Organizations nowadays often allow employees to use their own personal devices for work purposes, a practice known as BYOD (bring your own device). BYOD offers flexibility and convenience, but also introduces security risks, as personal devices lack the stringent protective measures of corporate hardware.
What is BYOD Security?
Definition and scope of BYOD security
BYOD security policy aims to establish guidelines and frameworks to manage and control the use of employees’ personal devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets. There are detrimental security risks in letting unmanaged devices access protected resources, such as data loss or malware infections.
Several key aspects of the IT infrastructure must be defined clearly in their BYOD scope of use. For example, organizations must decide which device types are permitted for business purposes, application types, or access to internal resources, as well as personnel eligible for personal device utilization.
Importance of securing employee-owned devices.
According to recent statistics, 83% of companies have certain BYOD policies and 75% of employees use their personal cell phones for work. Companies with remote and hybrid workers must often accommodate the use of personal devices, particularly in situations where timely hardware provision is a challenge.
BYOD policy proves beneficial to organizations, as it boosts employees’ productivity and work satisfaction through flexible work accommodation. Companies can also cut costs related to work laptop or smartphone provisioning, as they can allow employees to utilize their personal devices.
BYOD Security Risks
Secure Access
While working remotely, employees might connect their personal devices to unsecured Wi-Fi networks, which are vulnerable to interceptors, especially when employees accept sharing files and folders accessed within public networks.
Secure Browsing
Employees might use their own devices to visit and interact with malicious or phishing websites in the absence of effective tools to block access to harmful websites and ensure that the connection is encrypted.
Secure File Downloads
Unscanned files downloaded from the websites or messaging apps might include malware that could spread when employees connect their laptops to the company's network. Allowing unsecured file downloads carries a huge risk since it might lead to critical data leaks.
Unauthorized Access
When employees use personal devices to conduct their work, inadequate security can expose companies networks and data to unauthorized access. The risk is further compounded when employees’ family members also use these devices or USB drives to transfer data.
Software Vulnerabilities
Personal devices may not have the same level of security and patch updates as company-issued devices, making them more susceptible to malware and viruses. Users with BYOD access may unknowingly provide an opening for bad actors to exploit via devices with compromised software accessing company resources.
Data Leakage
Another significant consequence of lost, stolen, or compromised devices is data leakage. When unauthorized individuals gain access to BYOD devices, organizations face the risk of having sensitive information and data leaked.
Compliance Issues
Personal devices with lack of encryption, access control, and data protection can lead to challenges in complying with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. The legal consequences are especially damaging for financial and health institutions that must safeguard sensitive data.
Case Studies and Examples
Unauthorized Access to Slack’s Private Code Repositories
Suspicious activities were noticed on some of Slack's GitHub repositories in December 2022. Upon investigation, it was discovered that an unidentified individual had access to employees' access tokens, which were used to access private code repositories. After analyzing the data, it was found that the unauthorized user has downloaded a number of the collaboration platform’s private repositories.
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platform Data Leak
In 2017, South Korean cryptocurrency exchange Bithumb inadvertently leaked 30,000 customers’ personal information when an employee’s home computer was hacked. The attacker harvested data such as customer names, mobile phone numbers and email addresses, which were later leveraged for phishing phone calls. The cryptocurrency exchange later had to pay fines and reimburse all customers whose personal information was exposed and suffered financial loss.
Trojan Malware Disguised as Legitimate Mobile Apps
In 2016, DressCode trojan malware was discovered in games, themes, and smartphone performance boosters on the Google Play Store. Once a malicious app carrying DressCode was installed, it would communicate with the command server which could send instructions to infiltrate the network the infected device was connected to. Researchers have recognized over 400 instances of DressCode malware embedded apps available on Google Play. Other known or unknown threats embedded in apps could pose a significant risk to organizations with BYOD policies.
