We're entering a new phase of the virtual arms race. Attackers create highly evasive adaptive malware to hide from detection software. Cybercriminals are tirelessly working to exploit application vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to valuable data. This is why application security (AppSec) best practices are essential to understand and follow.
We've asked software security experts Vincent Lin and YiYi Miao for advice on best practices to implement proven application security. With their help, we dive deep into the most effective and practical ways to secure your apps and protect your organization from cyber threats.
Application Security Top Tips:
1. Understand why application security is important.
3. Establish a secure software development lifecycle (SDLC).
4. Follow the web application security best practices set by OWASP.
5. Create a security-focused culture.
6. Implement strong authentication and access controls.
7. Regularly update and patch your applications.
8. Regularly monitor and audit your application.
9. Implement encryption and other data protection measures.
10. Utilize prevention and detection technologies.
11. Follow cloud application security best practices.
12. Secure your network perimeter.
13. Perform regular security testing to find security issues.
1. Understand the Importance of Application Security (AppSec)
The Growing Threat Landscape
Cybersecurity threats are continually evolving, with attackers using increasingly sophisticated methods to compromise systems and steal data. The global cost of cybercrime is projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, making security a critical concern.
Vincent Lin, an expert at creating secure software for critical infrastructure protection (CIP), explained, "The threat landscape has changed drastically in recent years. There are actors out there whose only intention is to break into computer systems and networks to damage them, whether it is for fun or profit. There are many consequences, but eventually it costs organizations money and creates business risks."
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Various industries have regulations and standards for application security, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for the financial sector. Implementing robust security practices support compliance and avoid hefty fines.
According to software security expert Yiyi Miao, "Enforcing HIPAA technology compliance regulations across all employees and contractors can be a challenge for any healthcare organization. When you factor in the increased use of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) in organizations it quickly becomes an unmanageable situation."
2. Create a Threat Model
A crucial step to managing these challenges is understanding the risks you face. Threat modeling is a necessary step toward securing applications. It involves security teams finding potential threats and vulnerabilities in your applications so that you can prioritize security requirements and design applications with security in mind. Follow these steps to create a threat model for application security:
- Identify the assets and their value: The first step in threat modeling is finding the assets your application is designed to protect. This can include data, hardware, software, and other resources. Once you have recognized these assets, you should decide their value to the organization and prioritize them accordingly.
- Identify the potential threats: The next step is to find potential threats to your application. This can include attacks by hackers, insider threats, and physical security risks. Consider the potential impact of each threat on your application and prioritize them based on their likelihood and severity.
- Find vulnerabilities: Once you have found potential threats, you should find vulnerabilities in your application. This can include vulnerabilities in software code, network infrastructure, third party libraries, and user interfaces. Prioritize these vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on your application's security.
- Assess the likelihood of each threat: After finding potential threats and vulnerabilities, assess the probability of each threat occurring. This can help you prioritize your security requirements and ensure that your application is designed to protect against the most significant threats.
- Mitigation strategies: Finally, develop mitigation strategies to address potential threats and vulnerabilities in your application. Protect against possible attacks implementing access controls, encryption, and other security measures.
Remember, threat modeling is an ongoing process, so it's essential to continually assess and improve your application security measures based on the results of your threat modeling.
3. Establish a Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SSDLC)
Once you've set up a threat model for your organization, development teams can implement a secure software development life cycle (SSDLC) for your app development process. Lin explains, "SSDLC is a process consisting of a series of planned activities to develop software products. The SSDLC incorporates security into every phase of the software development life cycle—including requirement gathering, design, development, testing, and operation/maintenance."

Integrate Security into Each Phase
Integrating security measures throughout the development process is essential to ensure an effective application security program. This includes:
- Requirement gathering: Clearly define security requirements for the application, such as data encryption, user authentication, and access control.
- Design: Develop a secure application architecture that reduces the attack surface and incorporates security controls.
- Implementation: Use secure coding practices and follow industry-standard guidelines, such as the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) Top Ten, to minimize vulnerabilities in your code.
- Testing: Perform regular application security testing, including penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code review, to find and remediate security flaws.
- Deployment: Implement proper security measures for the application's production environment, such as secure server configurations and network protections.
- Maintenance: Regularly update and patch your application, monitor for security incidents, and respond to new threats as they emerge.
