What is Secure Managed File Transfer?
Managed File Transfer is a centralized software solution designed to automate, secure, and monitor the movement of data within an organization and across external networks. It provides centralized file transfer management for sensitive data and uses encryption, access controls, automation, and audit logging to protect that data in transit and at rest. This allows organizations to securely transfer large volumes of sensitive files without relying on ad hoc methods.
- What is Secure Managed File Transfer?
- Why a Secure MFT is Critical for Cybersecurity
- On-Premises vs Hybrid Cloud vs Cloud-Native MFT Deployment
- What Type of Organization Needs a Secure MFT?
- Common MFT Use Cases
- 4 Pillars of a Secure MFT Solution
- When Should an Organization Implement a Secure MFT?
- 4 Benefits of a Secure MFT
- How to Implement Secure Managed File Transfer
- Strengthening Your Secure File Transfer Strategy
- FAQs
Why a Secure MFT is Critical for Cybersecurity
According to SonicWall’s 2025 Cyber Threat Report, threat actors now exploit newly disclosed vulnerabilities within 48 hours, and file-based attacks remain a common method of entry. Unmanaged file transfers can open the door to data breaches, malware infiltration, compliance violations, and workflow disruptions. Every file that moves without proper oversight increases the risk of sensitive data being intercepted or altered.
A secure MFT solution addresses these risks by:
- Enhanced security: Enforces strict access controls, encrypts files in transit and at rest, and scans for malware or hidden threats so that sensitive data remains protected
- Visual Orchestration: Provides visualization of each step in the workflow so that administrators can ensure that every file transfer meets organizational and regulatory requirements
- Operational efficiency: Automates routine transfers, reduces human error, and frees teams from slow manual processes
- Regulatory compliance & governance: Provides detailed audit logs, role-based access controls, and data loss prevention to help meet GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and ISO 27001 standards
MFT also reduces the risk of shadow IT, where employees rely on unapproved tools for file sharing. Centralizing and auditing all file transfers helps maintain both security and operational trust. Most MFT platforms support on-premises, cloud, and hybrid cloud deployments, giving organizations flexibility while keeping control of sensitive data.
To explore the capabilities that make modern MFT essential for secure, flexible file transfers, download our ebook below.
On-Premises vs Hybrid Cloud vs Cloud-Native MFT Deployment
When evaluating managed file transfer solutions, compare the three main deployment approaches: cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid cloud. Each has strengths and trade-offs, and the right choice depends on the sensitivity of your data, regulatory requirements, and operational needs.
Organizations of all sizes exchange large volumes of files every day with internal teams, external partners, and connected systems. Managed File Transfer (MFT) solutions protect sensitive information during these transfers while supporting operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
1. On-Premises MFT Deployment
An on-premises MFT deployment keeps all file transfer operations inside your organization’s infrastructure. This option offers maximum control and is often preferred when sensitive data must remain on local networks or when internet access is limited. On-premises deployments can also be fully air-gapped, where file transfers are isolated from external networks to meet high security requirements (mainly in OT and critical infrastructure environments).
2. Hybrid Cloud MFT Deployment
Hybrid cloud MFT combines customer-managed cloud resources with local on-premises components. This approach provides flexibility and supports cloud scalability while allowing critical transfers to remain fully under your control. Hybrid cloud deployments are popular with organizations that need both agility and strict data governance.
3. Cloud-Native MFT Deployment (Software as a Service)
Cloud-native MFT solutions are delivered as a subscription service. They are quick to deploy and scale easily without the need to maintain local infrastructure. However, storing or processing sensitive files in a vendor-controlled cloud can introduce regulatory and data residency challenges. This model is often unsuitable for highly regulated industries or air-gapped and OT environments, such as critical infrastructure industries, where maintaining strict control over file flows is mandatory.
Many organizations choose hybrid cloud deployments to combine the convenience of cloud services with the control of local infrastructure. OPSWAT does not offer a fully cloud-native or SaaS MFT that hosts customer files. Instead, hybrid cloud deployments are customer-managed, allowing you to run MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) solution in your private or public cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP) while keeping full control of sensitive data.
