Third-party libraries are essential for speeding up the software development life cycle. Instead of coding from scratch, developers often integrate open-source libraries for various purposes—whether for cost-effectiveness, lack of resources, or better flexibility. Repositories like Maven Central and PyPI, along with dependency management tools, simplify this process and boost productivity. However, such reliance also brings potential security risks.
Managing a project's open-source dependencies can pose challenges, including nested dependencies (one or more dependencies within a dependency) and limited expertise in dependency management. The integration of external libraries expands the attack surface and heightens security risks. Discovering a vulnerability in a library can compromise all software reliant on that component. Therefore, it's essential to utilize dependency scanning tools to identify and address known vulnerabilities originating from third-party dependencies.
Software Reuse and Dependency Adoption
As distribution ecosystems become more accessible, developers opt for reusing existing software to expedite complex software development. However, this convenience can introduce unexpected security issues if not carefully managed. These existing software programs are primarily distributed via the Internet in the form of packages—archives containing release versions known as libraries, alongside metadata specifying version, author, license, references, and other relevant information. Packaging software streamlines distribution and version control processes.
Developers often share their code publicly under open-source licenses, enabling code review, community collaboration, and easy integration. Any developer can reuse, modify, or contribute to the codebase. Projects vary widely in quality, maintenance, and support. Authors release these packages to make them more easily accessible, but support and liability depend on the license.
Once a package is referenced in another project, it becomes a project dependency, representing an external package reference. Dependencies create one-way relationships between software packages, where one relies on another for proper functioning. Developers include dependencies in their applications, resolving them at build time and fetching the necessary ones.
The supply chain refers to all external suppliers involved in the process, particularly those providing software dependencies. Supply chain management has gained prominence in software development in recent years, with companies establishing policies encompassing supplier requirements, legal documents, and contracts to ensure compliance before accepting a supplier.
Dependency Management
Managing dependencies can quickly become overwhelming, leading to what's known as "dependency hell." Modern applications may have hundreds or even thousands of direct dependencies, making it challenging to track vulnerabilities. Here are some scenarios where managing large volumes of dependencies becomes challenges.
- Lack of code review: Despite open-source transparency, sometimes teams might skip reviewing the code, leading to a false sense of security.
- Implicit trust: Developers often include dependencies without thoroughly vetting authors, relying solely on repository inclusion.
- Extensive dependency use: Developers often rely heavily on packages, even if only a fraction of their functionality is needed, leading to bloated dependencies.
- Breaking changes: Updating packages can be complex and may introduce breaking changes, leading to hesitation and outdated packages.
- Liability issues: Open-source maintenance and support standards fall short of those required for commercial software, leading to disputes and unrealistic expectations from project developers, potentially resulting in insecure packages.
The rise in attacks targeting third-party dependencies has raised concerns about software security. High-profile incidents like the Log4Shell vulnerability in 2021 or the XZ Utils backdoor recently in March 2024, affecting thousands of Maven packages, underscored the widespread impact of such vulnerabilities. In the same year, the discovery of malware in a popular NPM package ua-parser-jswas highlighted the risks associated with using third-party libraries in application stacks.
Another noteworthy attack in January 2024 is MavenGate, a new software supply chain attack method, hijacked dependencies via abandoned libraries. Successful exploitation of these shortcomings could allow nefarious actors to find vulnerable artifacts in dependencies and inject malicious code into the application, and worse, compromise the build process through a malicious plugin.
As the use of open-source libraries increases, understanding and mitigating these risks becomes paramount. This prompts further investigation into the prevalence, types, and persistence of vulnerabilities in open-source libraries, as well as their relationship with project attributes and commits.

Securing Dependencies with OPSWAT SBOM
As a reaction to supply chain attacks, the United States of America approved the "Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity" in May 2021 which defines steps for improving supply chain policies. One of the key requirements is to provide an SBOM for each product.
OPSWAT Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is continuously evolving to cater to the growing needs of software development in a secure environment. One of the key features of OPSWAT SBOM is dependency scanning. This feature is designed to enhance the visibility of your codebase by identifying vulnerabilities in the dependencies your projects rely on.
Package Dependency Scanning
OPSWAT SBOM automatically detects security vulnerabilities in software dependencies during development and testing. For instance, SBOM lets teams know if the application uses an open-source library that is known to be vulnerable. Teams can then take action to protect the application.

