As our reliance on the cloud grows, it’s easy to envision a world where everything—from knowledge to critical infrastructure—is stored in a massive digital vault.
By 2025, global cloud storage will hit 200 zettabytes, equivalent to storing 200 billion 4k movies or 200 quadrillion books.
According to the 2024 Thales Cloud Security Study, 44% of organizations have faced a cloud data breach this year, with 14% reporting cloud security issues within the last year.
With cloud security threats like malware, ransomware, and DoS attacks on the rise, and the added challenge of user non-compliance, protecting cloud environments against threat actors has never been more crucial.
In this article, we’ll walk through the biggest cloud security risks, threats, and challenges, and explain how organizations can address them to secure sensitive information effectively.
Top 6 Cloud Security Risks
In the context of cloud security, risk refers to the potential for harm due to weaknesses within your infrastructure. Before fixing your potential security gaps, you first need to understand where your vulnerabilities exist.
To that end, here are some of the most common risks found within cloud infrastructure.

1. Data Breaches
Data breaches are among the most damaging security threats to cloud systems, often caused by weak access controls, misconfigured cloud settings, or unsecured APIs.
Sensitive information can be stolen, altered, or destroyed, resulting in staggering financial and reputational costs with the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.45 million in 2023.
Hackers only need to find one vulnerability to get in and damage a company’s reputation forever, as seen in Yahoo’s 2013 breach, which led to a $350 million discount on its acquisition price.
2. Data Loss and Corruption
The impact data loss has on your organization can range from temporary disruptions to a total loss of business continuity, completely paralyzing your operations.
While backing up data and having a recovery plan can minimize this risk, maintaining data integrity is equally important.
This involves properly configuring your cloud environments to prevent unauthorized changes or data corruption.
3. Account Hijacking
Account hijacking occurs when cybercriminals steal legitimate user accounts to access sensitive data or launch further attacks.
Common methods of hijacking include phishing, credential stuffing, and brute-force attacks.
To protect against these threats, it’s essential to implement (MFA) Multi-Factor Authentication, enforce strong password policies, and monitor for unusual account activity
The goal is to make it as difficult as possible for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
4. Insider Threats
Not all threats come from outside your organization, with insider threats becoming a growing concern in cloud security.
Employees, contractors, and third-party vendors with access to critical systems and sensitive data, can misuse the privilege and compromise cloud security — whether out of malice or by accident.
To mitigate insider risks, enforce the principle of least privilege and carefully monitor user activity.
5. Misconfiguration and Weak Access Controls
One of the most frustrating cloud vulnerability roots is misconfiguration.
When cloud environments are not set up correctly, they leave doors wide open for attackers. This can happen during the initial setup or when resources are updated or scaled.
It’s crucial to secure public-facing resources and ensure only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
Regularly auditing configurations, automating security checks, and applying the principle of least privilege are essential practices to avoid misconfigurations.
6. Insecure APIs
APIs are integral to cloud services, enabling communication between different systems. However, unsecured APIs can become entry points for attackers.
Common security gaps include poor authentication practices, unencrypted data, and weak rate-limiting.
Secure your APIs with strong authentication methods (such as tokens), data encryptions and API gateways that monitor and control API traffic.
Top 5 Cloud Security Threats
If risks are possibilities of damage or loss, then the threat is the actual source or event that could trigger that damage.
While you can't fully control threats, you can still take proactive steps to mitigate their impact.
Here’s an overview of the most common threats faced by cloud-based organizations, based on real-world cybersecurity scenarios.

1. Malware and Ransomware Attacks
Malware and ransomware are among the most dangerous threats to cloud environments.
Cybercriminals can infiltrate your cloud services, encrypt your data, and demand a ransom for its release. The average extortion demand per ransomware attack exceeded USD 5.2 million this year.
A strong defense against ransomware requires a multi-layered approach, including secure backup solutions, endpoint protection, and malware detection.
For even greater protection, consider OPSWAT’s advanced technologies: multiscanning, CDR, and Sandboxing.
2. DoS Attacks
(DoS) Denial of Service attacks overwhelm cloud services with a flood of traffic, rendering them unavailable to legitimate users.
While they may not result in data loss, they can severely disrupt operations and impact productivity.
Defenses include traffic filtering, rate-limiting, and automated systems to detect and respond to abnormal activity.
With DoS, you must guarantee that your resources can handle heavy traffic loads without crashing under pressure.
