- What Is Data Security Management?
- Why is Data Security Management Important?
- Core Principles: The CIA Triad
- Key Components and Technologies in Data Security Management
- Security Policies, Governance, and Training
- How to Implement Data Security Management: Step-by-Step Approach
- Data Security Management in Practice: Use Cases and Industry Examples
- Learn More
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Data Security Management?
Data security management is the process of protecting digital information throughout its lifecycle from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft. It involves the implementation of policies, technologies, and procedures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data (also known as the CIA triad).
Organizations rely on data security management to enforce compliance with data privacy regulations, reduce the risk of data loss or breach, and maintain trust with stakeholders. It incorporates strategies such as DLP (data loss prevention), encryption, and access control to manage and mitigate risks across a digital ecosystem.
Data Security Management vs. Information Security Management vs. Cybersecurity Management
While closely related, data security management, information security management, and cybersecurity management encompass different scopes:
- Data security management focuses specifically on protecting data assets from threats.
- Information security management is broader, encompassing the protection of all forms of information, whether digital or physical.
- Cybersecurity management covers the defense of systems, networks, and programs against digital attacks.
In short, data security is a subset of information security, which in turn falls under the larger umbrella of cybersecurity.
Why is Data Security Management Important?
Poor data security management can result in data breaches, regulatory fines, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. With increasing data volumes and cyberthreats, organizations must proactively manage how data is stored, accessed, and protected.
Effective data security management plays a vital role in data resilience, enabling businesses to recover from incidents and maintain continuity. It is also key to meeting regulatory compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI DSS.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Obligations
Data security management directly supports regulatory compliance by establishing controls that align with data protection laws. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and penalties, legal liability, and loss of customer trust.
By implementing DLP, encryption, and secure storage protocols, organizations can demonstrate due diligence in safeguarding sensitive information.
Core Principles: The CIA Triad
The CIA triad forms the foundation of data security management with three core principles:
- Confidentiality ensures only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- Integrity guarantees that data is accurate, reliable, and unaltered.
- Availability makes sure data is accessible when needed.
Balancing all three of these three pillars helps organizations meet security goals while supporting operational efficiency.
Applying the CIA Triad in Data Security Management
The CIA triad—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—is fundamental to data security. Each element plays a critical role in protecting data across its lifecycle, and real-world scenarios often require prioritizing different aspects depending on the use case.
Confidentiality: Protecting Sensitive Data
Confidentiality ensures that only authorized individuals access sensitive data. Key implementations include:
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control): Assigns access based on user roles, limiting data exposure to those who need it.
- Encryption: Secures data both at rest and in transit, making it unreadable without the correct decryption key.
In healthcare, for instance, patient records are encrypted to maintain confidentiality, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
Integrity: Ensuring Data Accuracy
Integrity ensures data remains accurate and unaltered. Techniques include:
- Checksums: Verify data integrity by comparing checksums to ensure no unauthorized changes.
- Version Control: Tracks and manages changes to data, enabling recovery of previous versions if needed.
In finance, version control ensures that financial data remains accurate and auditable, preventing errors in reporting.
Availability: Ensuring Access When Needed
Availability ensures data is accessible to authorized users. Key practices include:
- Redundant Systems: Ensure continuous access by having backup systems that kick in if one fails.
- Regular Backups: Ensure data can be restored in case of accidental loss, hardware failure, or cyberattacks.
In healthcare, backup systems are essential to ensure real-time access to critical patient data.
Key Components and Technologies in Data Security Management
Modern data security management relies on a combination of technologies and strategic controls to protect sensitive information throughout its lifecycle. Each element plays a critical role in forming a comprehensive, layered defense system:
Access Control and Authentication
These mechanisms ensure that only authorized users can access specific data. Techniques like RBAC, MFA (multi-factor authentication), and centralized IAM (identity and access management) systems restrict access and reduce the risk of data exposure due to compromised credentials.
Encryption and Data Masking
Encryption secures data both at rest and in transit by converting it into unreadable formats without the appropriate decryption key. Data masking, on the other hand, protects sensitive information by obscuring it—especially in non-production environments such as testing or training—to prevent accidental leaks.
Data Loss Prevention
DLP tools monitor data usage and movement to detect and prevent unauthorized sharing, leaks, or transfers of sensitive information. DLP solutions can automatically block risky behavior or alert administrators to potential policy violations.
Backup and Recovery
Backups are essential for data resilience. By regularly creating and storing copies of data, organizations can restore information quickly after accidental deletion, hardware failures, ransomware attacks, or natural disasters. Disaster recovery plans define how this restoration process should occur efficiently.
Threat Detection and Incident Response
Proactive monitoring tools detect unusual or malicious activity in real time. When threats are identified, a structured incident response plan helps contain the breach, investigate its root cause, and apply lessons learned to bolster defenses going forward.
