Organizations of all sizes store sensitive information – from financial records to intellectual property – and protecting these types of data is crucial. Unfortunately, cyber threats are constantly evolving, and staying ahead of the curve requires vigilance and proactive measures.
Here are some of the most common data storage security risks and blind spots that potentially put organizations in jeopardy, from business disruption to financial and reputational damage. Additionally, we recommend the equivalent solutions that organizations can incorporate to their 2024 cybersecurity strategy to mitigate these risks:
1. Malware
Malware poses a significant threat to the security of data stored in both on-premises and cloud environments. While the methods of attack may differ between the two, the consequences of a data breach event can be equally devastating.
Approximately 450,000 new instances of malware are detected daily, serving as a significant warning for all enterprises to enhance their readiness for emerging threats. Files in storage are often exploited by attackers to deliver covert malware. This enables attackers to move laterally within the storage infrastructure, putting organizations’ digital assets and sensitive data at risk.
Solutions


Multiscanning
A single antivirus engine can detect 4% to 76% of malware, making it easy for malicious files to slip through the cracks. OPSWAT Multiscanning integrates the power of over 30 anti-malware engines on-premises and in the cloud, boosting detection rates to nearly 100%.
File Sanitization
Trust no file. Deep CDR (Content Disarm and Reconstruction) sanitizes more than 150 file types, and recursively sanitizes multi-level nested archives, helping organizations prevent zero-day attacks.
2. Data Breaches
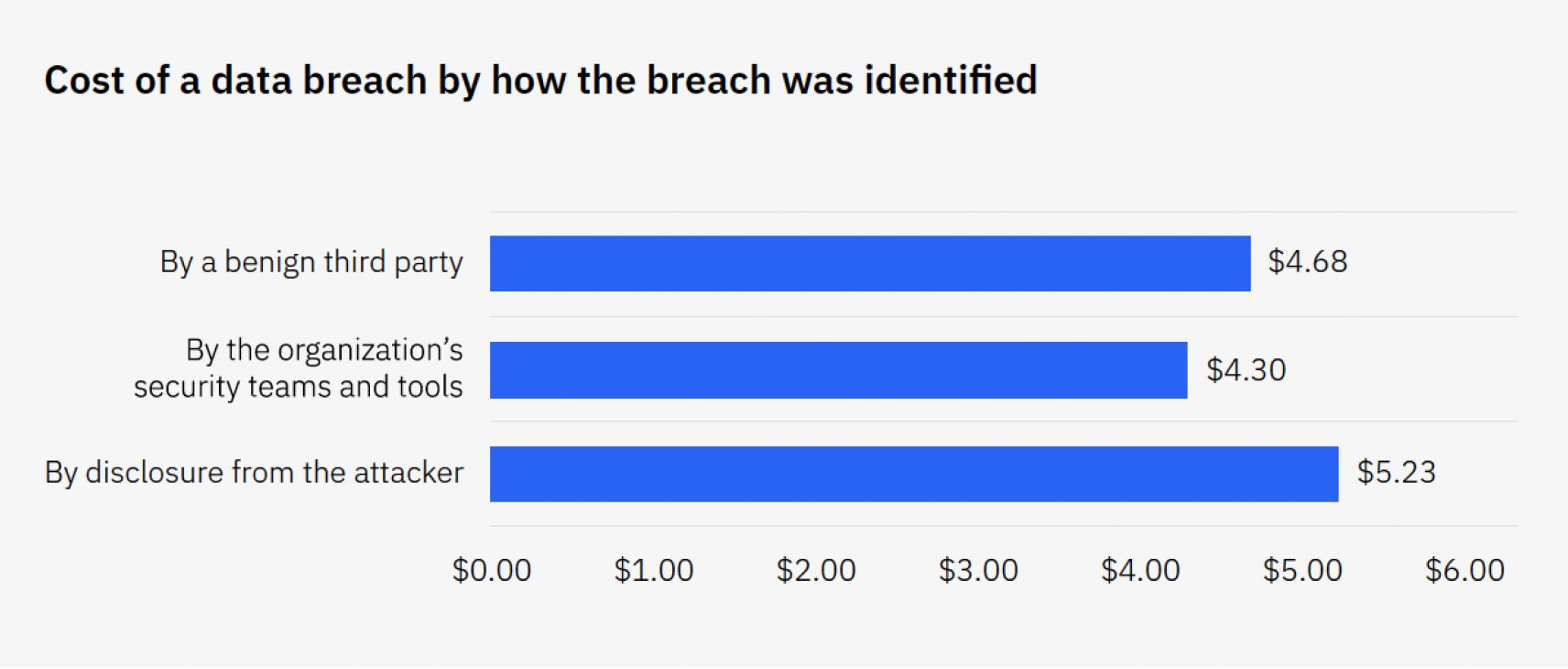
An organization’s risk of a data breach is directly impacted by the type of storage used. Cloud storage providers typically have robust security measures in place, but they are not foolproof. On-premises data storage systems can also be secure, but they may be more vulnerable if they are not properly managed.
