Modern cybercriminals have changed the rules of data protection. Backups, once considered a simple safety net, are now primary targets for ransomware and advanced cyberattacks.
Attackers know that compromising recovery systems can deliver a knockout blow to organizations. Having backups is no longer enough; you need to proactively secure your backup data lifecycle to achieve true cyber resilience.
Why do Traditional Backup Checks Fall Short?
Traditional backup checks often provide a false sense of security, failing to detect the evolving threats that put organizations at risk. While conventional methods focus on basic integrity and availability, they overlook critical vulnerabilities such as:
- File-borne threats like file-based vulnerabilities, zero-day exploits, or sophisticated malware hidden in backup files, especially in archives, databases and machine images
- Polymorphic ransomware that bypasses signature-based detection
- Subtle but malicious file modifications caused through file drift or metadata drift
- Restoring infected data triggers immediate re-infection, failed recovery, and extended downtime
- Stringent regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, PCI DSS, SOX, and Sheltered Harbor)
The reality of recovery falls short of expectations, revealing a significant gap between what organizations believe they can achieve and their actual performance during downtime. A recent survey shows that while over 60% of respondents believed they could recover in under a day, only 35% actually managed to do so when faced with an actual event.
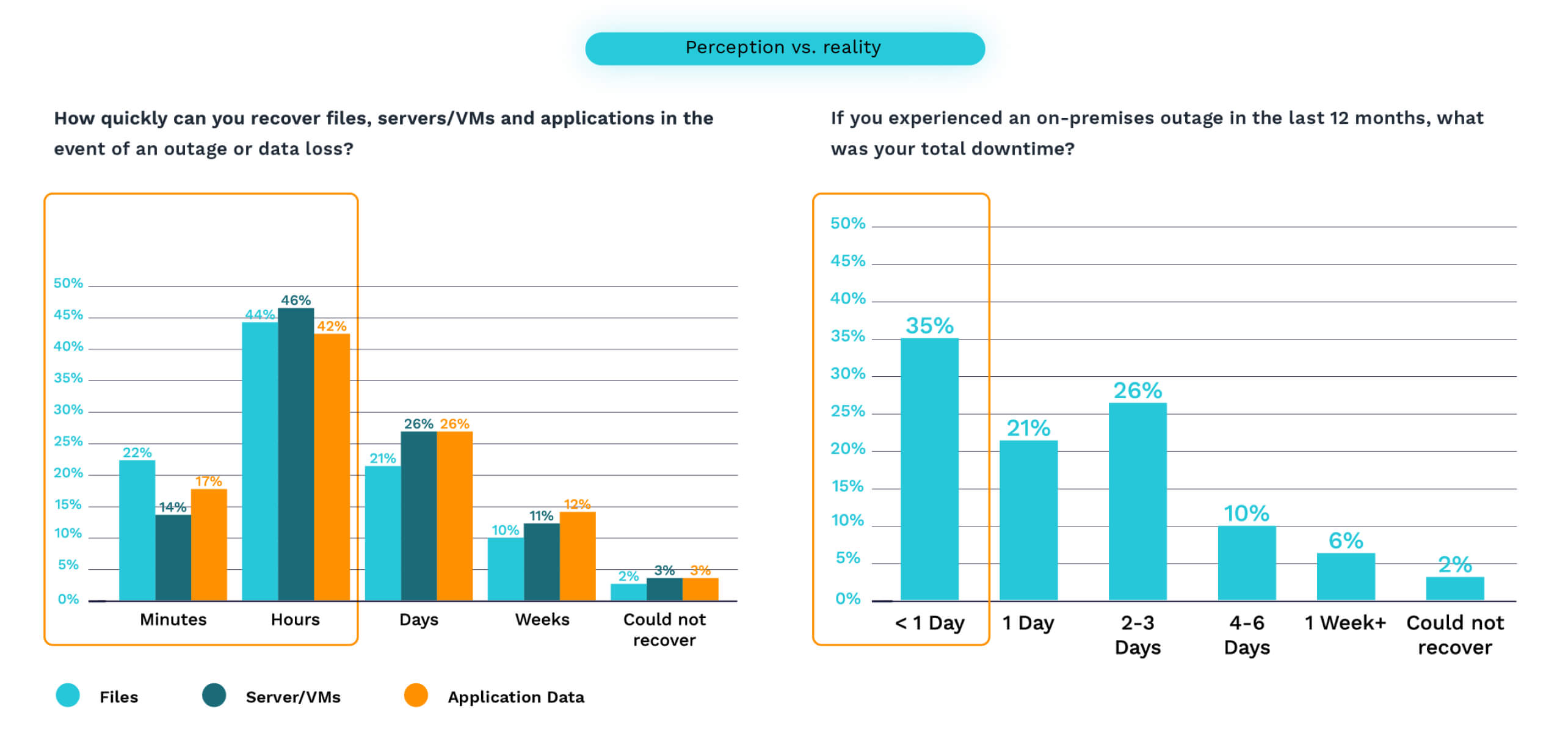
Addressing these shortcomings requires a fundamental shift in how organizations approach backup security, moving beyond simplistic verification to comprehensive threat detection and prevention. Without this evolution, backup systems remain dangerously exposed to sophisticated attacks that can render recovery efforts futile precisely when they're most needed.
Organizations must implement multi-layered security practices that specifically target these blind spots, combining advanced technologies with strategic processes to ensure backups remain both available and uncompromised. The growing disparity between recovery expectations and reality serves as a stark warning: traditional approaches no longer provide adequate protection.
8 Critical Practices to Secure Your Backups