How to Secure BYOD
Establishing BYOD Policies

The first critical step to a secure BYOD environment is formally establishing essential elements of a BYOD security policy:
- User Agreement: Outlines all that is expected of employees in terms of securing their personal devices. Typical user agreement elements include acceptable use policy, security compliance requirements, and liability and responsibility, especially for instances of termination and device removal.
- Permitted and Prohibited Activities: Defines work-related tasks employees can perform on their personal devices, such as allowed applications, accessing emails, or accessing internal documents. Activities that can pose risks to the company must be prohibited, such as storing sensitive data on personal devices or downloading unauthorized files.
- Permitted Devices: Specifies which personal devices are permitted, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, including specific models, brands, operating systems (e.g., iOS, Android, macOS, Windows) to ensure the devices are compatible with the company security configuration.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
MDM technology provisions, manages, and controls devices that are used for work at enterprises. Besides controlling corporate devices, an MDM program can also enroll employees’ personal devices. MDM software onboards devices with profile data, VPNs, necessary applications and resources, as well as tools for monitoring device activity.
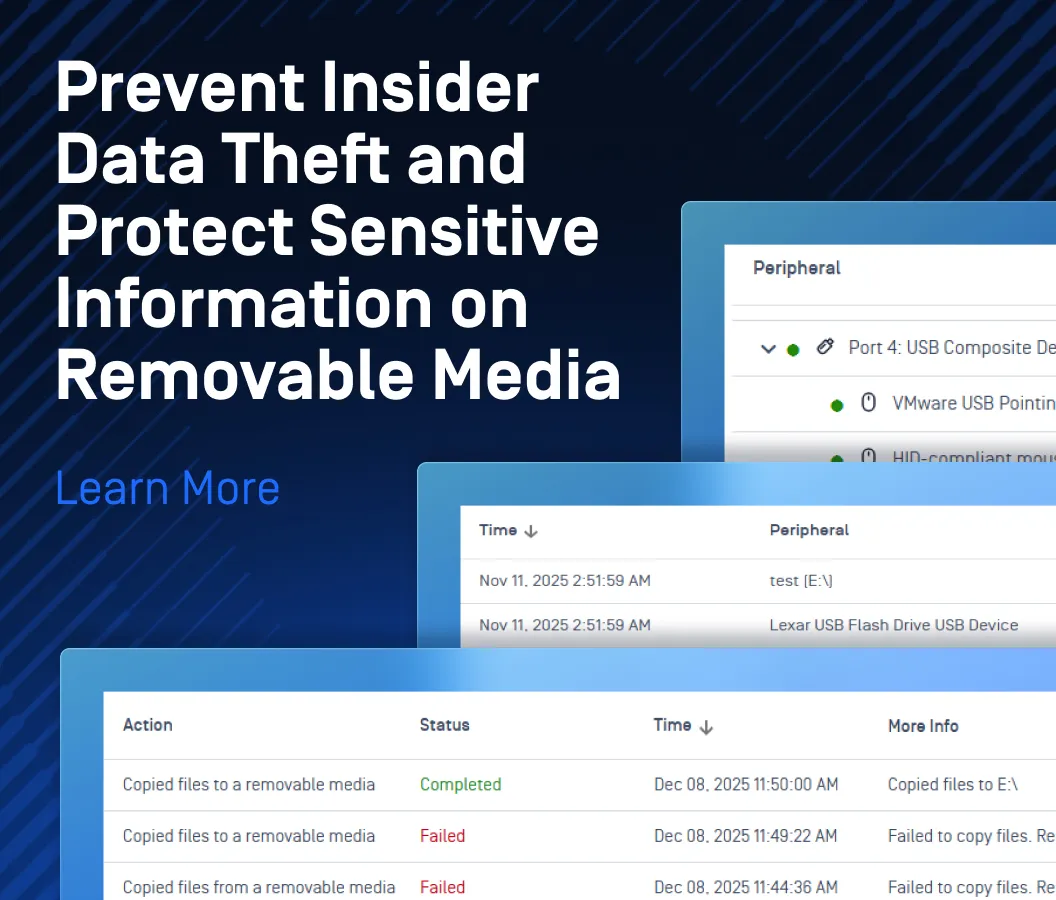
Establishing a Removable Media Policy
Using removable media, such as USB and external hard drives, to transfer data poses significant security risks. Such devices can introduce malware into a network, which might lead to data breaches or system disruptions. A physical solution, like MetaDefender Kiosk™, can scan removable media using multiple anti-malware engines to ensure its safety.
