AI (artificial intelligence) is rapidly impacting cybersecurity on both sides of the battlefield. As defenders harness AI to detect threats faster, attackers are deploying intelligent tools to breach systems, evade detection, and automate malicious activity at scale. The result? A constantly evolving threat landscape where understanding the capabilities of AI-powered attacks becomes essential to building resilient defenses.
What is an AI-Powered Cyberattack?
AI-powered cyberattacks use artificial intelligence and machine learning to execute attacks with greater speed, precision, and deception. These operations go beyond conventional cyberthreats, learning from each attempt and adapting to their targets. Unlike traditional methods that follow static rules, these attacks can pivot in real time, often with human-like behavior.
To illustrate, imagine a phishing email that adjusts its tone based on your job title. This email sounds exactly like a message your CFO would send—urgent, polished, and referencing current budget matters. Behind the scenes, AI crafted the message using public data about your role. You click the attachment, but nothing seems to happen. What you don't see is the malware silently trying different ways to bypass your company's defenses, switching tactics until it finds one that works. This is no longer a hypothetical scenario. It is happening now.
AI-based cyberattacks encompass a wide array of intelligent threat vectors, from deep learning exploits that manipulate systems in unexpected ways to cognitive hacking strategies that mimic human decision-making. This marks a shift from simple exploits to algorithm-driven breaches designed to outmaneuver even advanced defenses.
| Traditional Attacks | AI-Powered Attacks |
|---|---|
| Manual execution | Automated logic |
| Static payloads | Adaptive code |
| Known exploits | Zero-day exploits |
| Phishing templates | Context-aware bait |
| Linear infiltration | Dynamic decision-making |
The Growing Threat of AI in Cybersecurity
AI amplifies the capabilities of attackers, enabling them to work faster and at a larger scale. With generative AI, a single operator can now generate thousands of phishing emails, deepfake videos, or tailored exploits in minutes. And because these tools improve continuously, each failed attempt can inform a more effective next one.
According to IBM X-Force®, identity-based attacks made up 30% of total intrusions in 2024, largely fueled by the surge in phishing emails delivering infostealer malware and the use of AI to scale credential harvesting efforts. This statistic underscores the growing danger of compromised credentials and highlights the urgent need for proactive, AI-aware defense strategies.
AI-powered attacks appeal to threat actors because they enable automated hacking techniques that adapt to defenses in real time, making static firewalls and outdated antivirus tools insufficient. In particular, neural network intrusions can uncover patterns humans may overlook, and smart malware operations allow persistent, stealthy access across segmented networks.
Types & Examples of AI-Powered Cyberattacks
Let’s explore how these threats play out in the real world. From impersonation scams to deeply embedded payloads, attackers are using AI to scale and personalize intrusions at unprecedented levels. These tactics often combine social engineering with automated code execution. Understanding the structure of these attacks helps in building effective mitigation strategies.
3 Common Types of AI-Generated Attacks
AI's versatility enables a range of attack formats that are often designed to bypass both technical defenses and human intuition.
Phishing with AI
Large language models (LLMs) can draft tailored emails that mimic internal communication styles, making detection harder
AI-Driven Ransomware
Attackers use algorithms to pinpoint high-value targets and choose optimal attack timing
Deepfake Social Engineering
Synthetic audio or video content can impersonate executives to approve fraudulent transactions
How AI Enhances Social Engineering
AI can generate tactics that exploit trust and familiarity, making social engineering faster, more scalable, and harder to spot.
- Text that mimics corporate tone and vocabulary
- Tutorials and guidance using video language models
- Synthetic images or credentials to support identity fraud

Exploiting Machine Learning Systems
Some machine learning attacks focus on the AI systems themselves. They often fly under the radar as they don’t trigger traditional alerting systems. Some examples include:
- Poisoning training datasets
- Creating adversarial inputs to confuse models
- Generating fake telemetry or logs to bypass monitoring tools
Case Studies & Real-World Examples
The threat isn’t theoretical. Across sectors, real companies are applying AI—both defensively and operationally—to solve long-standing challenges. These use cases highlight practical implementations that balance cybersecurity, productivity, and adaptability.
All of the following examples are drawn from actual OPSWAT customer deployments. While each example reflects a different business need, the common thread is the use of intelligent solutions to securely solve real problems.