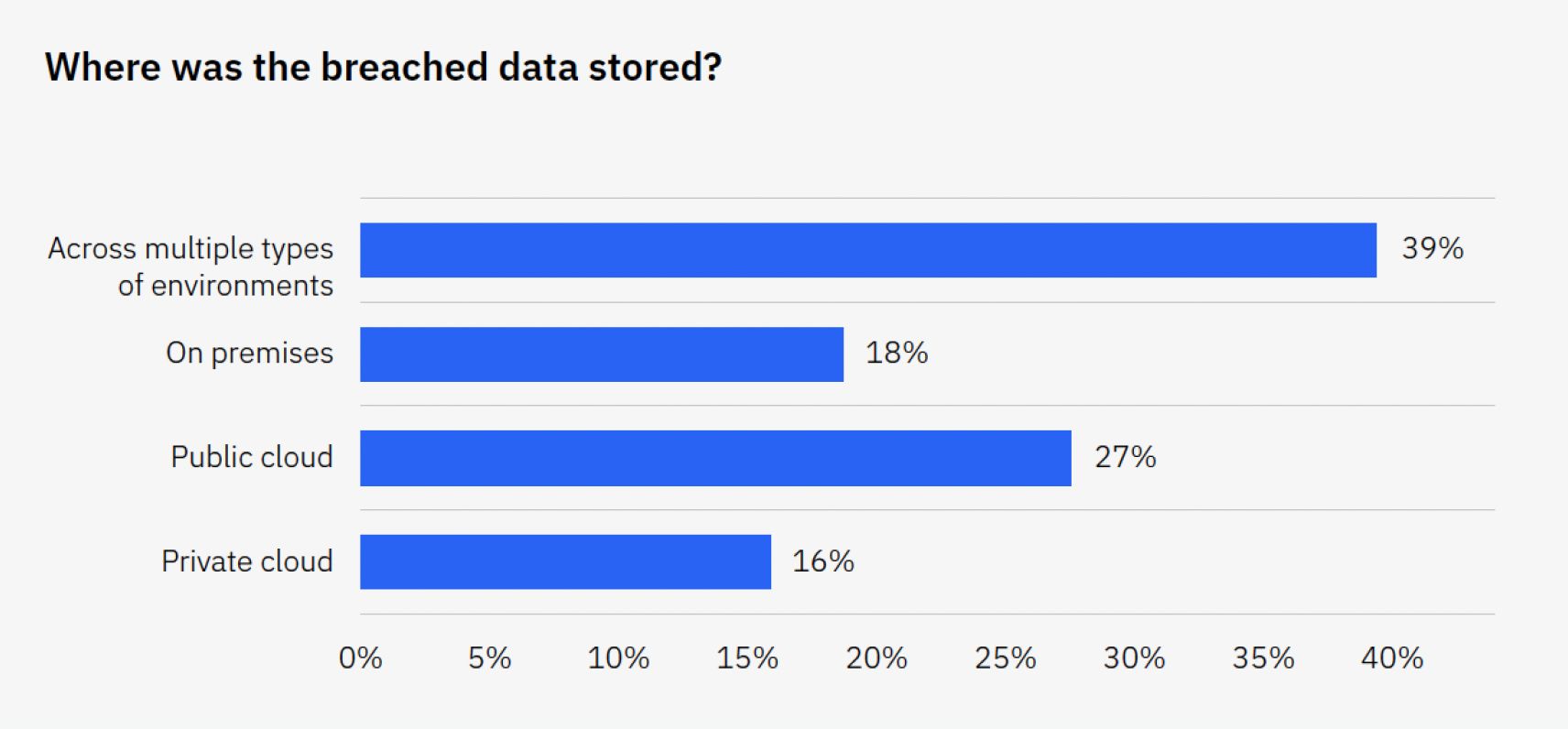
Organizations are increasingly embracing a multi-environment storage approach, spreading data across on-premises infrastructure, public clouds, and private clouds. This hybrid strategy offers scalability, redundancy, and cost-effectiveness, but comes with a heightened risk of data breaches due to the dispersed nature of the information.
The cost of data breaches across multiple environments reached US$4.75 million, exceeding the average cost of a data breach of US$4.45 million by a margin of 6.5%.
Solutions

Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data loss prevention (DLP) technology detects and blocks sensitive, out-of-policy, and confidential data in files from leaving or entering the organization’s systems. To take it to the next level, OPSWAT Proactive DLP automatically redacts the sensitive information, whether text-based or image-based.
