The rapid rise of technology has created a high demand for skilled developers. Open-source software (OSS) has become a vital tool for this growing workforce. Hundreds of thousands of well-established OSS packages now exist across various programming languages. Over 90% of developers leverage these open-source components within their proprietary applications, highlighting the efficiency and value proposition of OSS. Further emphasizing its importance, the global OSS market is expected to reach $80.7 billion by 2030, reflecting a projected growth rate of 16.7% annually.
However, the widespread adoption of OSS also introduces a new layer of complexity: security vulnerabilities. The vast number of interconnected OSS components creates a broader attack surface for malicious actors to exploit. Managing dependencies across various OSS packages can be complex, making it difficult to identify and patch vulnerabilities promptly. Additionally, the security of OSS often relies on the vigilance and contributions of the developer community. This can lead to delays in patching vulnerabilities, especially for less popular projects.
In this article, OPSWAT Graduate Fellows examine CVE-2023-33733, a security flaw discovered in the popular open-source library ReportLab. Their analysis is coupled with a simulated attack that leverages MetaDefender Core with its Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) capabilities to identify vulnerabilities in an application's dependencies, including the vulnerable ReportLab library.
Reportlab Library Introduction

ReportLab, a powerful and open-source Python library, empowers users to generate feature-rich PDFs from Python code. It offers developers a winning combination: flexibility, ease of use, and extensive customization options for creating dynamic documents. The library gives developer-enhanced control over their PDFs, allowing for the precise incorporation of text, images, tables, and charts with meticulous precision. This level of customization makes ReportLab a valuable tool for generating dynamic documents such as invoices and data-driven reports.
CVE-2023-33733 Background
CVE-2023-33733 highlights a security vulnerability within the ReportLab library, impacting multiple versions of the ReportLab Library.
- ReportLab versions prior to version 3.6.13 were found to be vulnerable to sandbox evasion, specifically within the
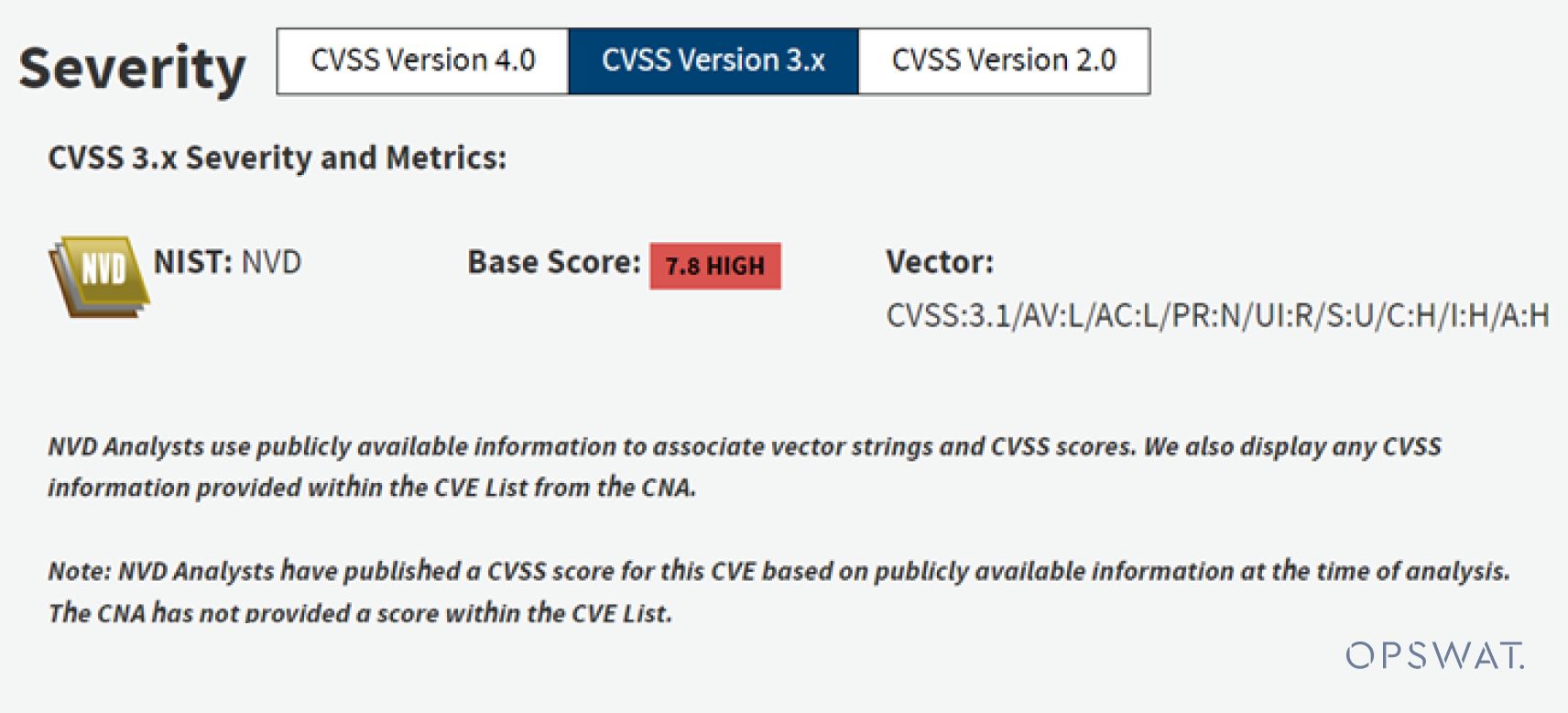
'rl_safe_eval'function. Exploitation was achieved through the color attribute of HTML tags, which was directly assessed as a Python expression using theeval()function, ultimately leading to remote code execution. - NVD Analysts assigned a CVSS score of 7.8 HIGH to CVE-2023-33733.
Analysis of ReportLab Security Vulnerability
OPSWAT Graduate Fellows conducted a deep analysis of ReportLab workflow, identifying the root cause of the CVE-2023-33733 security vulnerability.
ReportLab empowers developers to create PDFs efficiently. The library allows for effortless integration: import the library, define the HTML content, and generate the PDF in a single line of code using the result function.

