Nineteen years after their development, QR codes have progressed from niche barcode alternatives to enabling trillions of dollars in financial transactions. They connect the physical and digital worlds. Now, they're used to attack critical infrastructure.
As we've observed with URL shorteners and embedded hyperlinks, obfuscating endpoints is an effective method for tricking people into accessing malicious content. Attackers only need to embed a malicious link in a QR code, send an email, employ social engineering techniques, and you have an effective QR code phishing campaign.
We will walk you through how attackers use QR codes to target organizations and how you can prevent such attacks.
QR Code Phishing:
An Emerging Attack Vector
Historically, QR codes were an uncommon choice for cybercriminals targeting enterprises and critical infrastructure. However, they offer several advantages over embedding a phishing link directly in an email. QR code delivery methods have a much better chance of reaching a target’s inbox by avoiding antimalware and spam filters because attackers can embed QR codes within a PNG image or PDF attachment.

While using QR codes for phishing might seem counterintuitive at first—the victim must use their phone's camera to scan the code on another device for the scheme to work—the prevalence of QR codes for financial transactions and 2FA creates a sense of legitimacy and urgency that manipulates users into scanning the code. Moreover, the encoding masks the URL they lead to, making it harder for users to judge its legitimacy.
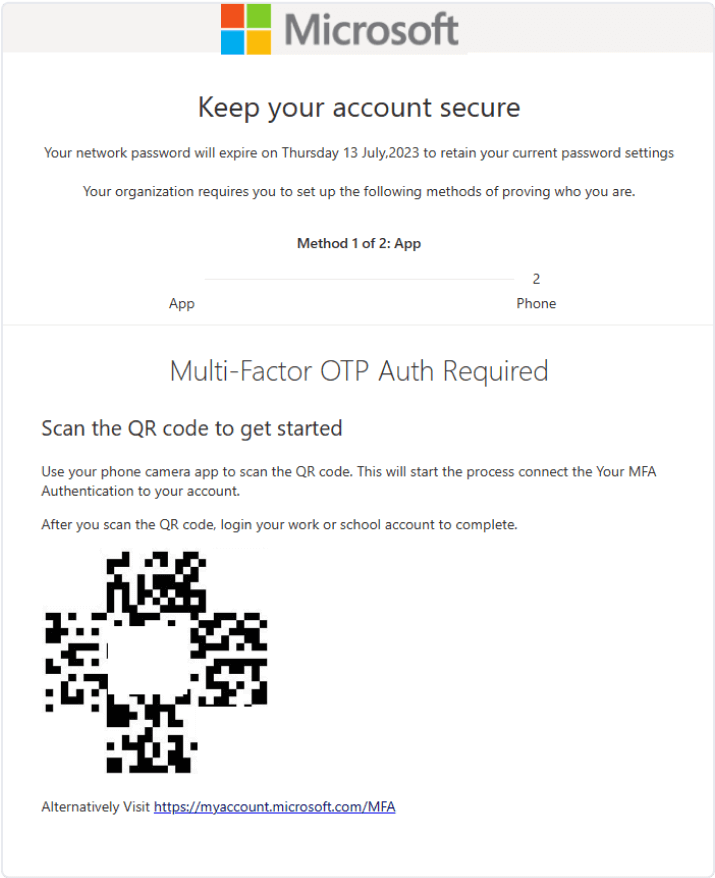

Source: link
A recent phishing campaign, ongoing since May 2023, has unleashed a series of malicious QR codes to acquire Microsoft account credentials from unsuspecting users. The most notable target is a prominent energy firm based in the US.
However, it's not just the energy sector that's under threat. Organizations spanning the finance, insurance, manufacturing, and tech sectors have also been in the crosshairs. Since its discovery, the campaign has seen a staggering growth of over 2,400%.
Disarm Malicious QR codes with Deep CDR™ Technology
QR code attacks exploit the fact that the human eye cannot read the encoded information. Consequently, users trust that the code will lead to the correct URL or carry out its intended function. OPSWAT Deep Content Disarm and Reconstruction (Deep CDR™ Technology] displays the human-readable URL encoded in the QR code, users can check the legitimacy of the URL before they scan.