4. Essential Web Application Security Best Practices from OWASP
Web applications are among the most common apps used today. Web application security is crucial for any organization that wants to protect its data and reputation. The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) provides guidance from security teams and professionals. Unfortunately, many organizations still need to implement these best practices.
OWASP offers open-source resources to enhance web application security. Here are some of their best practices:
- Ensure that all user input is validated before processing. This includes checking for correct data types, length, format, and range. By implementing input validation, you can prevent a range of vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Use strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to control access to your application. This includes using secure password storage mechanisms, two-factor authentication, and other security measures to prevent unauthorized access.
- Follow secure coding practices to minimize the risk of vulnerabilities. This includes using secure coding techniques, avoiding insecure functions, and using frameworks and libraries that have been security reviewed. If you make sure you have secure code, you can prevent buffer overflows and format string vulnerabilities.
- Ensure that error messages do not reveal sensitive information and log all security-related events. This includes failed login attempts and other suspicious activities. By logging security-related events, you can quickly detect and respond to security incidents.
- Use secure session management techniques to prevent session hijacking and other attacks. This includes using secure session IDs, enforcing session timeouts, and invalidating sessions when users log out or after a period of inactivity. By implementing secure session management, you can prevent attackers from accessing sensitive information or taking unauthorized actions.
- Implement strong encryption and decryption techniques to protect data in transit and at rest. This includes using industry-standard algorithms and key lengths and properly protecting encryption keys. By implementing strong cryptography, you can prevent attackers from accessing or modifying data.
- Use access control mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive resources and functionality. This includes ensuring that users only have the permissions they need to perform their tasks and enforcing access controls at every application level. You can prevent unauthorized access to data or functionality by implementing access controls.
- Perform regular security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability scanning, to identify and address security weaknesses. Use automated tools and manual techniques to ensure that your application is secure.
- Follow secure deployment practices to prevent security risks during installation and configuration. This includes using secure protocols, avoiding default settings, and configuring security settings according to best practices.
- Have an incident response plan to respond quickly and effectively to security incidents. This includes ensuring that all staff members are aware of the plan and their roles in it and practicing the plan regularly to ensure that it is effective.
These best practices can help secure web applications and protect your organization's data and reputation. However, you’ll need to implement a security-focused culture in your organization that puts best practices in place.
5. Embrace a Culture of Security Awareness
Security Training for Developers
Developers play a crucial role in DevSecOps (development, security, and operations), as the code they write can create or prevent vulnerabilities. Providing regular security training for your development team, including secure coding practices, awareness of common attack vectors, and industry-specific compliance requirements, is important.
Conduct Security Awareness Programs
A strong security culture extends beyond the development team. Educate all employees about the importance of security and their role in maintaining it. Conduct regular security awareness programs that cover topics such as recognizing phishing attacks, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activities.
6. Implement Robust Authentication and Access Control Mechanisms
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing an application. Implement MFA using a combination of knowledge-based (passwords), possession-based (tokens), and inherence-based (biometrics) factors.
Apply the Principle of Least Privilege
The principle of least privilege restricts user access to only the minimum necessary resources and permissions. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to define and enforce appropriate user access levels.
7. Keep Your Application Updated and Patched
Stay Informed About Vulnerabilities and Patches
Regularly monitor industry sources, such as vendor websites and security blogs, for information about new vulnerabilities and patches. Subscribe to security mailing lists and vulnerability notification services to stay up to date on the latest threats.
Implement a Patch Management Process
Develop a patch management that evaluates, tests, and promptly deploys patches. This process should include a rollback plan if a patch introduces new issues or conflicts.
Russ Miller, an expert in patch management, explains, "Staying on top of a never-ending stream of patches for vulnerabilities is challenging, especially for larger enterprises. However, time is of the essence, and most organizations give potential adversaries ample time to attack."
8. Regularly Monitor and Audit Your Application
Implement Continuous Monitoring
Continuously monitor your applications for security incidents and anomalies, such as unauthorized access attempts, data breaches, and suspicious activities. Use security tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, and application performance monitoring (APM) tools to gain insights into the security status of your application.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Perform periodic security audits to evaluate the effectiveness of your security measures. These audits should include a combination of internal and external assessments, such as penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and compliance reviews.
9. Leverage Encryption and Secure Data Storage
Encrypt Data
Use encryption to protect data, both in transit and at rest. Implement protocols like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) for secure data transmission and use encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for data storage.
Follow Data Storage Best Practices
Adopt best practices for secure data storage, such as segregating sensitive data from other data, using secure database configurations, and regularly backing up your data to protect against data loss.