3. Inadequate Diligence by Providers and Users
Cloud security is a shared responsibility between the user and the provider.
But not everyone understands the full extent of their role, leaving room for vulnerabilities to creep in.
To mitigate this, perform due diligence on providers’ security practices, supplement them with your protocols, and schedule third-party audits to assess your cloud compliance.
4. Abuse of Cloud Services by Threat Actors
Malicious actors often exploit cloud services like computing power, storage, and cloud databases for cryptojacking (using your computing power to mine cryptocurrencies) or distributing malware.
For cloud users, these abuses translate into system slowdowns or data loss, while providers suffer from financial and regulatory fines.
To catch suspicious activity before it’s too late, watch for unusual spikes in processing power or unexpected file sharing.
5. Threats from Shared Tenancy
In a shared cloud environment, your data coexists with data from other organizations.
While cloud providers ensure logical separation, vulnerabilities can still arise from misconfigurations or issues like “noisy neighbors” — where the activities of other tenants affect your resources.
Using virtual private clouds (VPCs) or dedicated instances can reduce these risks.
Top 5 Cloud Security Challenges
Your cloud security strategy isn’t limited to identifying risks and mitigating threats.
A strong defense also involves overcoming challenges like monitoring an expanding attack surface, ensuring compliance, managing visibility and control, understanding the shared responsibility model, and balancing speed with security.
Let’s look at some of the obstacles which will demand your careful attention, resources, and planning along the way.
1. Ensuring Compliance in a Multi-Cloud Environment
Different cloud providers have varying security standards, making compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA risky and complex.
If you’re operating in a multi-cloud environment, use compliance tools and frameworks to streamline the process and ensure your infrastructure meets all requirements.
2. Lack of Visibility and Control
Unlike on-prem solutions, cloud environments lack direct visibility and control.
Cloud-native security monitoring tools can provide insight into all activities, allowing you to detect and respond to threats proactively.
3. Complexity of the Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model, where providers secure infrastructure and users secure data, can create confusion and gaps.
To address this, clearly define roles, review responsibilities regularly, and ensure all parties understand their obligations.
4. Difficulty in Monitoring the Expanding Attack Surface
With more devices, remote workforces, and third-party integrations, the number of potential entry points for attackers increases.
Use security solutions with strong monitoring capabilities across all cloud resources to spot potential threats and react before they become serious incidents.
5. Balancing Agility and Security
The cloud enables rapid deployment of new services and features, but speed often comes at the cost of security.
To balance agility and security, adopt DevSecOps practices to ensure that security is built into every stage of your development cycle.
Automated security checks in your continuous integration deployment (CI/CD) pipelines will help catch vulnerabilities before they reach production.
When New Technologies Become Vulnerabilities
Before exploring cloud security solutions, it’s essential to address the vulnerabilities that come with new technologies.
Think of these vulnerabilities as challenges you must consider before fully embracing the advancements in the tech world.
Fortunately, for every vulnerability, there are strategies to address and mitigate its impact.
Here are some vulnerabilities that are currently a cause of concern in the cybersecurity world.

1. Quantum Computing
Quantum could render current encryption methods obsolete, allowing attackers to decrypt data with ease.
Researchers are now exploring quantum-resistant encryption algorithms designed to withstand quantum decryption capabilities, marking a crucial step toward securing the cloud in a post-quantum era.
2. AI and Machine Learning Vulnerabilities
While AI and Machine Learning systems are increasingly used in cloud environments, these models present specific vulnerabilities.
Some of these are adversarial attacks and data poisoning, where attackers subtly manipulate data to trick the system.
Protect these systems using anomaly detection and secure data handling, and train models to recognize data poisoning.
3. IoT and Edge Computing Security
The rise of the IoT and edge computing has opened new entry points for attackers.
To secure IoT devices, enforce strong authentication, implement regular software updates, and ensure that all data communications are encrypted.
Essentially, if you secure the endpoints, you can protect the cloud infrastructure from potential exploits.
How to Mitigate Cloud Security Risks
Now that you have a better understanding of the risks, threats, and challenges found in a cloud-based infrastructure, it’s time to focus on how to protect both yourself and your organization from the threat actors lurking in the cloud.
Let’s go through the essential actions you can take to strengthen your defenses and operate in an environment that is as secure as possible.