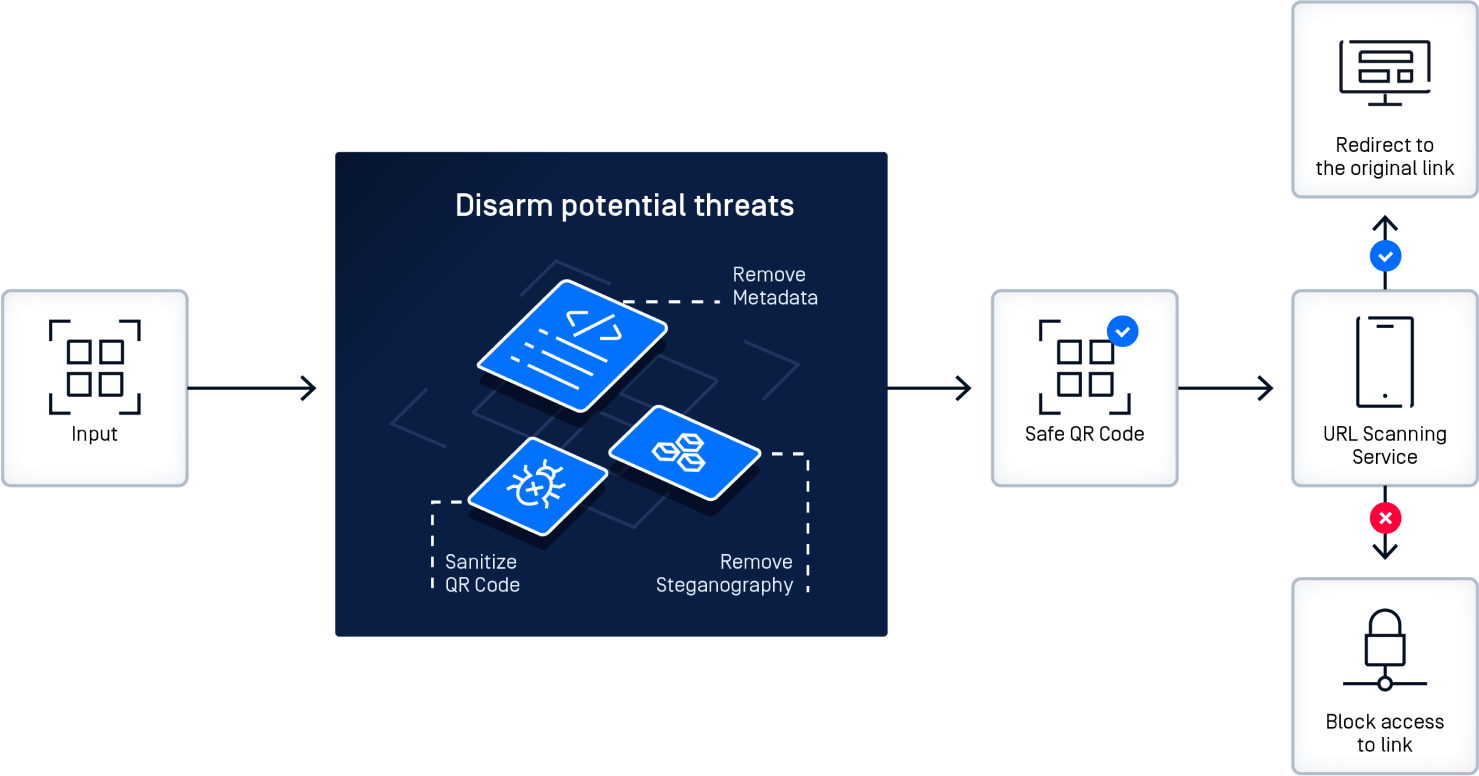
A diagram depicting how Deep CDR™ Technology disarms threats in QR Code.