The following comprehensive strategies form the foundation of a truly secure backup ecosystem—one that not only preserves your data but ensures its integrity and availability when recovery becomes necessary. By implementing these eight critical practices, organizations can transform vulnerable backup repositories into resilient assets that maintain business continuity even in the face of determined adversaries.
1. The 3-2-1-1-0 rule
The 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule represents a modernized evolution of the traditional 3-2-1 approach, specifically designed to enhance cyber resilience and security within your disaster recovery strategy:
- Three Copies of Data: Maintain three total copies of your data (one primary and two backups).
- Two Different Media Types: Store your backups on two distinct media types. While traditionally this might have included disk and tape, modern approaches often incorporate cloud storage or SSDs.
- One Copy Offsite: Keep at least one copy in a separate location, easily achievable with cloud backup solutions (in an alternate region or with a different cloud provider).
- One Copy Offline, Air-gapped, or Immutable: Maintain one copy that is either completely disconnected from networks (offline/air-gapped) or cannot be altered once written (immutable). This is crucial for ransomware protection, providing a clean recovery option that attackers cannot compromise.
- Zero Errors: Regularly verify your backups to ensure they're error-free and actually usable when needed.

Having multiple backups is only half the equation. Organizations must focus equally on Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs), defining how quickly and safely critical services can be restored. In a disaster scenario, whether ransomware, sophisticated threats, or targeted cyber-attacks, the ability to recover within minutes without reintroducing malware or violating compliance, is what separates a cyber-resilient organization from a vulnerable one.
The next planning stage is ensuring security, reliability, and readiness. This is where a multi-layered storage security solution plays a critical role.
2. Periodic Scanning
Implementing periodic scanning represents a critical defense layer beyond initial backup verification. While point-in-time scans provide a snapshot of backup integrity, regular scheduled scanning ensures continuous protection against emerging threats that may have been undetectable when backups were first created.
Malware detection is a non-negotiable part of periodic recovery testing. Without robust malware scanning integrated into your backup verification process, even the most meticulous backup strategy can fail during actual recovery scenarios by reintroducing the very threats organizations are trying to recover from.