Check Dependency with Python

Container Image Scanning
OPSWAT SBOM examines every layer of a container image to identify vulnerabilities or threats, covering operating system (OS) packages and dependent software libraries used by the application. This proactive approach enables the detection and resolution of potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
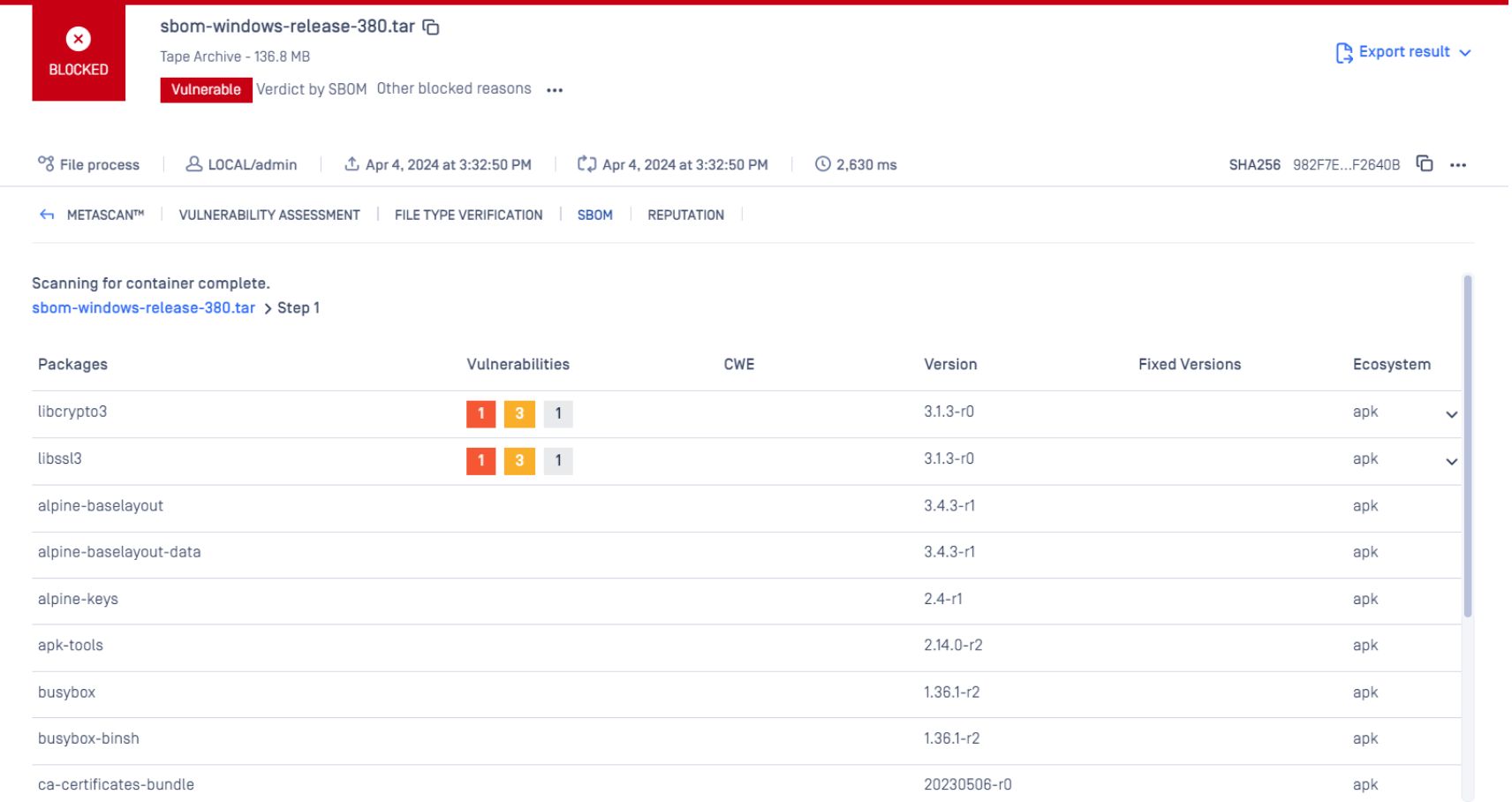
Check Dependency with Alpine