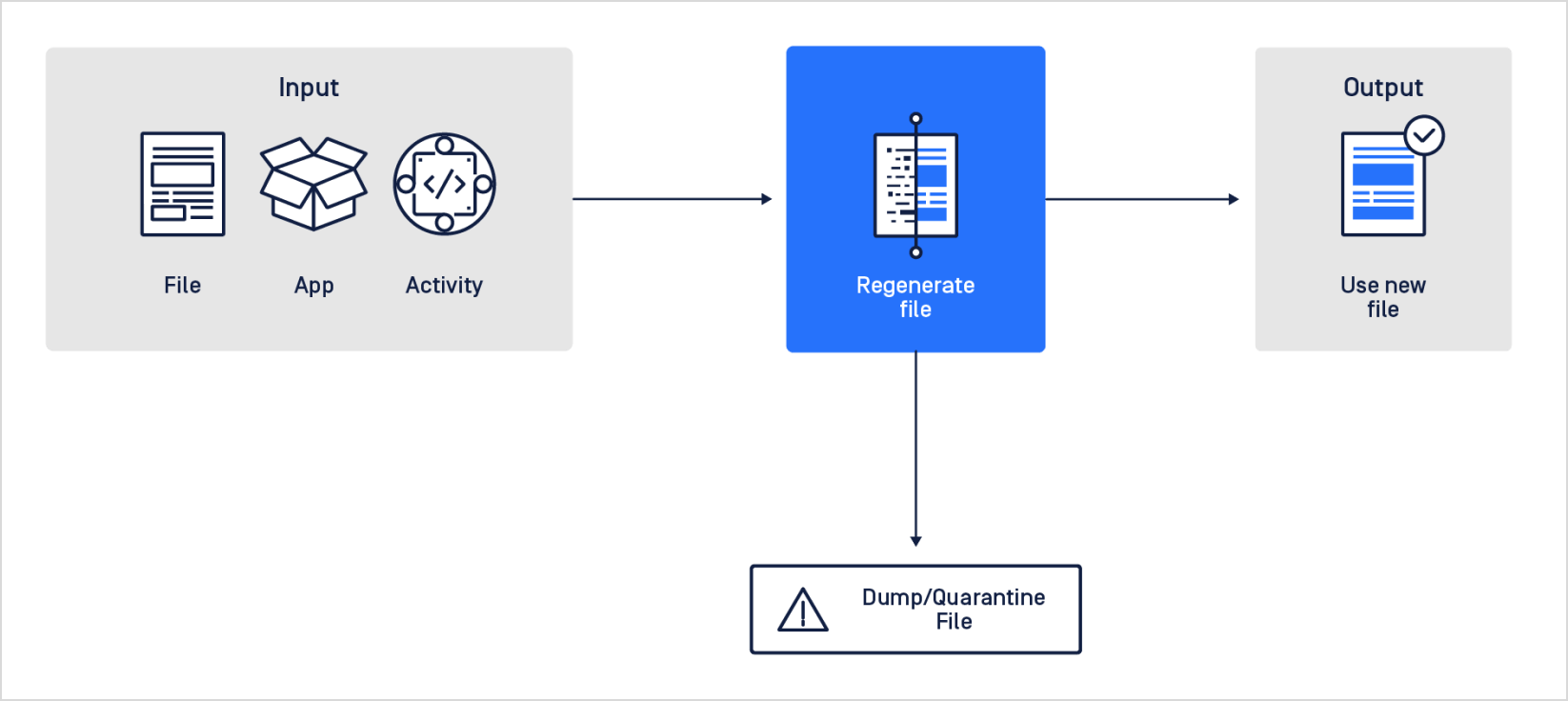
10. Utilize prevention and detection technologies
The latest proactive technologies offer a more effective and efficient approach to protecting organizations from file upload threats.
Choose technologies that leverage advanced automation features such as content disarm and reconstruction, machine learning, sandboxing, and multi-scanning engines to provide a comprehensive defense against file-based attacks. With these technologies, organizations can automate the scanning and analysis of uploaded files, including emails, attachments, and archives, to detect and prevent malware, zero-day exploits, and other threats.
Ensure that these technologies include artificial intelligence, behavior analysis, and user behavior analytics can also enhance file upload security. By utilizing these technologies, organizations can gain greater visibility into their network, detect anomalous behavior, and proactively prevent potential threats before they cause harm.
