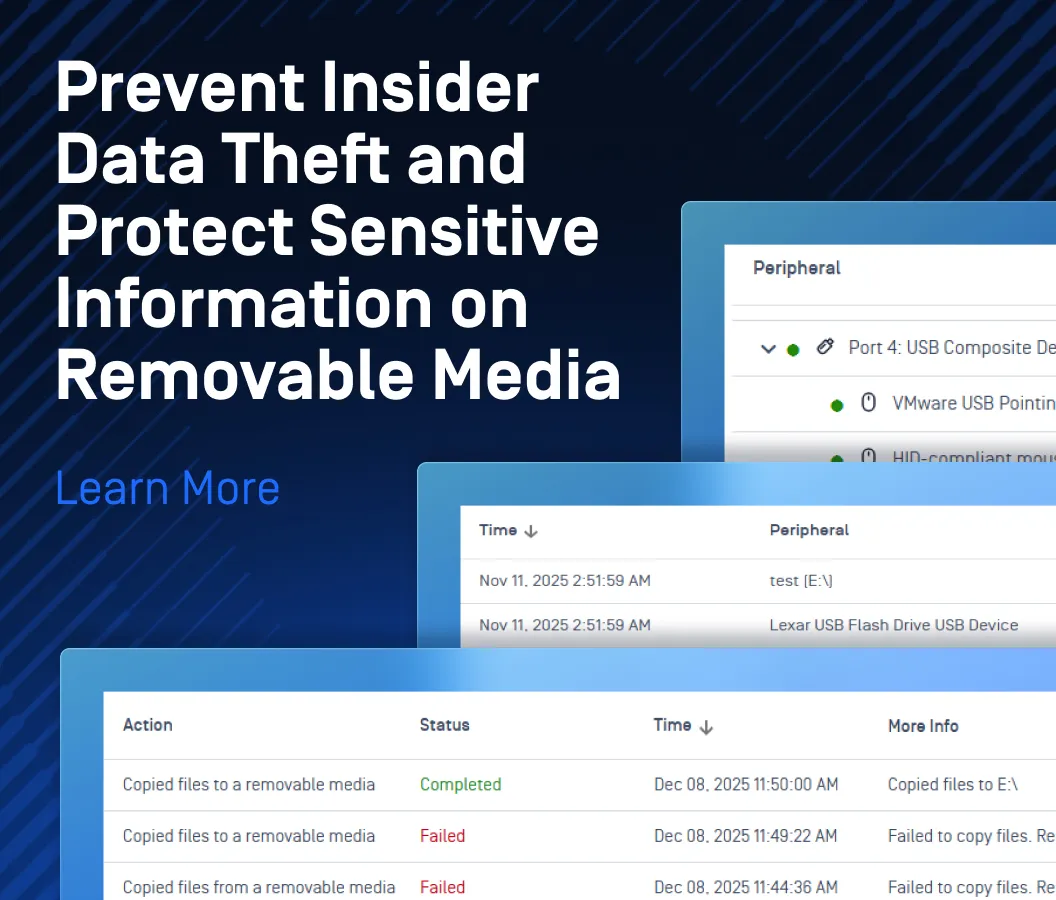
What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
A virtual desktop is a virtualized workstation where operating systems, applications, folders, and other resources are run on a server. Virtual desktops allow users to access remotely over the Internet from a separate device.
VDI, or virtual desktop infrastructure, refers to the entire IT infrastructure that facilitates the process of delivering virtual desktops to end-users. VDI enables users to access enterprise systems and work from their personal devices (laptops, smartphones, tablets, etc.), while the computing workload is handled from the controlled server side.
What are the benefits of VDI?
- Productivity for a remote and dynamic workforce: Because software and data are not bound to users’ endpoints, remote workers or sales representatives in the field for example, can access the enterprise system from any devices available, making sure productivity is prioritized.
- Advanced security: VDI offers more comprehensive security capabilities thanks to on-premises oversight. Organizations can deploy their VDI on trusted third-party cloud or datacenter vendors, many of which provide the latest infrastructure, security, backup, and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Improved Compliance: By managing a centralized computing resource, organizations can improve their compliance posture without additional time and effort. Centralized management simplifies regulation compliance by ensuring consistent adherence of security policies and a consolidated auditing process.
- Streamlined IT administration: With VDI, organizations can also reduce efforts on IT administration tasks such as troubleshooting and repair, thanks to a centralized, “big computer” server instead of having to attend to each physical device individually.
VDI Architecture
VDI deploys virtual machines, or configured programs of multiple desktop environments to centralized, physical server hardware. Organizations can manage the server on-premises or choose specialized third-party service providers such as Microsoft Azure or VMware to manage from the cloud.
