History of NERC CIP and Why It Was Created
The NERC CIP (North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection) standards were established in response to the growing recognition of vulnerabilities within the BES (North American Bulk Electric System). The early 2000s saw a significant rise in the number of blackouts and cyberattacks, highlighting the need for standardized grid protection regulations. The primary goal was to safeguard the electric grids against threats to physical and digital infrastructure, ensuring the continuous delivery of electricity, which is vital for national security and stability.
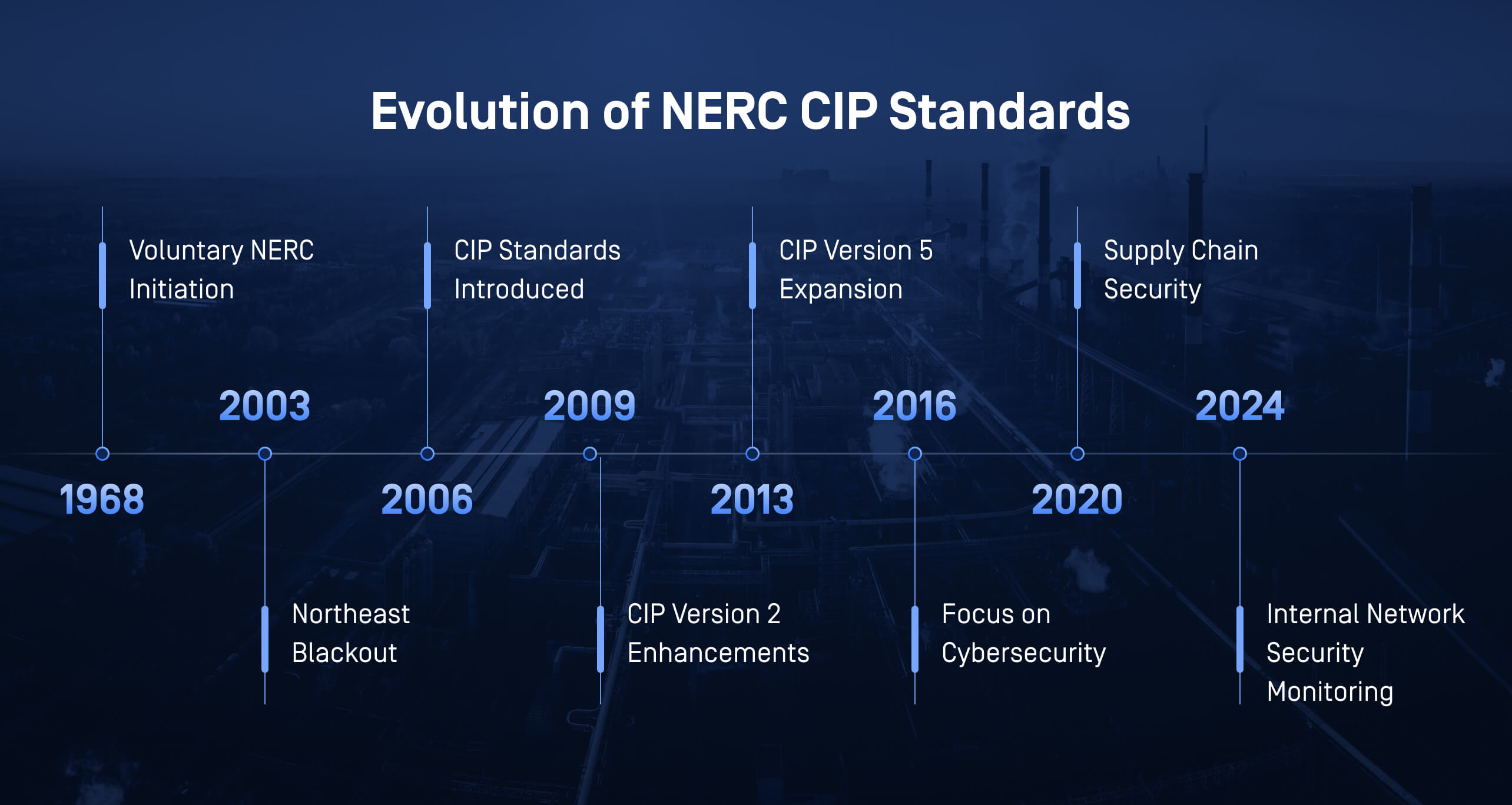
Evolution of NERC CIP Regulations for Industrial Cybersecurity
Since its inception in 1968, NERC CIP has undergone multiple revisions to adapt to the changing threat landscape. Initially focused on physical security, the standards expanded to include cybersecurity measures as cyberthreats became more sophisticated. The focus of NERC CIP has gradually expanded to more comprehensive grid protection measures, such as access management, system integrity, and incident response. This shift reflects a move from simple protection to ensuring operational resilience, safety, and uptime.