Implementing Security Solutions

BYOD devices can be protected by endpoint security solutions like MetaDefender Endpoint™. This endpoint security program enforces crucial security measures on devices to ward off threats.
Safeguards confidentiality by requiring users to provide multiple layers of verification like password, second-device OTP code, or biometric data.
Protects sensitive data both at rest and in transit. By encrypting readable data throughout its lifecycle, organizations can ensure information remains unintelligible to unauthorized users in case of devices being lost, stolen or compromised.
Enforces policies, ensuring devices are compliant before accessing corporate resources. These policies often include anti-malware scan schedules, vulnerability and patch management, keylogging blockers, and screen capture prevention.
Some compliance mandates don't allow software installation on third-party transient devices, prohibiting the installation of endpoint solutions. To ensure compliance with such mandates, a solution like MetaDefender Drive™ can be deployed to perform bare-metal scans without booting from transient devices’ operating systems.
Network Security Measures
Network security allows for management and access control from endpoints to corporate networks, ensuring only authorized and compliant devices can connect.
Secure Access
Enforces policies that protect the connection from endpoints to the network such as firewalls, secure VPNs for remote access, and role-based privileges for accessing files and data.
Network Segmentation
Separates BYOD devices from critical company network segments. By isolating BYOD traffic, in case of any compromised devices, attackers wouldn’t have access to other sensitive parts of the network.
Regular Audits and Monitoring
Establishes visibility into all connected devices, enabling continuous monitoring of network activity. By conducting regular vulnerability assessment, organizations can proactively identify anomalies and security gaps.
Best Practices for BYOD Security
Employee Training and Awareness
Regular Training Sessions
Educate employees on BYOD security best practices, such as password hygiene, device security settings, safe browsing habits, and mitigating the latest cyberthreats.
Phishing Simulations
Conduct simulated phishing attacks to test user awareness, helping employees to recognize and respond to phishing attempts.
Incident Response Planning
Developing an Incident Response Plan
Defines roles and responsibilities, identifies possible consequences, and prescribes action steps before, during, and after a BYOD security incident. A comprehensive response plan involves a clear chain of command, from the security team to other stakeholders, and communication protocols to mitigate consequences from a security incident.
Maintaining a Holistic Approach
BYOD policy offers significant benefits to organizations, such as greater employee satisfaction through flexibility and work-life balance, as well as cost savings from reduced device procurement. The accompanying challenges, such as unauthorized access, regulatory compliance, and vulnerable points of entry for threat actors, are not to be underestimated.
Organizations adopting BYOD must take a holistic approach, addressing risks in every aspect, from establishing formal policies and user agreements, to enforcing endpoint security, and providing training to boost employee awareness. Through comprehensive execution and continuous improvement, enterprises can reap the full benefits of BYOD while staying ahead of threats to their organizational infrastructure.
BYOD Security with OPSWAT MetaDefender IT Access™
Addressing BYOD challenges, MetaDefender IT Access is a unified endpoint security management platform, ensuring security compliance, visibility, and control for BYOD users accessing enterprise resources. Utilizing SDP (software-defined perimeter) technology, it performs comprehensive device posture checks, including risk and vulnerability evaluations, and can detect nearly 10,000 third-party applications. MetaDefender IT Access, built on a ZTNA (zero-trust network access) philosophy, ensures only authorized identities can access the network, providing a secure work environment without hindering workflows.