Global Automotive Leader
Faced with the need to allow vendor access via USB, this firm deployed OPSWAT's MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT)™,Kiosk™, and Diode technologies. These tools provided multilayered scanning, while managing access and unidirectional transfer into OT. This helped prevent the introduction of AI-driven malware through removable media. Read the full story here.

US Energy Company
To protect isolated systems and meet evolving regulations, this utility deployed MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) with AI-based, built-in sandboxing and data loss prevention. This combination of solutions enforces secure, policy-based file transfers to defend against malware and zero-day threats. These AI-powered technologies maintain operational continuity even across the company’s air-gapped environments. Learn more about this story here.

Healthcare Recovery
After a ransomware attack encrypted an entire healthcare provider’s network, forensic experts used MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) to securely migrate files from compromised systems to clean infrastructure. The solution isolated, filtered, and controlled access to all incoming data, ensuring that no contaminated files re-entered the restored environment. Its deployment was seamless, with full business continuity during recovery. Read how it was done here.
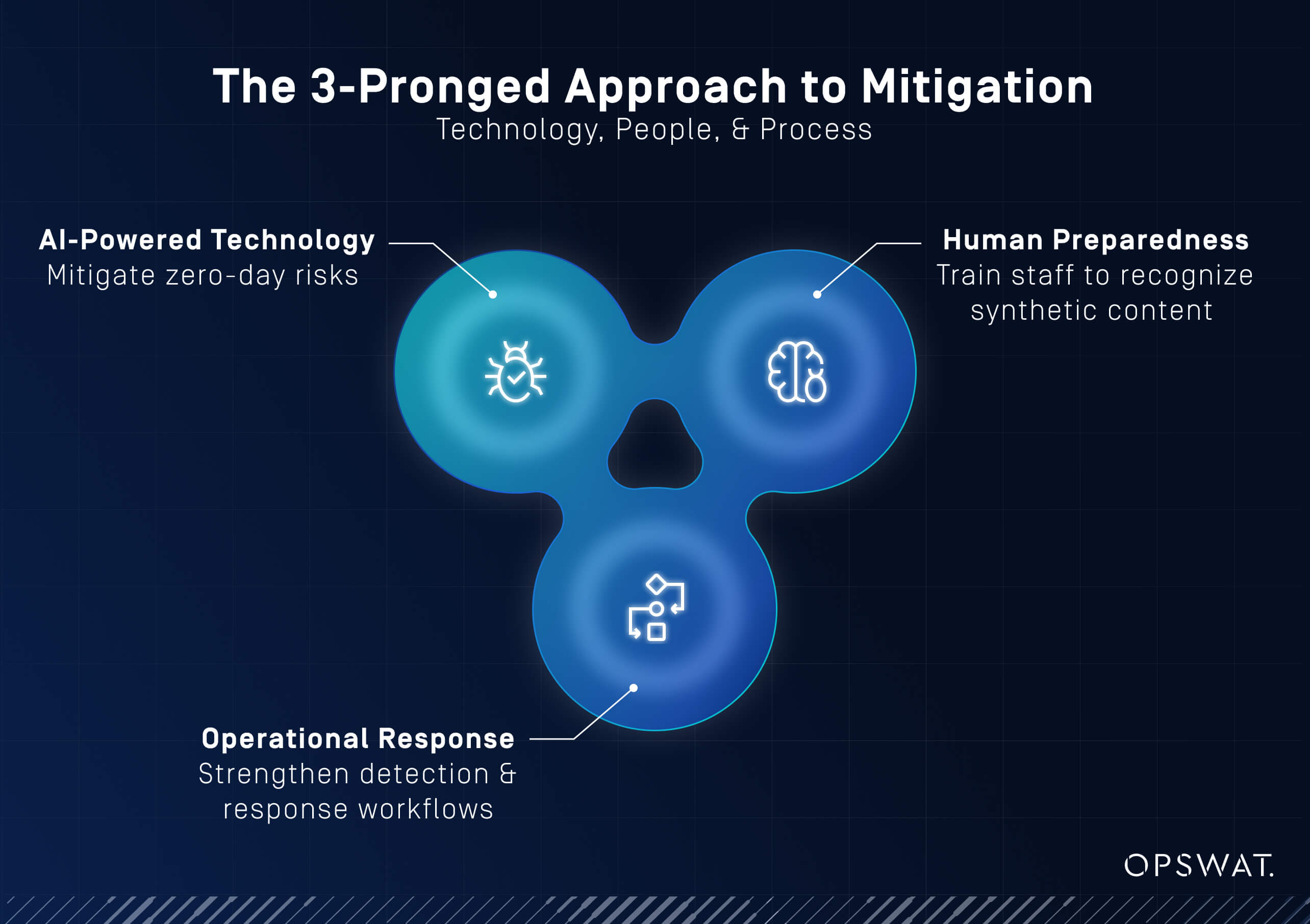
Mitigation Strategies for AI-Powered Cyberattacks
How can organizations defend themselves against such intelligent and adaptive threats?
The good news is that AI can be used as a force multiplier for defenders, too. From automated file inspection to policy-driven enforcement, the right tools can provide a powerful countermeasure. But success requires more than just technology. It takes strategy, governance, and cross-functional coordination.
Exploiting Machine Learning Systems
Defense requires adopting AI, but on your terms:
- Integrate multilayer scanning (multiscanning, CDR, sandboxing) into every file exchange
- Use domain-specific AI models, not public LLMs
- Build systems with security built in, not added later
Building Security Culture & Skills
AI threats aren’t only a technical challenge; they’re also human. To prepare your workforce for unexpected attacks, consider these preemptive measures:
- Train employees to recognize AI-generated content
- Build AI literacy within technical and operational teams
- Capture expert knowledge before it exits the workforce, then digitize it for reuse
Creating a Modern Incident Response Plan
Response plans must evolve, too. Traditional playbooks may fall short when dealing with adaptive, AI-driven threats. Teams need to account for faster decision cycles and more complex attack behaviors. Here is what you can do:
- Include signs of AI-generated anomalies
- Test responses against simulated intelligent threats
- Log and analyze actions for continuous improvement and audit readiness
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
We’re entering a phase where attacks can be fully autonomous. Malware will not just be written by AI, but it will also decide when, where, and how to launch. These autonomous cyber offensives demand new thinking. To counteract them, organizations need to:
- Adopt modular architectures that adapt with threats
- Prioritize explainable AI to maintain trust in their tools
- Tune models to industrial workflows and unique datasets
The Role of a Secure MFT in AI-Resilient Cybersecurity
As cyberattacks become more intelligent, file transfers remain a vulnerable entry point, especially in operational environments. This is where secure Managed File Transfer (MFT) solutions play a critical role. Unlike ad hoc transfer methods, MFT platforms offer policy-based control, audit trails, and layered scanning, that are all essential for withstanding modern AI-enhanced threats.
Jeremy Fong, VP of Product at OPSWAT, emphasized this evolution: “MFT used to be about business efficiency. Today, it's about visibility, control, and compliance. We’ve moved from just moving files to showing how those files were inspected, secured, and tracked.” This shift reflects the growing need for transparency and auditability in the face of increasingly intelligent and automated cyberthreats.
OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) combines multiple layers of protection with centralized governance. It can enforce policies based on user roles, asset risk, or even the source of the file. As Jeremy Fong noted, “We built this platform to work in air-gapped and OT environments. It’s not just secure—it fits how teams actually operate.”