Now that you know the key deployment options, it’s time to make sure your MFT can fully protect your files. Watch this webinar to learn the eight security capabilities every secure MFT solution should have.
What Type of Organization Needs a Secure MFT?
Any business facing data security, compliance, or workflow challenges with their file transfers can improve control and efficiency with a managed approach.
Key industries include:
- Financial institutions: Protect personal and transactional data across banking, payments, and trading systems while ensuring compliance with standards like SOX and PCI-DSS, and local financial oversight frameworks.
- Healthcare providers: Ensure HIPAA-compliant transfers of patient data across internal systems, cloud environments, and external partners while maintaining strict data privacy and integrity.
- Government agencies: Secure the movement of classified information across departments, remote offices, and external contractors and protect against file-based cyberattacks.
- Energy and utility companies: Secure file flows for power generation and distribution, meet NERC CIP and other regulatory requirements, and defend against zero-day and file-borne attacks targeting OT and IT networks.
- Legal and professional services: Protect sensitive client files, prevent data leaks, and maintain confidentiality for high-profile legal matters and transactions.
- Automotive and industrial manufacturing: Protect production and OT environments from file-borne threats, secure visitor file handling, and streamline file transfers across global facilities.
- Global automotive and industrial operations: Secure IT and OT file flows, protect production lines from contractor-introduced threats, and enable automated, large-scale file movement with full visibility and control.
- Large enterprises: Facilitate safe data exchange across departments and external partners to reduce the operational risk of shadow IT or ad-hoc transfers.
Common MFT Use Cases
- Internal transfers: Move data securely between departments, applications, and internal systems
- External transfers: Exchange files with partners, vendors, and regulators while maintaining compliance
- Cross-network or multi-site transfers: Send and receive files safely across branch offices or distributed locations
- Automated machine-to-machine transfers: Eliminate manual steps, reduce error-prone ad hoc sharing, and streamline recurring workflows
4 Pillars of a Secure MFT Solution
A reliable Managed File Transfer (MFT) solution does more than move files. It actively protects, verifies, and governs every single file transfer. OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) solution achieves this with four core pillars:
1. Multi-Layered Security
Every file should be verified as ‘safe’ before it reaches your work environment. MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) combines Metascan™ Multiscanning with over 30 anti-malware engines, Deep CDR™ to remove hidden threats, emulation-based MetaDefender Sandbox™ for zero-day detection, and file-based vulnerability assessment to catch risky executables and installers.
Get the eBook: 8 Must-Have MFT Capabilities to Secure File Transfers
2. Policy-Based File Transfer Enforcement
Security and efficiency go hand in hand when file transfers follow strict, automated rules. Policy-based workflows run automatically, moving files based on type, origin, or security posture. Supervisor approvals and MFT-to-MFT enforcement ensure that only verified, sanitized files reach sensitive environments.
3. Centralized Visibility and Control
You gain complete oversight of your file flows with real-time dashboards, unified audit logs, and SIEM integration to maintain chain-of-custody and simplify compliance. MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT)’s Visual Orchestration provides a clear, drag-and-drop view of MFT-to-MFT and cross-network transfers, showing connection status, directionality, and applied policies. This visual approach simplifies complex workflows and ensures consistent policy enforcement across SFTP, SMB, and SharePoint Online.
4. Data Security Compliance
OPSWAT's MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) enforces strict access policies to ensure that only authorized users and trusted networks can interact with your files. End-to-end encryption (TLS 1.3 in transit and AES-256 at rest), RBAC (role-based access control), MFA, SSO integration, and IP-based restrictions all work together to maintain a Zero Trust posture.
When Should an Organization Implement a Secure MFT?
Consider implementing a security-first MFT solution if your organization faces any of these challenges:
Data Security Concerns
If an organization is concerned about the security of its data during file transfers, implementing a secure MFT solution can provide the necessary defense measures to protect sensitive information. Read about how you can protect your data during transit here.
Increasing Volume of File Transfers
As organizations grow, the volume of file transfers increases. Implementing an MFT solution ensures that these transfers are managed securely and efficiently, reducing the risk of data breaches and operational inefficiencies.