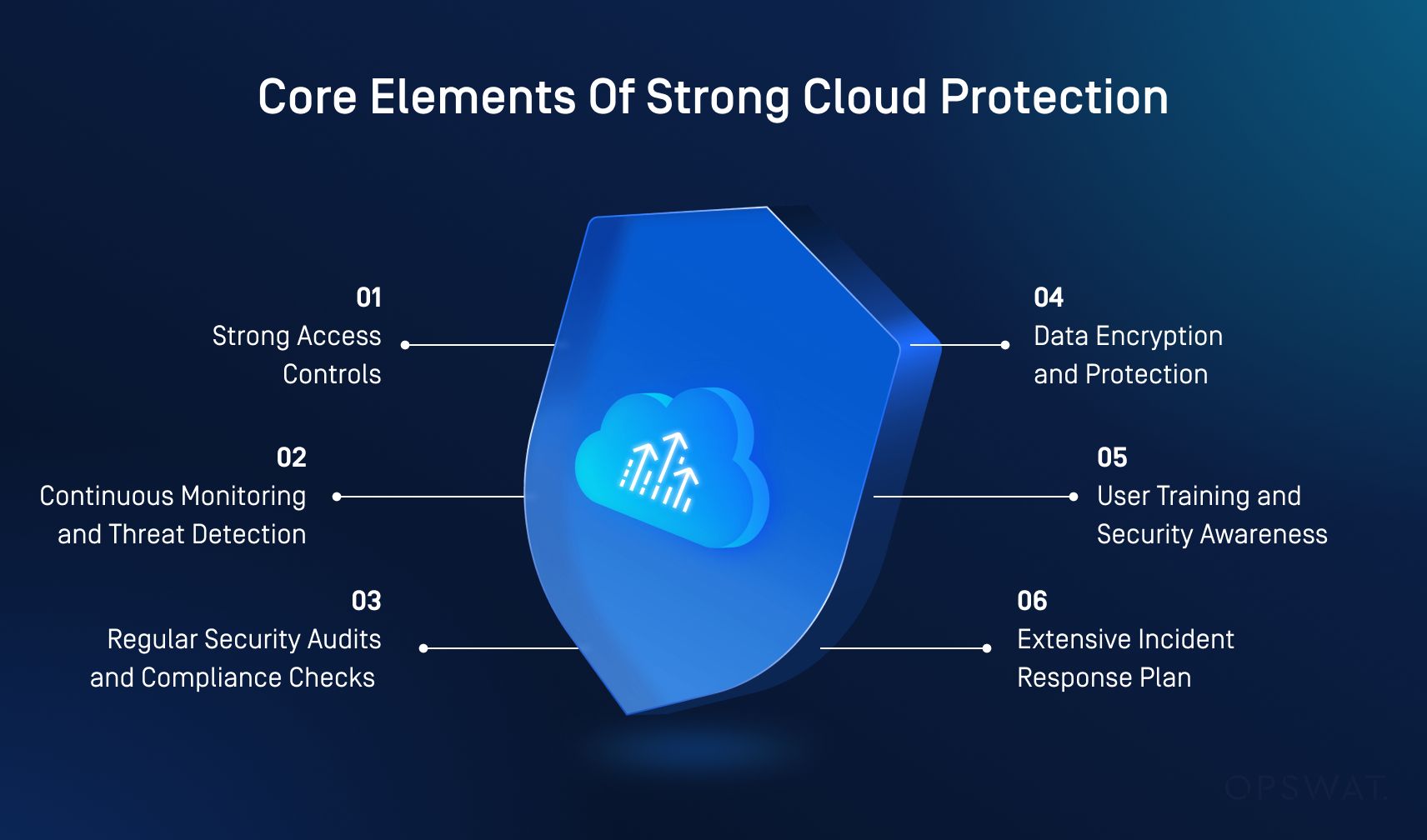
1. Strong Access Controls
Enforce the principle of least privilege and role-based access control to ensure that users have only the access they need to do their tasks.
Identity and access management systems can enforce these policies by verifying user identities, controlling access based on roles and permissions, and monitoring activities to ensure only authorized individuals can access cloud resources.
2. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Implement continuous monitoring solutions that detect abnormal behavior and potential threats.
Security Information and Event Management systems, intrusion detection systems, and Cloud Security Posture Management tools are invaluable in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they become major issues.
3. Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks
Schedule routine security audits to ensure compliance with best practices and regulatory standards.
Automated tools can help regularly review cloud configurations, access logs, and user activity.