3. Multiscanning Approach
All files should be scanned for malware before they're allowed inside your network or backup storage. To achieve the highest detection rates and the shortest window of exposure to malware outbreaks, scan files with multiple anti-malware engines (using a combination of signatures, heuristics, and machine learning detection methods) with a multiscanning solution.
4. Yara-Based Detection
YARA rules empower security teams to identify sophisticated malware within backup repositories using customized rules based on specific file characteristics. By implementing precisely defined strings and conditional logic, organizations can detect threats that signature-based solutions may miss, including targeted and emerging attacks.
YARA's adaptable framework allows continuous refinement of detection capabilities, creating a dynamic defense layer that significantly enhances the precision of backup verification processes.
5. Adaptive Threat Analysis
Sandbox technology enables organizations to detect and analyze zero-day malware in isolated, controlled environments before they can compromise recovery operations. By leveraging this technology with deep static analysis capabilities, advanced threat intelligence integration, and high-speed emulation techniques, security teams can effectively identify sophisticated malware variants or IOCs (indicators of compromise) that traditional signature-based scanning might miss.
6. Content Disarm and Reconstruction
Files such as Microsoft Office, PDF and image files can have embedded threats in hidden scripts and macros that aren't always detected by anti-malware engines. To remove risk and ensure backup files contain no hidden threats, it's best practice to remove any possible embedded objects by using CDR (content disarm and reconstruction).
7. Differential Scanning
8. Data Loss Prevention
All sensitive data like social security numbers, bank account details, or PII (personally identifiable information) should be redacted, masked, or blocked using DLP (data loss prevention) technology.
