Introduction
QR codes have become indispensable for authentication, device pairing, and file sharing on collaboration platforms. However, their convenience has made them a prime target for cybercriminals. According to Egress, QR code phishing (quishing) surged from 0.8% of phishing emails in 2021 to 12.4% in 2023, with a sustained rate of 10.8% in 2024. This exponential growth reflects a strategic shift by attackers to exploit trusted tools like Signal and Microsoft Teams, which are now central to enterprise communication.
This blog explores how QR code-based attacks bypass traditional defenses, highlight real-world incidents, and outlines how MetaDefender Core mitigates these risks through Deep CDR™, InSights Threat Intelligence, and API-based integrations.
Top QR Code-Based Attacks Making Headlines in Q1 2025
Signal’s Linked Devices Attack—Bypassing Authentication
Signal, a leading encrypted messaging app, allows users to link devices via QR code scans instead of passwords. A critical flaw enables attackers to permanently link malicious devices if the primary device is compromised.
Attack Method
- Phishing emails or social engineering schemes trick users into scanning QR codes under the guise of “account verification.”
- Once scanned, the attacker’s device gains full access to messages, contacts, and communications—no password required.
Real-World Impact
- Russian espionage groups, identified by Google’s Threat Analysis Group, exploited this flaw to target Ukrainian users (Wired).
Black Basta’s QR Code Phishing in Microsoft Teams
Black Basta, a notorious ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) group active since 2022, has pivoted to QR code phishing in Microsoft Teams.
Attack Method
- Fake IT security alerts are sent via Teams, urging employees to scan a QR code to “verify” Microsoft 365 credentials.
- QR codes obscure malicious URLs, evading email security tools.
- Victims are redirected to fake login pages, enabling credential theft, privilege escalation, and ransomware deployment.

How MetaDefender Core™ Prevents QR Code-Based Attacks
To combat these evolving threats, organizations need advanced security solutions that go beyond traditional phishing detection. MetaDefender Core utilizes multi-layered technologies specifically designed to neutralize file-borne and credential-based threats in collaboration platforms.
Deep CDR
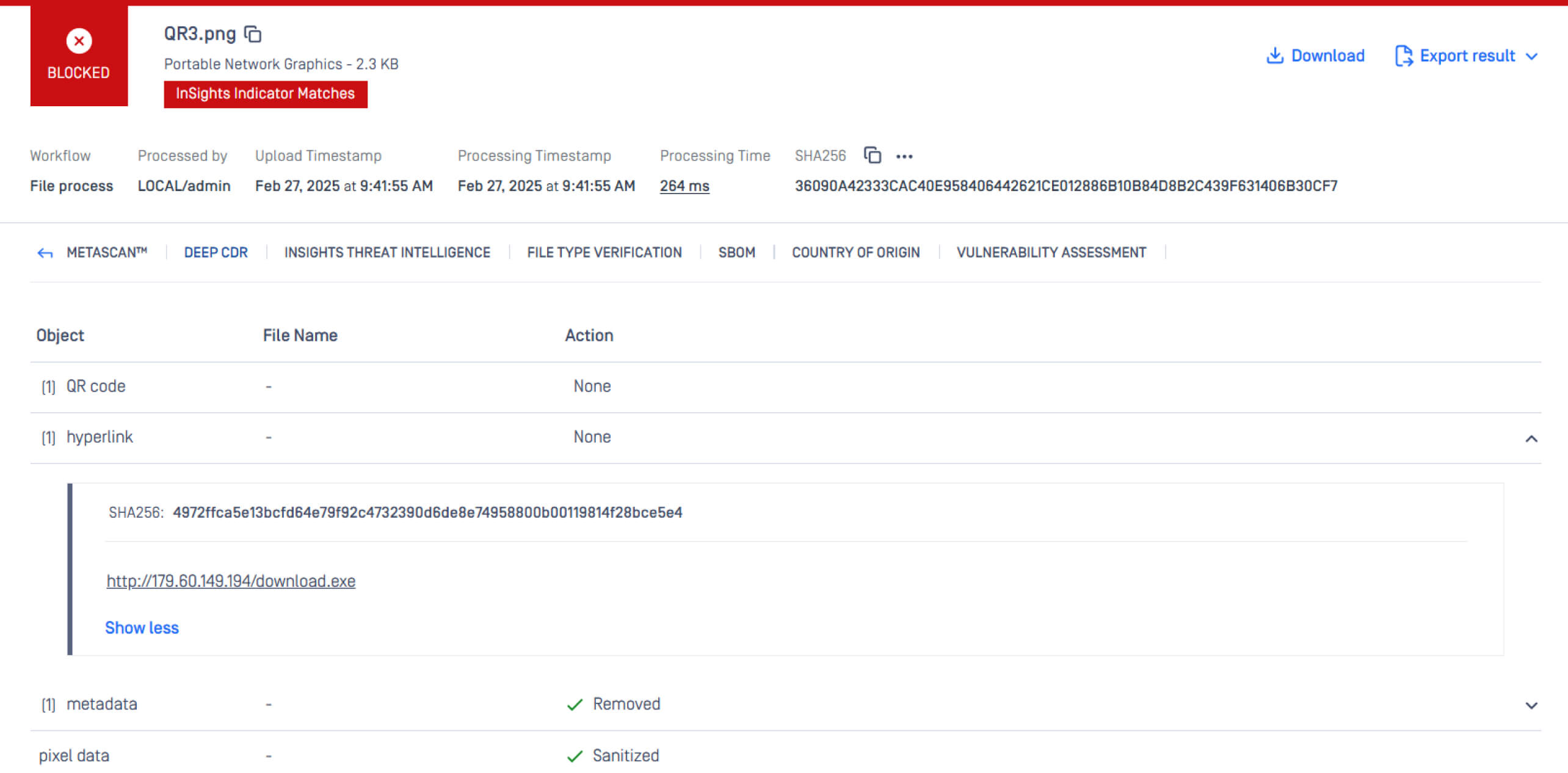
Deep CDR sanitizes image files by removing potentially malicious elements and out-of-policy content (e.g., obfuscated URLs) and regenerating new, safe-to-use files. To prevent quishing attacks, Deep CDR:
- Extracts the hyperlink from the QR code and neutralizes threats.
