Device security is a set of cybersecurity measures to protect enterprise endpoint devices. In critical infrastructure organizations, devices for work purposes such as PCs, laptops, mobile devices, and tablets must be safeguarded from numerous cybersecurity threats and unauthorized access. Effective device security is often rooted in strong authentication, endpoint device management, and network access control.
Why is Device Security Important?
The rapid pace of technological advancement has increased the rise of cybersecurity threats, especially for enterprise endpoint devices. Critical infrastructure organizations employ a wide range of information and operation technology (IT, OT) devices, which interconnect and interact within complex networks. The rise of remote work, BYOD policies, and diverse work device options introduce threats like malicious apps, unauthorized access, phishing attacks, and unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
How to Maintain Device Security Strategy?
Users with direct access to devices are key factors in device security strategy. Employees must be educated to make sure they thoroughly understand threats such as data phishing, leakage, and how to avoid risky behaviors.
Device security must include a zero-trust security principle in its enterprise implementations. Zero-trust is the cybersecurity model that assumes no device or user can be trusted by default, even if they are connected to a permissioned network. The concept behind this philosophy is “never trust, always verify”, shifting away from traditional trust-based assumptions.
Technologies to protect devices from cyberthreats may be implemented for different use cases. Multiscanning uses 30+ antivirus engines to detect 99% of threats before they can infiltrate any endpoints. Deep CDR™ Technology (Content Disarm and Reconstruction) removes any potentially malicious code and sanitizes files, and an Industrial Firewall can help ensure only authorized files have access to organizations’ systems. Staying up to date with the latest technological developments and adapting to changing corporate needs are crucial practices to ensure device security.
What are the Main Types of Device Security?
There are several types of device security:

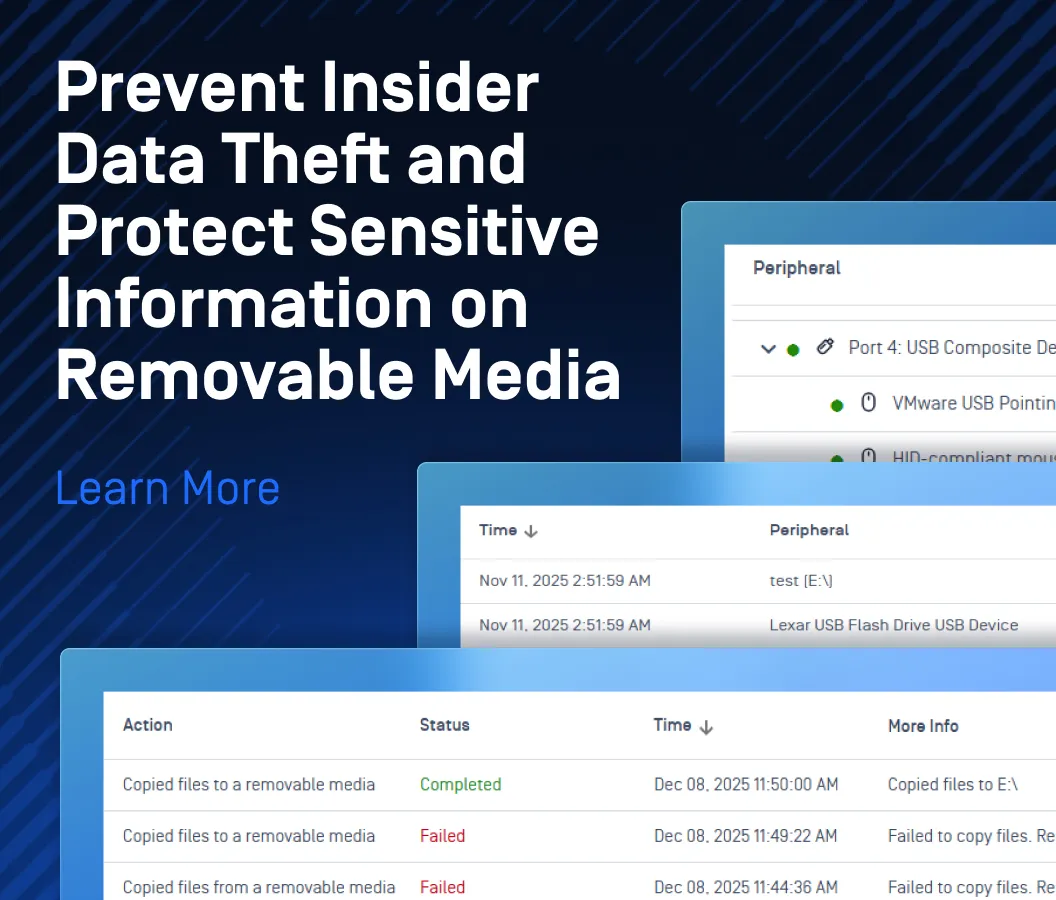
Every endpoint must be protected with technical solutions like strong authentication methods, anti-malware protection, compliance checks, removable media protection, vulnerability, and security patch management.

Sensitive information such as login credentials contained on each device must be protected to ensure overall device and network security. If this data is compromised, it can be used to gain unauthorized access to other devices on the network, leading to potential sabotage and broader breaches.

It is crucial for organizations to create a secure infrastructure for devices, users, and applications to work together securely. Network security solutions include, but are not limited to, monitoring and maintaining devices visibility, and implementing an automated risk response mechanism.
How to Implement Device Security
Critical infrastructure organizations often rely on a combination of IT and OT devices as well as BYOD remote work devices.
IT, OT Device Security
To prevent threats, organizations must maintain holistic visibility across all devices on the network. This can be achieved with device and network inventory and management solutions. Constant visibility on networks and devices allows administrators to stay vigilant for incidents and respond appropriately. Along with visibility, organizations must implement automatic responses to any anomalies, setting varying levels of alarms based on the threat assessment. IT and OT systems also need to implement least-privilege access control, which ensures that users have only the minimum necessary access, reducing the risk of unauthorized actions that could bypass security measures.
BYOD Device Security
Organizations are adapting to their remote workforce needs with BYOD policies. To control these devices, organizations need to adopt and install robust antivirus and anti-malware software on every endpoint device. Secondly, data encryption must be enforced on BYODs to make sure sensitive data is secured even in the worst case of device theft or compromise. Full disk encryption is the most common method to make sure the data is unreadable to any unauthorized reader. Deep endpoint management and compliance tools are also imperative for BYOD security to ensure corporate network, data and system integrity.
Maintaining Device Security Against Evolving Cybersecurity Threats
Protecting enterprise endpoint devices from a myriad of cybersecurity threats is a growing concern for organizations around the world. By educating users, adopting zero-trust principles, and leveraging advanced technologies, organizations can safeguard their networks and data. Continuously adapting to evolving threats and maintaining robust security measures are essential strategies for ensuring the integrity and safety of enterprise devices.