespaces: Organize cloud resources to separate workloads and environments.
Traffic filtering: Uses firewalls and intrusion detection to block unwanted activity.
Encryption: Secures data in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access.
Overlay networks: Enable secure communication between cloud resources across different infrastructures.
Why is cloud network security important?
Cloud environments are frequent targets for attackers due to misconfigurations, weak access controls, and unprotected APIs. Strong cloud network security helps prevent data theft, operational disruption, and regulatory non-compliance. It also improves visibility, simplifies policy enforcement, and enhances protection with automated and AI-powered tools.
What challenges exist in securing cloud networks?
Challenges include:
Shared infrastructure risks: Attacks on other tenants may impact your systems.
Shadow IT: Unauthorized cloud use bypasses IT controls and creates security gaps.
Dynamic environments: Rapid changes make traditional security monitoring harder.
Limited visibility: Teams may miss misconfigurations or unauthorized changes.
Human error: Misconfigured settings are a leading cause of data breaches.
What are the best practices for cloud network security?
Effective practices include:
Adopting a zero-trust model with role-based access and multi-factor authentication.
Enforcing strict network policies and conducting regular audits.
Using continuous traffic monitoring and DDoS protection.
Implementing automated security tools for consistent enforcement and rapid response.
How does cloud network security differ from traditional network security?
Traditional network security relies on perimeter defenses and physical hardware, while cloud network security uses software-defined tools that integrate directly with cloud environments. Cloud security is more scalable, uses AI for real-time threat detection, and adapts to dynamic infrastructure more efficiently.
What is the difference between private and public cloud network security?
Private clouds offer more control over security configurations and are preferred in regulated industries. However, they require internal management of all security operations. Public clouds rely on the provider for infrastructure security but offer scalability and automation. Misconfigurations, not the cloud model itself, are often the biggest risk.
What is hybrid cloud network security?
Hybrid cloud security combines private and public cloud strategies, offering flexibility with added complexity. It requires consistent identity and access management (IAM), unified encryption standards, and segmentation policies like zero-trust to maintain strong security across all environments.
How does AI enhance cloud network security?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) improve threat detection by analyzing network behavior and identifying anomalies in real time. These tools can detect threats earlier in the attack cycle and help predict emerging threats based on historical data. Blockchain may also be used for secure, tamper-resistant financial transactions.
Why is cloud network security a priority today?
Cyberattacks are becoming stealthier, often blending into normal activity. Traditional defenses are no longer enough. Cloud network security provides proactive protection against these threats, helping organizations reduce risk, protect sensitive data, and maintain business continuity.