4. Data Encryption and Protection
Always encrypt data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they can't interpret or use it.
You can use hardware security modules to manage encryption keys securely and maintain confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
5. User Training and Security Awareness
Human error remains one of the most significant causes of security breaches.
Security awareness training can teach employees how to recognize phishing attempts, secure passwords, and avoid social engineering scams.
However, training should not be viewed as optional.
Ensure that the content is up-to-date, engaging, and relevant, offering employees practical actions they can take to protect your cloud infrastructure.
6. Extensive Incident Response Plan
Finally, if all else fails, you should always have a cloud-specific incident response plan in place.
Unlike traditional IT systems, cloud environments present unique challenges due to their dynamic nature, shared responsibility models, and third-party integrations.
Considering its specific threat nature, your response plan should include steps like identifying the incident, containing its spread, and recovering data.
Identifying the breach helps contain the damage, while containment minimizes the impact.
Recovery restores normal operations, and all steps should be managed by a dedicated response team with clear roles and access to necessary resources.
Secure Your Cloud Before a Breach Happens
Cloud computing offers unparalleled advantages: more storage, next-level flexibility, fast scalability.
However, if an attacker has gained access to your infrastructure, all advantages can become your worst nightmare.
Proactive strategies, continuous monitoring, and employee training will keep you out of harm’s way.
Additionally, if you take your cloud security strategy seriously and reinforce your security controls, staying updated on threats and defenses will also be a definite advantage in the face of hackers.
Attackers never sleep, and neither should you.
Protect your business from file-based attacks with OPSWAT's MetaDefender Cloud.
Designed with a “Trust no file” philosophy, MetaDefender Cloud offers advanced cybersecurity tools to safeguard your digital environment.
FAQs
What are the top cloud security risks?
The top cloud security risks include:
Data breaches caused by weak access controls or misconfigured settings
Data loss and corruption that disrupts operations or compromises integrity
Account hijacking through phishing or stolen credentials
Insider threats from employees or third-party users misusing access
Misconfiguration and weak access controls that expose sensitive data
Insecure APIs that allow unauthorized access due to poor authentication
What are the most common cloud security threats?
The top cloud security threats include:
Malware and ransomware attacks that encrypt data and demand payment
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks that flood services and disrupt availability
Inadequate diligence by users or providers in enforcing proper security
Abuse of cloud services for activities like cryptojacking or malware hosting
Shared tenancy risks in multi-tenant environments that may allow cross-tenant impact
What are the main challenges in securing cloud environments?
Cloud security challenges include:
Ensuring compliance across multi-cloud infrastructures
Lack of visibility and control compared to traditional systems
Complexity of the shared responsibility model between users and providers
Monitoring an expanding attack surface caused by remote work and integrations
Balancing agility and security in fast-paced DevOps pipelines
How do new technologies create cloud security vulnerabilities?
Emerging technologies introduce new risks, including:
Quantum computing potentially breaking modern encryption
AI and machine learning vulnerabilities, such as data poisoning and adversarial inputs
IoT and edge computing security gaps that create new entry points for attackers
How can organizations mitigate cloud security risks?
Mitigation strategies include:
Enforcing strong access controls using IAM and role-based permissions
Continuous monitoring and threat detection with SIEM and CSPM tools
Conducting regular audits and compliance checks
Encrypting data at rest and in transit to ensure confidentiality
Training users on security awareness to reduce human error
Establishing a cloud-specific incident response plan for rapid containment and recovery
Why is misconfiguration such a critical cloud security risk?
Misconfiguration can expose public-facing resources or grant excessive permissions. These errors often happen during initial setup or updates and are a leading cause of cloud breaches. Regular audits and automated checks help prevent this issue.
How do shared cloud environments pose risks?
Shared tenancy can lead to risks such as "noisy neighbors" or misconfigured settings that impact multiple tenants. While providers maintain logical separation, users should use Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) or dedicated instances to reduce exposure.
What role do insiders play in cloud security risks?
Insider threats, accidental or intentional, stem from people within the organization, such as employees or vendors. They can misuse access to compromise systems or expose sensitive data. Least privilege access and activity monitoring help mitigate this risk.
How can inadequate diligence affect cloud security?
Failing to understand shared responsibility or assess provider security practices can create vulnerabilities. Organizations must conduct due diligence, establish their own protocols, and perform regular third-party audits to maintain compliance and security.