Elevating Backup Security from Defense to Resilience
Organizations that successfully protect their backup infrastructure gain more than just data security; they achieve true business resilience, regulatory compliance, and the confidence that recovery operations will succeed when needed most. The investment in properly secured backups delivers returns far beyond the resources required to implement them, particularly when compared to the devastating costs of ransomware attacks, data breaches, or failed recovery attempts.
The OPSWAT Advantage
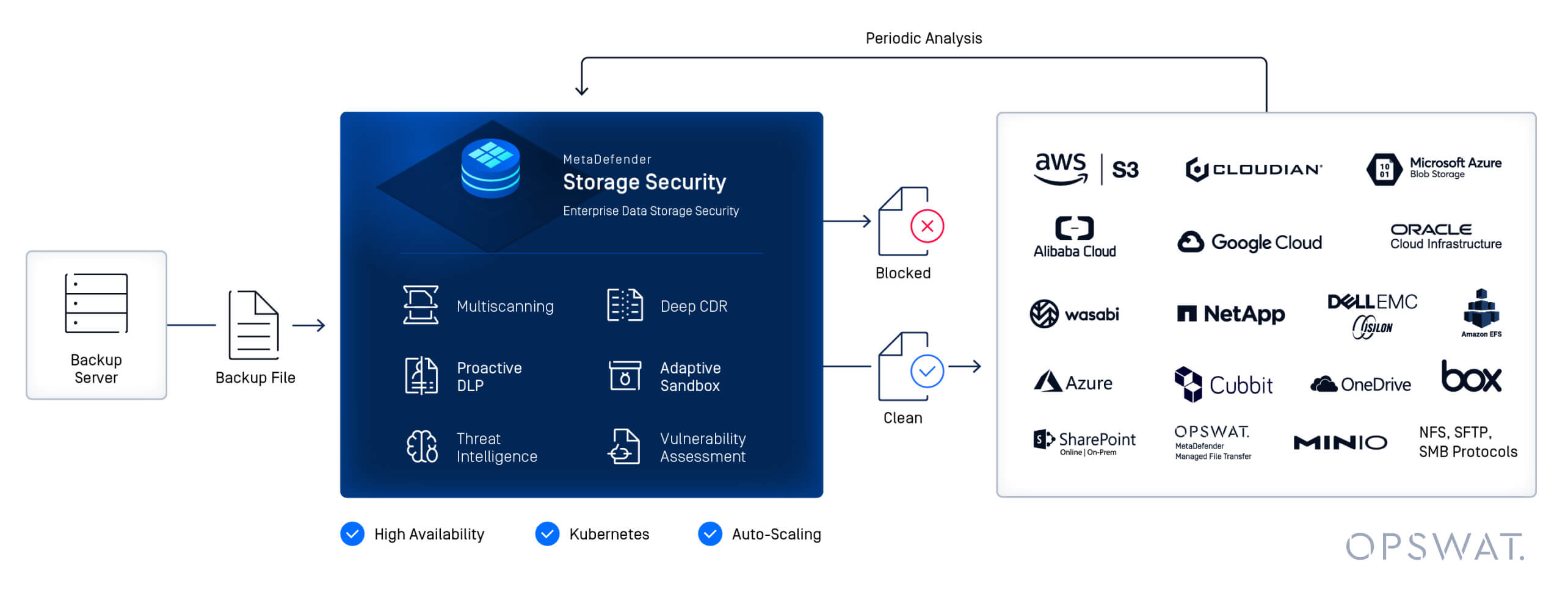
MetaDefender Storage Security™ unifies critical practices into a single solution. With OPSWAT’s leading technologies such as Metascan™ Multiscanning, Deep CDR™, Proactive DLP™, and Adaptive Sandbox, your backup data stays clean and readily accessible when every second counts.
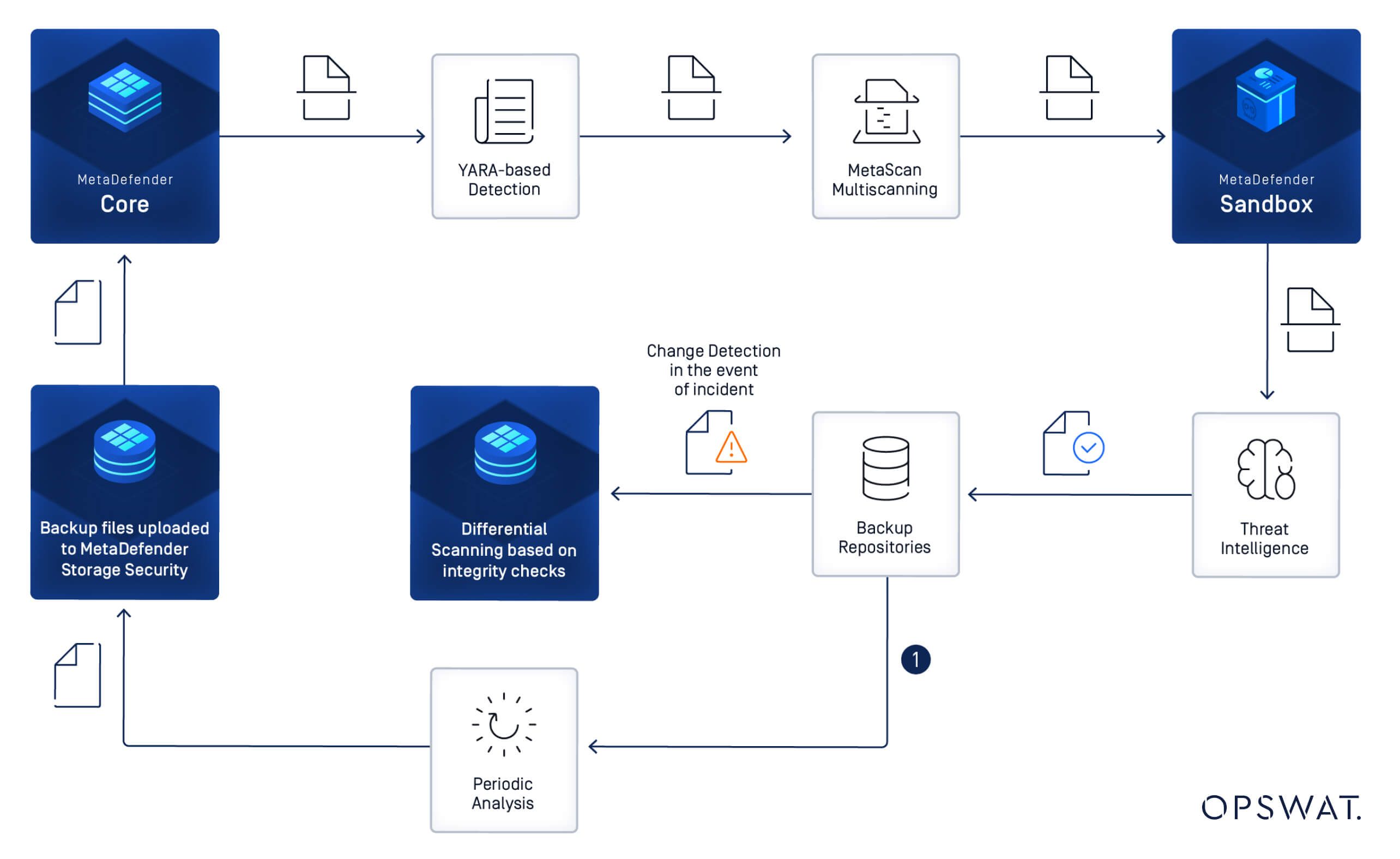
One of our key capabilities is our Rapid Change Detection. MetaDefender Storage Security continuously monitors backup repositories through periodic analysis. When a security incident or ransomware attack occurs, admin can activate differential scanning based on integrity checks of known files. This rapid change detection capability dramatically minimizes RTO (recovery time objectives) by quickly identifying which backup sets remain uncompromised, enabling organizations to restore operations from the most recent clean backup point.
Conclusion
Don't wait for a security incident to expose vulnerabilities in your backup strategy. Take proactive steps now to assess your current backup security posture and identify opportunities for improvement. Our security experts can help you evaluate your existing infrastructure, recommend tailored solutions that align with these best practices, and guide your implementation of a comprehensive backup security framework.
Contact our experts today to discuss how you can strengthen your backup security posture and achieve true cyber resilience in an increasingly hostile digital environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is data backup and recovery?