Developers and security teams benefit from understanding common types, prevalence, and persistence of dependency vulnerabilities, enabling them to gauge severity and explore remediation strategies.
SBOM scans your project's dependencies for known vulnerabilities. Upon detection, SBOM provides detailed information, including severity levels, vulnerability descriptions, and available fixes.
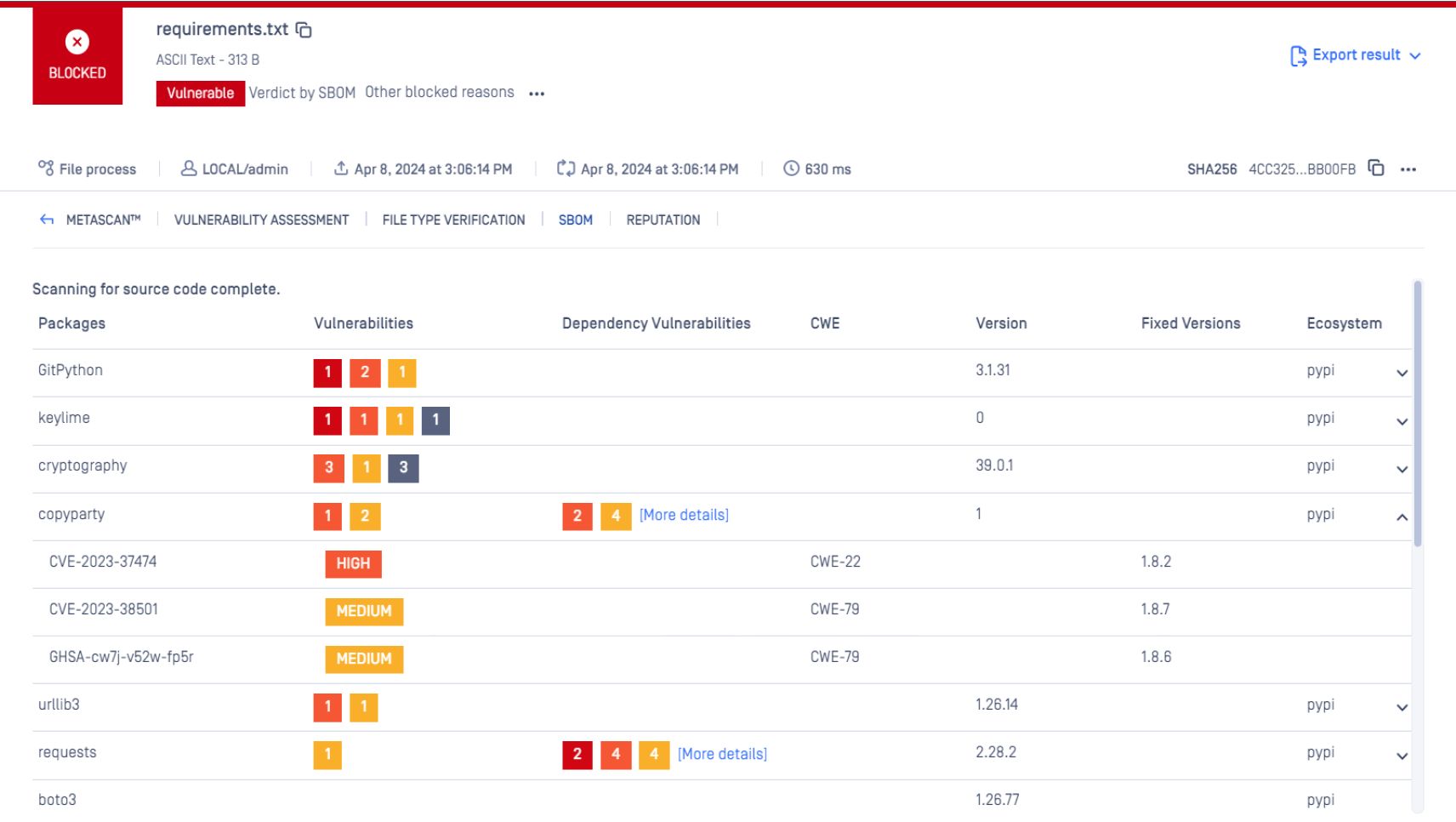
A detailed report can be exported for teams to keep track of:
- Total number of dependencies scanned
- Total number of vulnerabilities found across all dependencies
- A range of versions scanned
- Known CVEs
- Total number of critical, high, medium, and low severity vulnerabilities
OPSWAT SBOM recommends security teams update all vulnerable packages to the latest versions with vulnerability fixes. This enables teams to address the vulnerability of package maintainers or remove packages from the dependency tree. This proactive approach allows teams to address potential security risks before they become a problem, significantly enhancing the security and integrity of their software projects. Additionally, OPSWAT SBOM helps organizations to stay compliant and secure in the software supply chain. It is highly recommended that teams should:

Map Dependencies
Leverage tools to identify which dependencies exist in the environment and their relationships.
Eliminate Unnecessary Dependencies
Remove unnecessary or nonessential dependencies to reduce the attack surface.

Use Established Repositories
Ensure dependencies are obtained from reputable sources.

Scan All Dependencies
Before using dependencies in any software, scan them to be aware of security or quality issues.
Closing Thoughts
By leveraging dependency scanning tools like OPSWAT SBOM, you can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities in your project's dependencies, mitigating potential security risks before they can be exploited. Embrace the power of dependency scanning and SBOMs to build secure, compliant, and resilient software applications.