Strengthen Your Defense Strategy
AI is already reshaping the rules of cyber conflict. From critical infrastructure operators to enterprise security teams, the response must be swift and strategic.
OPSWAT delivers security-first tools like MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT)™, Sandbox™, and Metascan™ Multiscanning. These solutions help you detect, prevent, and recover from AI-enhanced threats without disrupting operations.
These technologies are built for modern threats:
- Deep CDR™ Technology detects hidden threats across file layers and neutralizes embedded risks without relying on detection alone.
- Sandboxing exposes malicious behavior in real time, and outbreak prevention stops the spread of new threats across environments.
- File-based vulnerability assessment and source verification ensure that files can be trusted.
With OPSWAT, you don’t just react to AI threats—you stay ahead of them.
Get started with proven use cases. Secure both your IT and OT workflows with a layered, adaptive defense.
AI-Powered Cyberattacks FAQs
What is an example of an AI attack?
A deepfake video impersonating a CFO to authorize fraudulent payments.
What is an example of an AI data breach?
An AI tool extracting sensitive insights from scanned documents in a shared drive.
Why is AI dangerous in cybersecurity?
It enables attackers to scale, personalize, and adapt faster than traditional methods.
What is weaponized AI in cyberattacks?
AI tools built to autonomously create, deploy, and adapt attack payloads.
What is the trend of AI-powered cyberattacks?
Attacks are becoming more automated, harder to detect, and capable of mimicking human or system behavior at scale.