Backup and Recovery
Maintain secure, regular backups to enable swift recovery in the case of unforeseen attacks.
3. Misconfiguration and Unauthorized Access
As stated by the National Security Agency (NSA), cloud misconfigurations are the most prevalent cloud vulnerability and can be exploited by hackers to access cloud data and services. Configuration errors due to incorrectly granted permissions, unchanged default configurations, and poorly managed security settings can expose sensitive data or services.
Solutions
4. Insecure APIs
Hackers exploit weaknesses in APIs to gain unauthorized access, tamper with data, and implant malicious code into cloud configurations. Both end-users, who access cloud services through APIs, and businesses, who rely on secure data exchanges, face these risks. With the increasing usage of APIs in programming, securing APIs is crucial in mitigating common attack vectors, like code injection and exploiting vulnerabilities in access controls and outdated components.
Solutions
5. Insider Threats
Disgruntled employees or malicious insiders can pose a significant security risk. A Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigation report revealed that 99% of breaches involving privilege misuse were carried out by insiders.
Solutions
6. Insufficient Data Encryption
Insufficient data encryption in cloud storage occurs when information is inadequately safeguarded during transit or at rest, leaving it vulnerable to unauthorized access. Lack of encryption poses significant risks, including unauthorized entry, interception during data transfer, compromise of confidentiality, data manipulation, and non-compliance with regulations.
Solutions
Server-side Encryption
Encrypt all sensitive data at rest and in transit using strong encryption algorithms like AES-256.
Conclusion
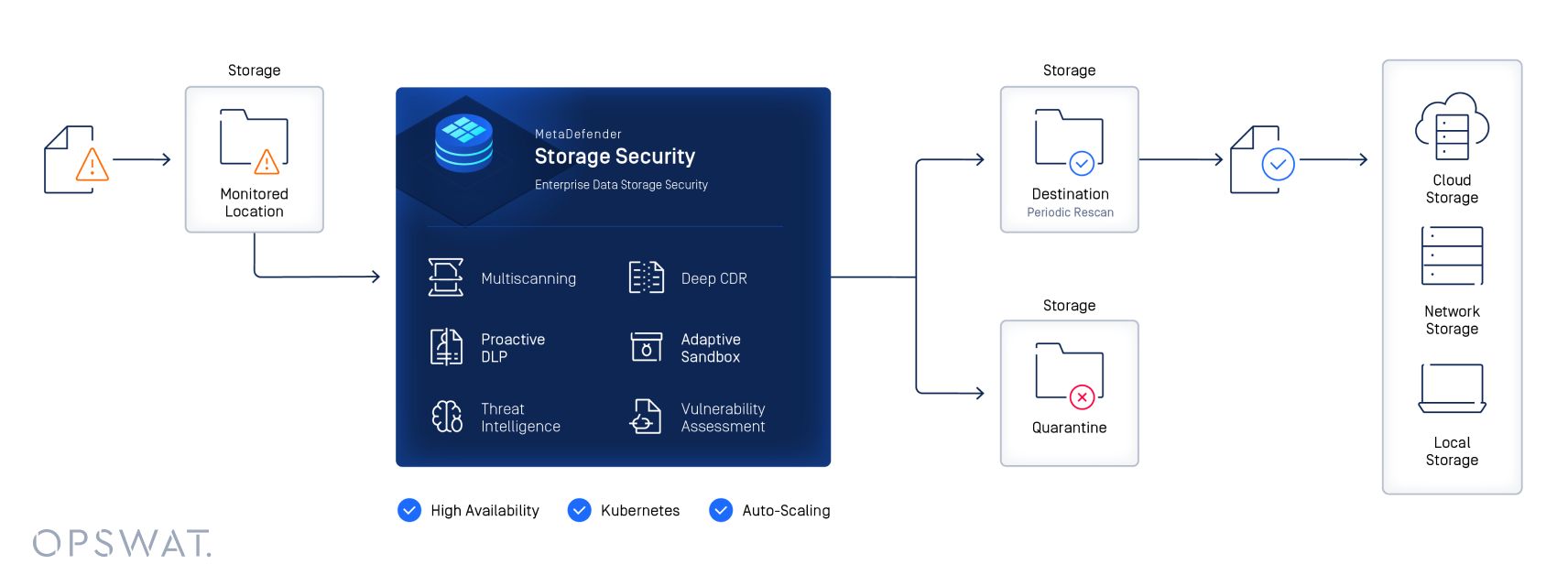
Navigating these individual solutions can be complex. OPSWAT MetaDefender Storage Security offers a unified platform that simplifies data security by seamlessly integrating with leading on-premises and cloud storage solutions.
MetaDefender Storage Security improves your organization’s security posture with a multi-layered defense strategy, which is critical to stay ahead of known and unknown threats.
Learn more about how you can protect your file storage with OPSWAT technologies.