Asset Visibility, Network Monitoring, and Threat Detection
In critical industrial environments, particularly those running on legacy systems, it is crucial to account for and monitor all assets to prevent disruptions from anomalous communications, behaviors, or misconfigurations. NERC CIP standards, from CIP-002 to CIP-011, highlight the requirements for identifying critical assets, ensuring their safety, and monitoring them for signs of compromise.
For network monitoring, NERC CIP requires systems that continuously track network traffic and activities, detecting any anomalies that could signal a security breach. Threat detection and prevention are also central to NERC CIP standards, as industrial environments need tools that can identify potential threats before they materialize into actual attacks. This includes both signature-based and behavioral-based methods to cover a wide range of potential attack vectors.
Tools: IDS (intrusion detection systems) and SIEM (security information and event management) are essential for real-time security insights.

What’s New and What to Expect from CIP-015-01
Critical infrastructure environments face vulnerabilities that can bypass traditional perimeter protection, which often focuses on the initial stages of attacks. CIP-015-01 introduces refinements to address emerging threats and incorporates the latest cybersecurity best practices. Key updates in CIP-015-01 focus on supply chain management, vulnerability assessment, and enhanced monitoring of electronic security perimeters and associated systems for high and medium impact BES Cyber Systems.
Historically, CIP standards primarily focused on protecting electronic security perimeters. However, in 2023, the FERC (Federal Energy Regulatory Commission) mandated improvements in INSM (internal network security monitoring) to address vulnerabilities within internal networks. NERC responded in January 2024 with a report on implementing INSM, emphasizing networks with “Low and Medium impact BES without external routable connectivity.” The continued direction is toward robust INSM implementation, ongoing network monitoring, and establishing a solid foundation for enhanced INSM strategies.
Key Updates in CIP-015-01:
Enhanced Internal Network Security Monitoring
More rigorous requirements for monitoring internal network traffic, focusing on detecting and preventing unauthorized access or movement within the network.
Improved Incident Response Approach
Strengthened protocols for responding to potential threats within internal networks, including better documentation and differentiation between baseline and unusual activities.
Focus on Analysis-Based Actionable Insights
Increased documentation requirements for maintaining and sharing event data, system configurations, and network communications, leading to better analysis and threat insights.
Why NERC CIP-015-01 Matters and Its Benefits for INSM
NERC CIP-015-01 represents a significant advancement in the development of comprehensive INSM practices within critical infrastructure. As cyberthreats evolve, the ability to monitor and respond to internal network activity becomes increasingly essential.

MetaDefender OT Security™: One Solution for Your NERC Needs
MetaDefender OT Security is designed to align with NERC CIP compliance requirements, offering solutions that address the need for asset visibility, network monitoring, and threat detection. Our product is developed with an in-depth understanding of these regulations, ensuring that your organization can meet the stringent standards set by NERC CIP, including the latest CIP-015-01 updates for INSM. By choosing MetaDefender OT Security, you're not just securing your critical infrastructure—you’re also ensuring regulatory compliance, reducing risk, and enhancing operational resilience.
Ready to strengthen your NERC CIP compliance? Contact us today to learn how MetaDefender OT Security can support your cybersecurity and compliance efforts.