11. Cloud Application Security Best Practices
As more organizations move their web applications to the cloud, cloud application security has become a critical concern. The industry has raced to develop best practices to help you protect your cloud-based applications. Here are a few examples:
- Ensure that your cloud applications are configured securely. This includes using strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, configuring network security controls, and ensuring that encryption protects data in transit and at rest.
- Use identity and access management (IAM) solutions to manage user identities and access to your cloud applications. This includes using multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and monitoring user activity.
- Implement strong data security measures to protect your cloud-based data. This includes encryption, access controls, and monitoring data access and usage. Make sure to understand shared responsibility model to secure web apps.
- Implement vulnerability management practices to identify and address security vulnerabilities in your cloud applications. This includes regularly scanning for vulnerabilities and patching known vulnerabilities as soon as possible.
- Choose a cloud provider with strong security measures in place. This includes ensuring the provider offers strong physical security, network security, and access controls.
- Implement continuous monitoring of your cloud applications to detect and respond to security incidents quickly. This includes monitoring unusual user activity, network traffic, and system activity.
Following these cloud security best practices can help ensure your cloud-based applications are secure and protected from potential threats. Staying current on the latest security threats and trends and continually assessing and improving your cloud security measures is crucial.
12. Secure Against Malware at the Network Parameter
Securing network parameters with ICAP (Internet Content Adaptation Protocol) is a powerful method for preventing malicious file uploads. ICAP enables organizations to scan and analyze content in real-time, allowing them to identify and block any malicious files before they reach their intended destination. By integrating ICAP with existing network devices such as web application firewalls, reverse proxies, and SSL inspectors, organizations can seamlessly add a layer of protection to their network.
Furthermore, ICAP's content adaptation and transformation capabilities allow organizations to enforce policies and modify content in transit, giving them granular control over the flow of data through their network. By utilizing ICAP, organizations can effectively secure their network parameters and prevent malicious file uploads, improving their overall cybersecurity posture.
13. Application Security Testing
Testing is a crucial part of any security program. Testing helps find and address potential security risks before attackers can exploit them. Several types of application security testing can be conducted, such as vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and code reviews. These tests help identify vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and buffer overflows.
It's important to conduct both manual and automated application security testing to ensure that all potential vulnerabilities are identified and addressed. Automated web application security testing tools help streamline the testing process and identify vulnerabilities more efficiently. However, automated tools may not catch all potential vulnerabilities, so manual testing is also necessary.
Third party testing is also beneficial, as it supplies an objective assessment of your security posture and identifies vulnerabilities that may have been missed by internal testing. By conducting regular testing, you can help ensure that your applications are secure and protected from potential security threats.
Conclusion
In today's digital landscape, security is crucial for businesses to safeguard their data and maintain customer trust. By adopting security best practices, you can significantly reduce security risk, cyber threats, and protect your organization's valuable assets.
App Sec FAQs
Q: What is app sec, and why is it important?
A: Application security refers to the measures and practices employed to protect applications from external threats, malware, data breaches, and vulnerabilities. It is crucial for safeguarding Personal Identifiable Information (PII), maintaining customer trust, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. It is an extension of software security best practices.
Q: What is a Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC)?
A: A Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) is an approach that integrates security measures throughout the software development process. It includes security-focused activities during requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance phases.
Q: How can I create a culture of security awareness within my organization?
A: Cultivate a security-aware culture by providing regular security training to developers, conducting security awareness programs for all employees, and promoting a shared responsibility for maintaining security.
Q: What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and why is it essential for security?
A: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing an application. It is essential for app security because it adds an extra layer of protection, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Q: What are some best practices for secure data storage?
A: Data storage security is essential for protecting sensitive information from cyber threats. To achieve this, organizations can implement best practices such as encrypting data, segregating data, using secure database configurations, and regularly backing up their data. Additionally, real-time threat intelligence and malware scanning is a powerful solution for preventing latent outbreaks and ensuring continuous protection against cyber-attacks.
Q: How often should I conduct security audits for my application?
A: The frequency of security audits depends on factors such as the complexity of your application, regulatory requirements, web server, security team, and your organization's risk profile. However, it is recommended to perform regular, periodic audits.
Q: What are some best practices for web applications?
A: Following web application security best practices from organizations like OWASP will limit security issues. You can learn more about how OWASP helps manage your web application security blueprint and prevent attackers from finding security issues before your security team.