- Regenerates a safe-to-use QR Code allows users to add a URL scanning service to it.
InSights Threat Intelligence
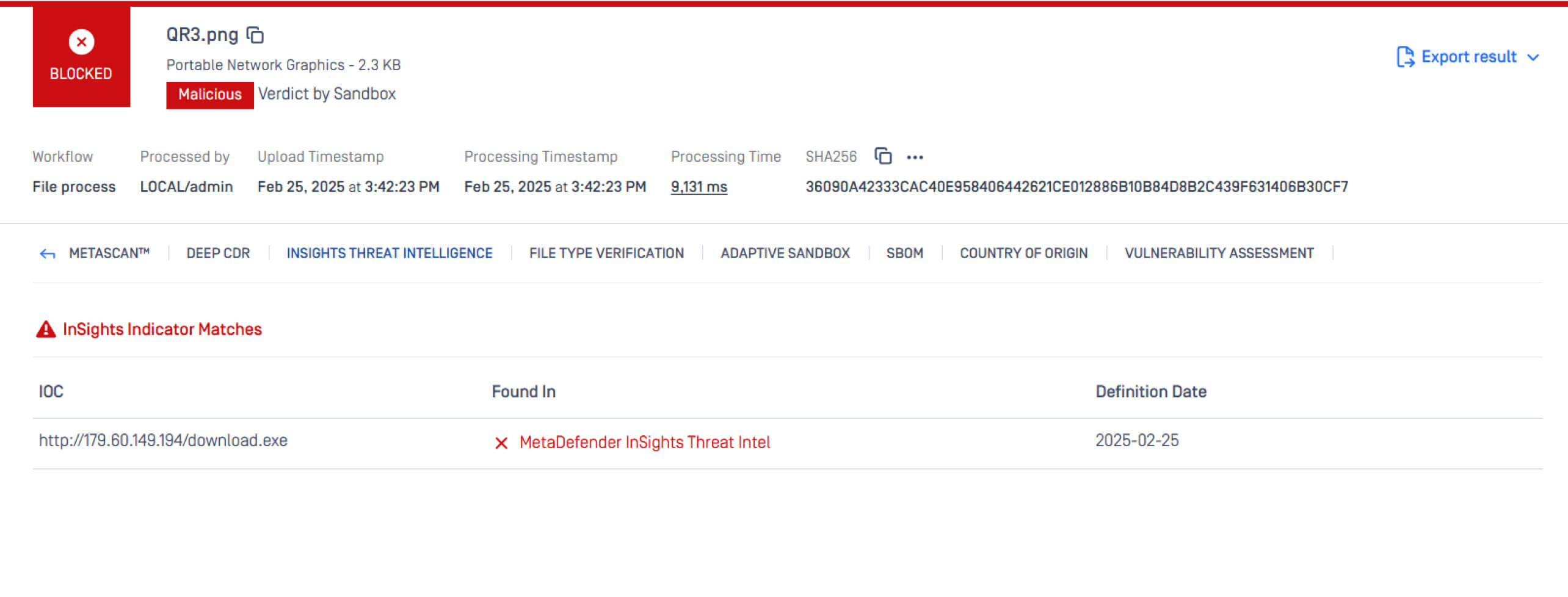
Use InSights Threat Intelligence to identify and block malicious domains and IPs in QR Codes in near real-time using curated threat intelligence from multiple sources.
- Detect the domain extracted from the QR codes by Deep CDR.
- Prevent employees from accessing blacklisted or suspicious domains.
- Continuously update risk intelligence based on evolving threats.
Keep Quishing at Bay with the Right Defenses
QR codes are no longer just a convenience—they have become a prime target for cybercriminals looking to steal credentials, bypass MFA, and deploy ransomware. To mitigate these risks, enterprises should adopt a zero-trust approach to QR code interactions, including:
- Educating employees on QR code phishing risks and attack methods.
- Strengthening mobile security policies to reduce the likelihood of unauthorized scans.
- Deploying proactive threat prevention solutions like MetaDefender Core to sanitize QR codes, block malicious domains, and integrate security into enterprise workflows.
One compromised QR code scan can lead to a full-scale security breach. Organizations must act now to stay ahead of attackers by going beyond traditional defenses and adopting multi-layered, defense-in-depth solutions.
Additional Resources
- Visit MetaDefender Core product page
- Download the File Upload Security Solution Brief
- Read this blog: Stop QR Code Phising – Protect Critical Infrastructure