Watch the Webinar: Secure or at Risk? 8 Security Capabilities Your MFT Must Have
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Organizations that need to comply with regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX should implement an MFT solution to ensure compliance. MFT solutions provide the necessary audit trails, data protection controls, and compliance reporting to meet these standards.
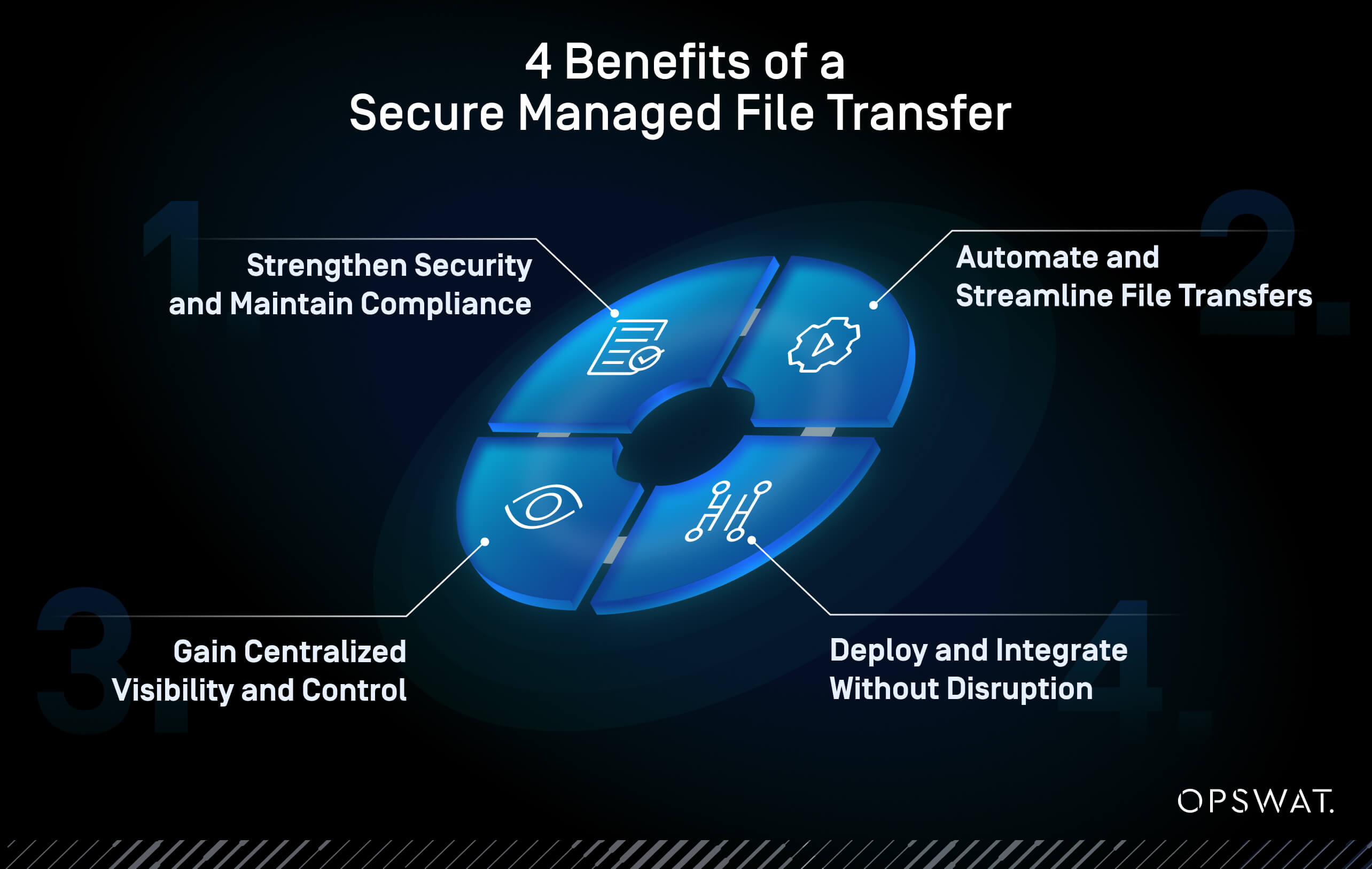
4 Benefits of a Secure MFT
If your organization handles sensitive or high-volume file transfers, adopting a secure Managed File Transfer (MFT) solution can strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity posture, simplify operations, and ensure compliance with confidence. Here are four areas where the right approach makes a real difference:
1. Strengthen Security and Maintain Compliance
Protect every file transfer with multi-layered security, including encryption, advanced malware scanning, Deep CDR, and checksum validation. These measures prevent threats from reaching critical systems and simplify compliance with regulations through audit logs and policy-based controls.