Together, these technologies and practices create a defense-in-depth architecture that minimizes vulnerabilities and maximizes the ability to respond effectively to threats.
Access Control and Authentication
Effective access management is key to ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
- RBAC restricts access based on the user's role, ensuring that employees only see the data relevant to their responsibilities.
- MFA (multi-factor authentication) adds another layer of protection, requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods.
- IAM (identity and access management) centralizes and simplifies the oversight of who has access to what, improving visibility and control over data access across an organization.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Data Masking
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools monitor and track the movement of sensitive data across systems, preventing unauthorized sharing or leaks. By identifying patterns of risky behavior, DLP can block or alert administrators to potential threats.
Data masking, on the other hand, obfuscates sensitive information, ensuring that it’s secure even in non-production environments like testing or development. This technique allows teams to work with realistic data without exposing it to unnecessary risk.
Encryption and Secure Storage
Encryption ensures that data remains unreadable to unauthorized users, whether it’s stored on a server (encryption at rest) or transmitted across networks (encryption in transit). By employing encryption, businesses can protect sensitive data from theft, even if the data is intercepted.
Secure storage solutions further enhance this protection by securing data repositories against attacks, ensuring that sensitive files are safeguarded from unauthorized access and breaches.
Threat Detection and Incident Response
Proactive threat detection systems enable organizations to identify and respond to potential security threats as they happen.
- Real-time monitoring alerts security teams to unusual activities, helping them act quickly.
- Incident response planning ensures that organizations are prepared for rapid and efficient action when a security breach occurs.
- Post-incident forensics allow teams to investigate what went wrong, learn from the event, and strengthen defenses to prevent future incidents.
Data Backup and Recovery
Implementing a strong backup strategy, such as the 3-2-1 rule (three copies of data, two different media, one off-site), ensures that critical data is always recoverable, even in the event of system failures or cyberattacks.
Disaster recovery planning outlines the steps to take in case of data loss, ensuring business continuity and minimal downtime. These measures ensure that an organization can quickly recover from unexpected disruptions and resume operations.
Data Lifecycle Management and Handling Procedures
Effective data security extends beyond protection during storage and transmission—it’s essential to manage data throughout its entire lifecycle, from creation to deletion. This includes securing data during creation, storage, and usage, as well as ensuring safe sharing and transfer between parties.
Archiving older data and properly disposing of obsolete or unnecessary data further reduce the risk of security breaches, ensuring sensitive information is never exposed once it’s no longer needed.
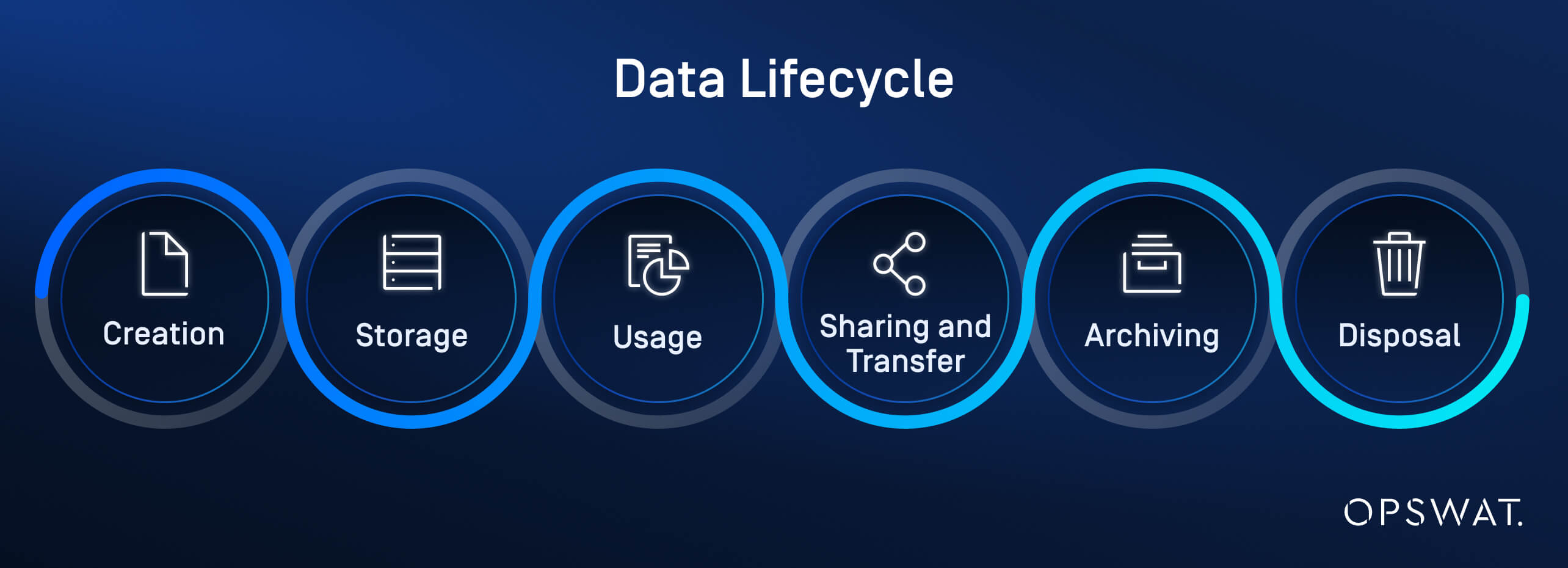
Best Practices for Data Handling
- Data minimization: Collect and retain only what’s necessary.