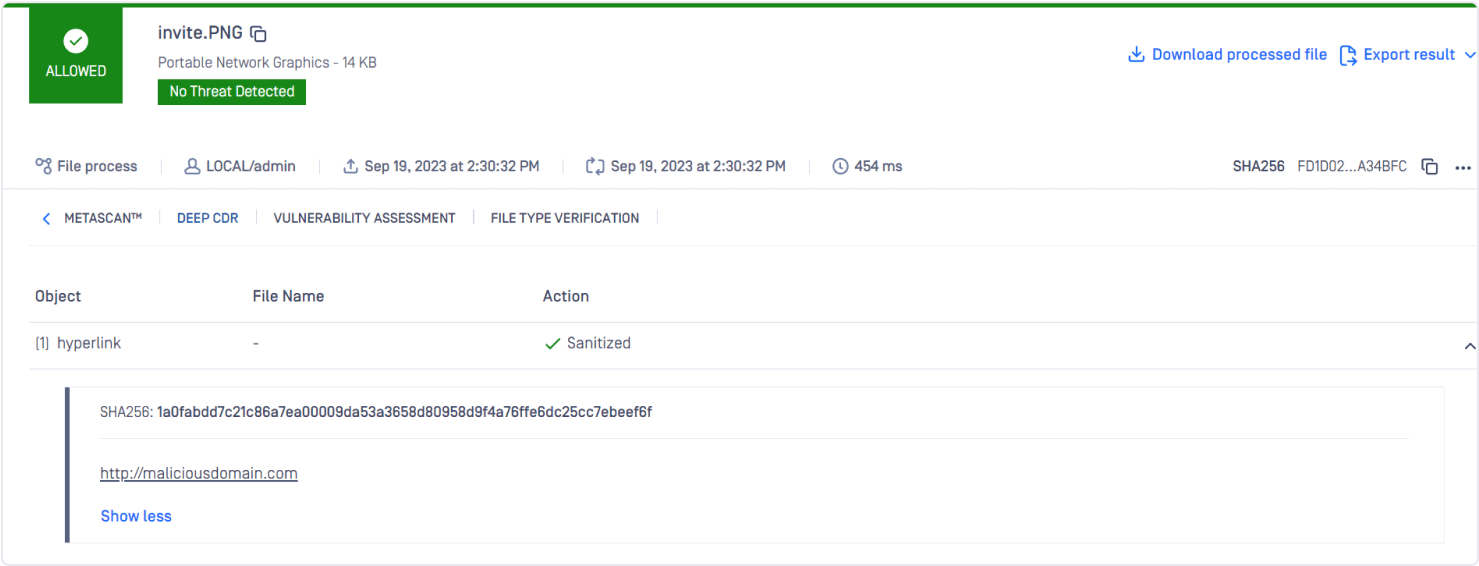
Attackers commonly use disguised or shortened URLs to deceive users. Deep CDR™ Technology can scan the URL with MetaDefender Cloud Safe URL Redirect to determine if it is malicious. If a URL is safe, users are directed to the location. If it's suspicious, they're alerted with a warning. You can configure Deep CDR™ Technology to work with any URL scanning service.
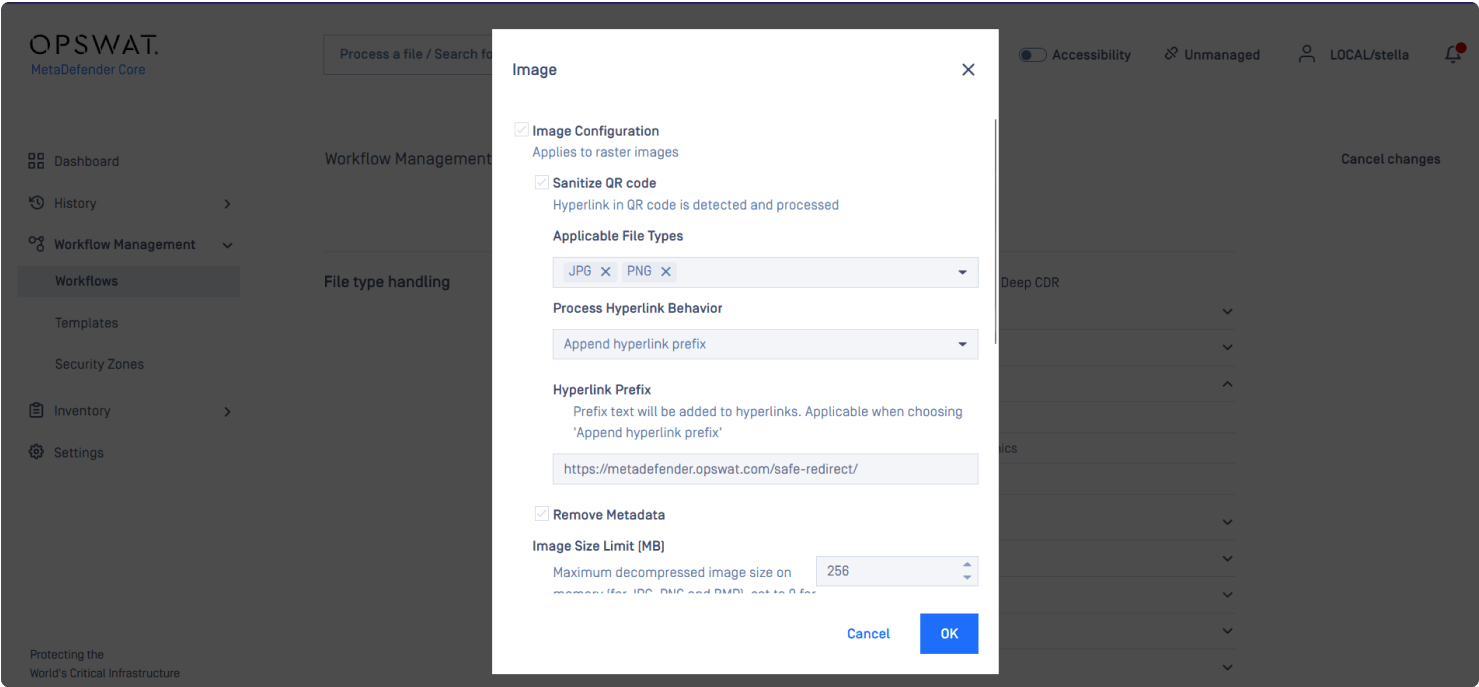
Since QR Codes are often image-based, they can hide threats using steganography. Deep CDR™ Technology can effectively mitigate these potential risks, as demonstrated here.