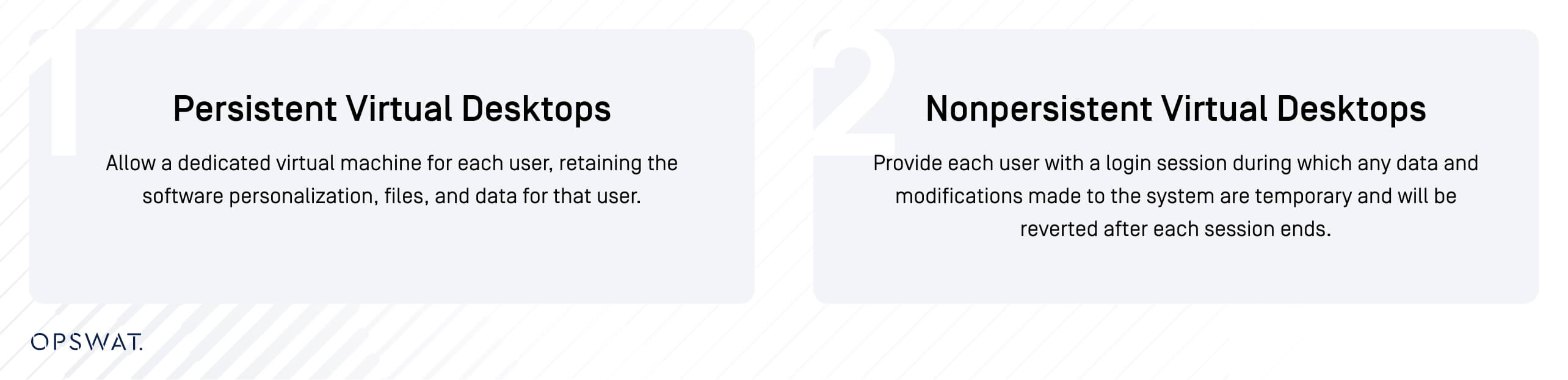
VDI partitions the physical server’s hardware resources to accommodate multiple virtual machines’ simultaneous operation. Virtual desktops are commonly deployed in two forms: persistent and non-persistent virtual desktops.
VDI Security Risks
VDI is managed centrally with fortified security capabilities in both on-premises and on-cloud setup. However, the most significant risk to VDI arises from users’ endpoint devices that access the virtual machines. Attackers can infiltrate and compromise VDI’s security by exploiting various endpoints vulnerabilities, the most notable of which are:

Malware
Endpoints containing malware from many sources nowadays, such as file downloads, emails from untrustworthy parties, and peripheral media

Patches and vulnerabilities
Endpoints with end-of-line operating systems or outdated software that contain security vulnerabilities

Unsecured networks
Endpoints connecting to weak protocol networks like public wireless networks

Data Leakage
Endpoints not adhering to data protection policies, leading to accidental and intentional data leakage
How OPSWAT Can Help
OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Access is purpose-built to address threats relating to endpoint devices accessing VDI. Underpinned by globally trusted technologies, MetaDefender Access enforces deep compliance checks on endpoint devices before they can start sessions with virtual machines. This ensures only compliant endpoints are granted access to virtual desktops; otherwise, remediation prompts will guide users through the process to address their security posture to continue. MetaDefender Access strictly enforces VDI security policies, preventing threats from any connecting endpoints, whether they are BYODs (bring your own devices), public computers, or third-party contractors.
OPSWAT MetaDefender Access has earned VMware’s trust as a key layer of defense for its Horizon VDI offerings. Discover more here. Speak with our experts today to learn how OPSWAT can fortify your virtual desktop infrastructure’s security.