Data backup and recovery is the process of creating copies of data to protect against loss or corruption and restoring that data when needed—whether due to accidental deletion, hardware failure, or cyberattacks like ransomware.
Why are data backup and recovery important?
It ensures business continuity by enabling organizations to restore critical systems and data after an incident, minimizing downtime, financial loss, and reputational damage. In today’s threat landscape, it also supports regulatory compliance and disaster recovery.
What is data backup security?
Data backup security refers to the practices and technologies used to protect backup data from unauthorized access, corruption, or cyber threats—ensuring backups remain usable, uninfected, and recoverable during a crisis.
What is the best way to secure a backup?
There are many best practices to secure backups; a multi-layered approach is among the most highly recommended by cybersecurity experts. Implement the 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule, scan backups regularly with multiple anti-malware engines, use CDR, sandboxing, and DLP technologies to eliminate embedded threats and protect sensitive data.
What are the three types of data backup?
1. Full Backup: A complete copy of all data.
2. Incremental Backup: Backs up only the data that changed since the last backup.
3. Differential Backup: Backs up all data changed since the last full backup.
What is the 3-2-1 backup rule?
Maintain three copies of your data, stored on two different types of media, with one copy kept offsite. This provides redundancy and safeguards against localized failures.
What is the 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule?
An advanced evolution of the traditional model:
- 3 total copies of your data
- 2 different media types
- 1 copy offsite
- 1 copy offline, air-gapped, or immutable
- 0 errors in backup verification, ensuring backups are usable when needed