2. Automate and Streamline File Transfers
Replace repetitive, error-prone processes with policy-based automation. Logic-driven routing, scheduled jobs, and visual file orchestration reduce manual effort, eliminate delays, and keep sensitive files moving securely without constant IT intervention.
3. Gain Centralized Visibility and Control
A single, clear view of file activity gives you confidence in your operations. Unified dashboards and audit logs help you monitor transfers, detect issues, and enforce access policies. This supports faster incident response and easier reporting.
4. Deploy and Integrate Without Disruption
Implement MFT on-premises, in hybrid environments, or even in air-gapped networks without interrupting business. Native integration with SFTP, SMB, and SharePoint Online ensures secure file flows complement your existing infrastructure rather than complicate it.
Strengthening Your Secure MFT
Managed File Transfer is a practical way to secure and streamline how your organization moves data. By automating transfers, enforcing encryption, and maintaining audit trails, MFT reduces risk, supports compliance, and improves efficiency.
To build a truly resilient file transfer strategy, combine policy-based automation with multi-layered threat inspection and centralized visibility. By deploying a hybrid cloud or on-premises MFT solution, you maintain full control over sensitive files while reducing the risk introduced by vendor-hosted cloud platforms.
Selecting the right MFT solution is an opportunity to significantly improve both security and efficiency. To make the best choice for your organization, start by exploring the eight must-have capabilities of a modern, secure MFT solution.
By combining these four pillars, organizations secure every step of the file transfer lifecycle. This reduces the risk of data breaches, supports regulatory compliance, and protects data that keeps critical operations running.
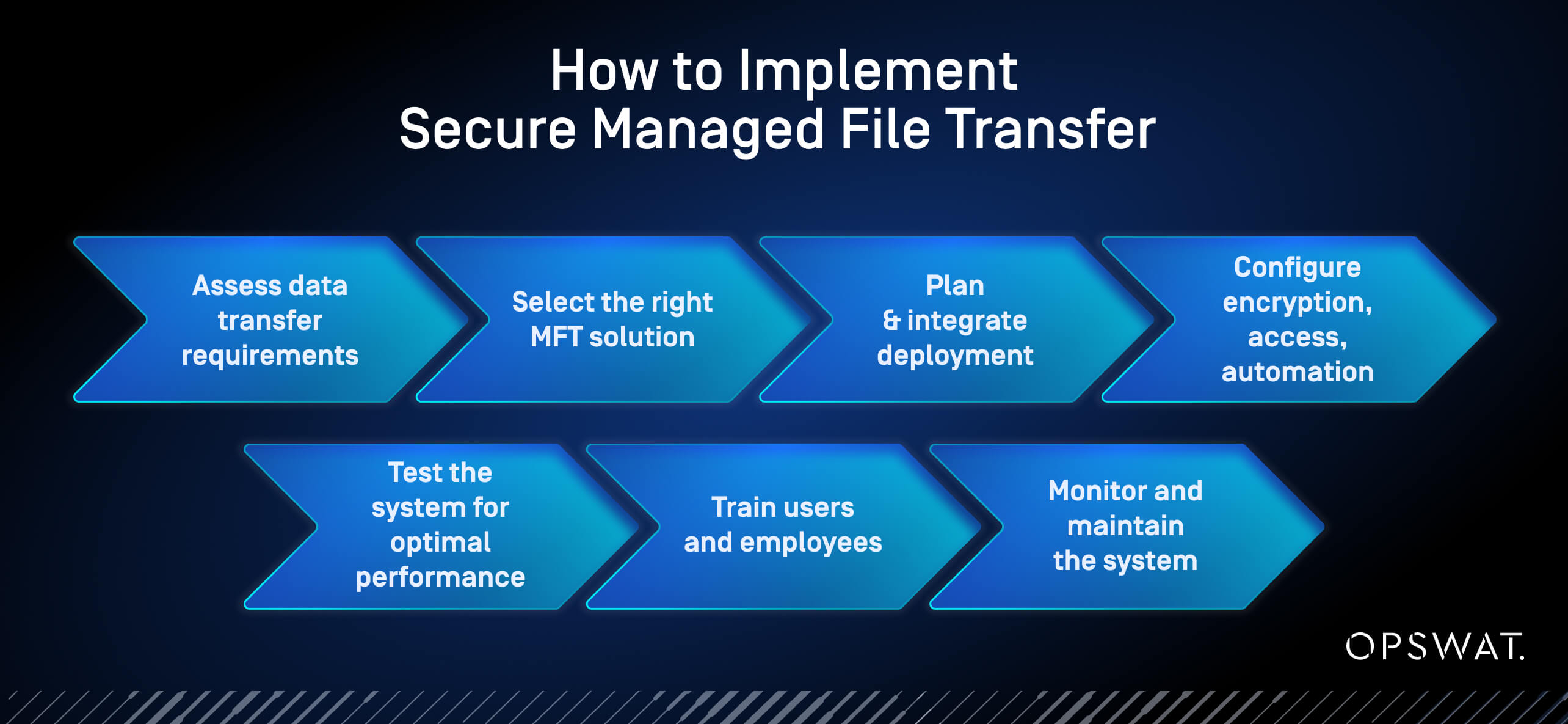
How to Implement Secure MFT
FAQs
What is a Managed File Transfer (MFT)?
Managed File Transfer is a secure, centralized platform that automates and governs the movement of files within and between organizations, partners, and endpoints. It ensures end-to-end encryption, policy enforcement, and visibility, unlike traditional FTP or cloud-sharing tools.
What is MFT vs SFTP?
- MFT is a secure, centralized solution that automates file transfers, enforces policies, and supports compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. It includes advanced features such as end-to-end encryption, malware scanning, audit logging, workflow automation, and centralized oversight.
- SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol), by contrast, is a basic protocol that encrypts files during transfer but lacks automation, scalability, centralized control, and compliance support. While SFTP may work for smaller businesses with simple needs, it introduces risks in complex, high-security environments. Read about the risks of using SFTP here.
What file-based attacks does MFT help protect against?
MFT helps prevent threats like malware hidden in PDFs or spreadsheets, ransomware delivered via file uploads, and tampered patches in transit. It defends against advanced attacks using Multiscanning, CDR, sandboxing, and vulnerability assessments, especially in OT and air-gapped systems.
How does MFT protect data in transit and at rest?
A secure MFT solution ensures that files are encrypted during transfer and verified for integrity with logging and validation. This prevents unauthorized access, tampering, and loss of chain-of-custody.
How does MFT help with compliance?
MFT platforms support compliance by providing audit trails, immutable logging, access controls, and policy enforcement for frameworks like GDPR, PCI-DSS, FISMA, HIPAA, NIST, and NIS2. They centralize governance, enabling traceable, policy-compliant file sharing across departments and partners.
What are some common use cases for MFT?
- Internal transfers: Moving files securely between departments, systems, or applications
- External transfers: Exchanging files with partners, vendors, or regulators while maintaining compliance
- Multi-site or cross-network transfers: Sending and receiving files safely across branch offices or distributed locations
- Automated machine-to-machine transfers: Eliminating manual steps to reduce errors and streamline recurring workflows
What makes MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) different?
OPSWAT MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) (MFT) secures the file whereas other legacy MFT solutions or file transfer tools may only secure the transfer. MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) inspects and sanitizes every file before access, automates secure transfers, enables role-based controls, and provides real-time monitoring across networks. Take control of your secure file transfers like never before with our latest feature, the Visual Orchestration Editor. Give your IT and OT teams a single, intuitive view to manage, automate and secure every file movement across all protocols and destinations. Watch this demo to learn more. MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT) is designed to secure critical file flows while simplifying compliance and boosting operational efficiency.