QR Code before and after Deep CDR™ Technology Sanitization. The image on the left has embedded code for a malicious QR code attack. The image on the right has been sanitized with MetaDefender Deep CDR™ Technology.
OPSWAT Best Practices for QR Code Security
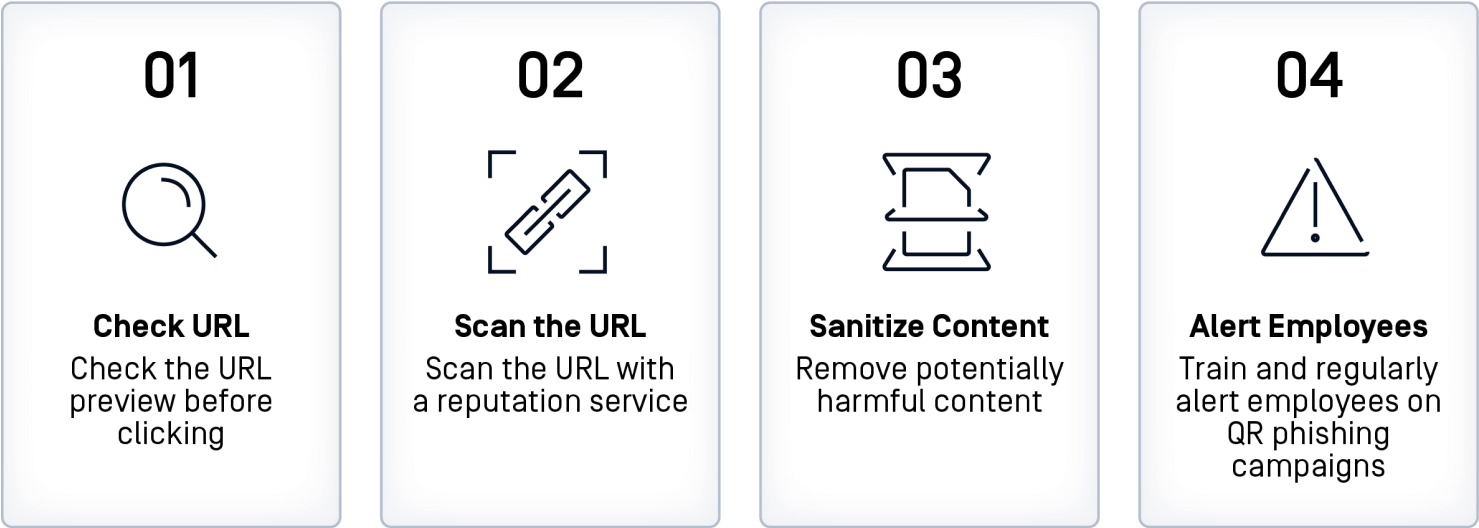
The ubiquity and trust in QR codes have expanded the attack surface. However, awareness of the rising threat of QR code phishing and taking proper precautions can help users and businesses stay protected. Deep CDR™ Technology delivers advanced security to combat this emerging attack vector.
As QR code usage continues to grow, so will exploits by cyber-criminals to
leverage them for phishing and malware campaigns. QR code phishing highlights
the importance of ongoing vigilance and the need to adopt innovative security solutions to counter an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Deep CDR™ Technology's capabilities provide an adequate safeguard against QR code phishing by extracting and inspecting QR code contents to intercept attacks before they compromise devices and data. Combining enhanced awareness, secure practices, and advanced technology allows us to reap the convenience of QR codes while mitigating their risks.