- Data classification: Label data by sensitivity.
- Secure migration: Use encrypted channels and access controls for data transfers.
Adopting best practices for data handling is critical to securing sensitive information. Data minimization involves only collecting the data that’s absolutely necessary and retaining it for no longer than needed. Data classification ensures that all data is labeled based on its sensitivity, so the appropriate level of security is applied.
Secure migration practices, such as using encrypted channels and access controls for data transfers, further reduce the risk of data loss or exposure during movement across systems.
Read about securing digital healthcare data.
Security Policies, Governance, and Training
Data security isn’t just about technology; it’s also about strong policies, governance, and training. Well-defined policies set expectations for data protection, while governance frameworks ensure those policies are implemented effectively. Ongoing training keeps employees informed about the latest security threats and best practices.
Policy Development and Enforcement
Security policies should align with organizational goals and define access controls and data handling procedures. Enforcement tools, like policy-based access control, ensure compliance, while regular audits assess the effectiveness of these policies.
Security Awareness and Insider Threat Management
Regular training helps employees recognize threats like phishing and follow secure practices. Monitoring user behavior for suspicious activity also helps detect insider threats, ensuring that risks are identified and mitigated early.
How to Implement Data Security Management: Step-by-Step Approach
1. Assess your current security posture.
2. Identify data assets, threats, and vulnerabilities.
3. Select technologies and controls.
4. Deploy and integrate tools.
5. Monitor continuously.
6. Improve with regular reviews and audits.

Data Security Management Frameworks and Standards
These popular frameworks provide detailed guidance that can help organizations avoid regulatory fines:
- ISO/IEC 27001: International information security management standard
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: U.S. standard for managing cybersecurity risk
- CIS Controls: Actionable best practices for cyber defense
Data Security Management in Practice: Use Cases and Industry Examples
Data security management is crucial across various industries, each with unique needs and challenges. Here are a few use cases that demonstrate how organizations implement data security in practice:
These use cases illustrate how different sectors implement a range of technologies and best practices to ensure data security and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Learn More
Learn how OPSWAT's MetaDefender Storage Security helps organizations scan, secure, and manage sensitive files across data repositories.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is data security management?
Data security management is the process of protecting digital information throughout its lifecycle from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft. It involves the implementation of policies, technologies, and procedures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data (also known as the CIA triad).
Why is data security management important?
Poor data security management can result in data breaches, regulatory fines, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
How does data management security work?
Data management security works by implementing layered controls, such as access control, encryption, DLP, and monitoring, to protect data across its lifecycle from threats and unauthorized access.
How do you implement data security management?
- Assess your current security posture.
- Identify data assets, threats, and vulnerabilities.
- Select technologies and controls.
- Deploy and integrate tools.
- Monitor continuously.
- Improve with regular reviews and audits.
What is data security management vs. information security management vs. cybersecurity management?
- Data security management focuses specifically on protecting data assets from threats.
- Information security management is broader, encompassing the protection of all forms of information, whether digital or physical.
- Cybersecurity management covers the defense of systems, networks, and programs against digital attacks.
In short, data security is a subset of information security, which in turn falls under the larger umbrella of cybersecurity.
What are the best practices for data handling?
- Data minimization: Collect and retain only what’s necessary.
- Data classification: Label data by sensitivity.
- Secure migration: Use encrypted channels and access controls for data transfers.
How does the CIA triad apply to data security management?
The CIA triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—is the foundation of data security management. It ensures that data is accessed only by authorized users, remains accurate and unaltered, and is available when needed.
What is data lifecycle management?
Data lifecycle management includes securing data during creation, storage, and usage, as well as ensuring safe sharing and transfer between parties.
What are the key components of data security management?
Key components of data security management include access control and authentication, encryption and data masking, data loss prevention (DLP), backup and recovery, threat detection and incident response, and data lifecycle management.
What are the three pillars of data security and management?
The three pillars are confidentiality, integrity, and availability, collectively known as the CIA triad. These principles guide all data security strategies.
What is the biggest risk to data security?
The biggest risks include insider threats, misconfigured systems, and sophisticated cyberattacks such as ransomware.
Who is responsible for data security?
Responsibility is shared across IT teams, data owners, compliance officers, and employees. A culture of security and clearly defined roles help ensure accountability.