Our graduate fellows uncovered a 5-step process for creating PDFs from HTML with ReportLab.

Within the 5-step process for creating PDFs from HTML with ReportLab, three main processes stand out: paragraph processing, paraparser processing, and the HTML handling process.

As illustrated in the figure above, the HTML handling process within ReportLab utilizes the eval() function specifically on color attribute. Serving as a focal point for executing malicious code, the eval() function prompts researchers to seek control over its input to exploit the application. However, this is challenging due to the sandbox enforced by the __rl_safe_eval__ function within ReportLab.

ReportLab has implemented a sandbox called __rl_safe_eval__. This sandbox excludes all built-in Python functions and includes several overridden built-in functions. This restriction allows the execution of safe code within the library while preventing access to dangerous functions and libraries that could be used for malicious purposes (e.g. file system access, network communication).
The rl_safe_eval sandbox function implements various conditions to ensure the invoked attribute is safe before using Python’s built-in getattr() function to retrieve it and return the result.

The safe eval function aims to secure the environment by excluding dangerous functions and preventing malicious actions. However, if a way is found to bypass its conditions and access a powerful built-in function, it could be exploited.
Building on this idea, the security researchers attempted to bypass the restrictions. Initially, they exploited object injection using the type() function to construct an object and redefine its attributes and methods to circumvent the checks within __rl_safe_eval__. Furthermore, as the ReportLab library overrides built-in functions and makes them as globals into the eval context, the researcher could leverage this implementation to access one of the original built-in functions. This could enable them to bypass the sandbox environment and execute malicious code.

The payload is prepared as follows:

Nevertheless, executing a multiline expression within an eval context is not possible. However, a list comprehension trick can be employed, and the payload to exploit this CVE is as follows:

ReportLab Exploitation Simulation
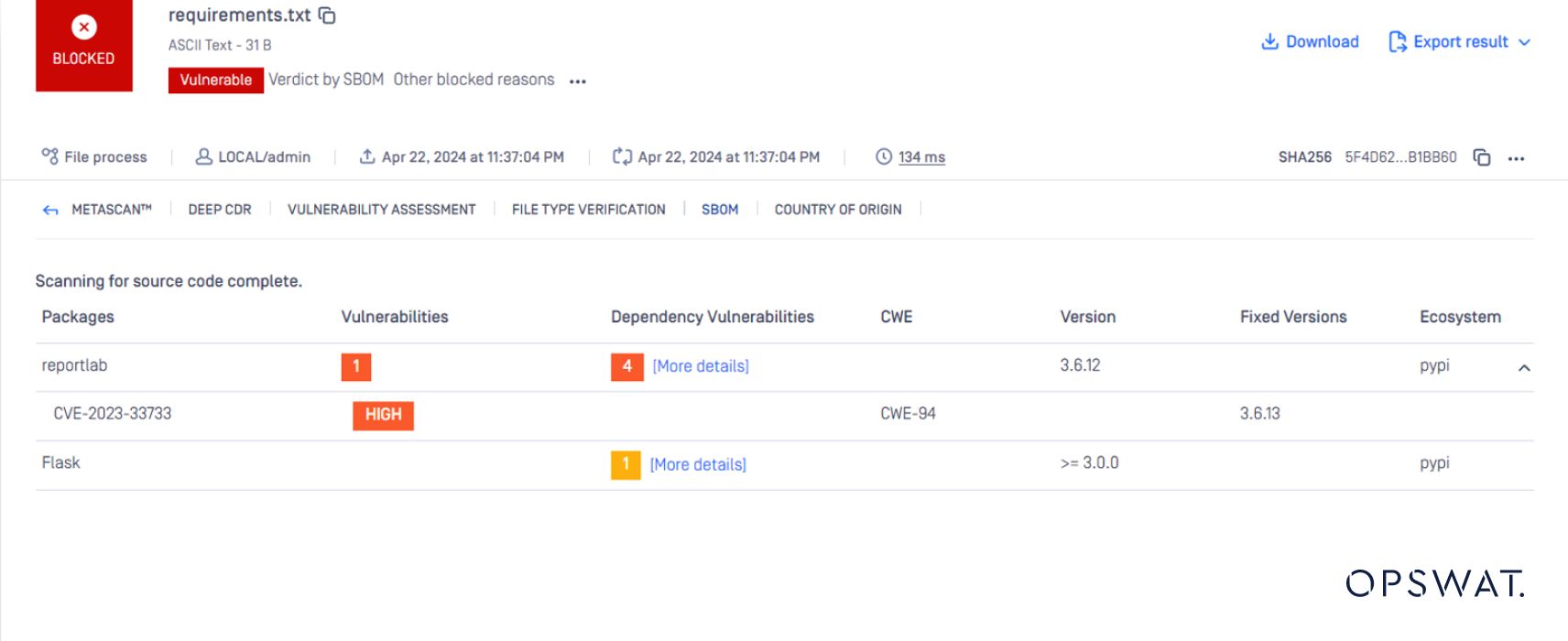
Researchers have published a Proof of Concept (POC) for CVE-2023-33733, demonstrating that applications built with vulnerable versions of ReportLab could be susceptible to cyberattacks. To assess this potential threat, OSPWAT Graduate Fellows conducted a simulated attack on a web application. They leveraged MetaDefender Core with SBOM capabilities to identify the security vulnerabilities within the application software dependencies, including the presence of the affected ReportLab library.
To simulate this exploitation as a real-world scenario, OPSWAT Graduate Fellows developed a web application using Python and the vulnerable version of the ReportLab library. This application mimics a typical use case: users can upload an HTML file and convert it into a PDF file.
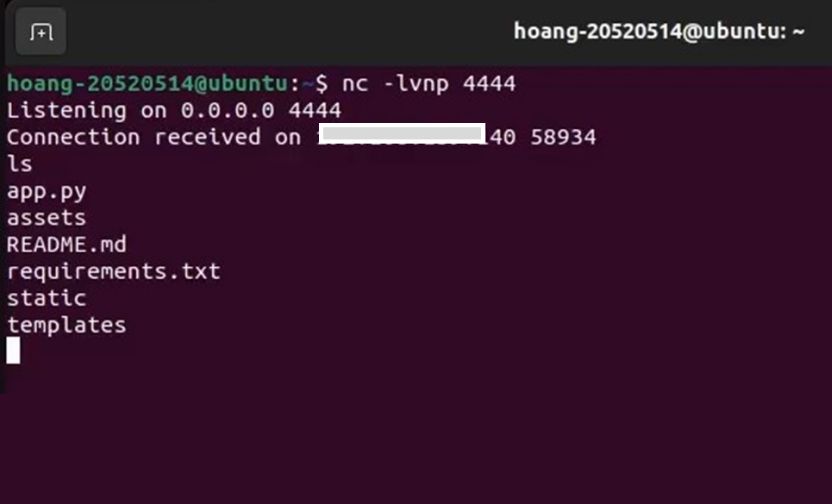
An attacker could craft a malicious HTML file containing code designed to exploit CVE-2023-33733. This code could bypass the sandbox and compromise the web server by triggering a reverse shell through the eval() function.

A successful upload of malicious file would allow the attacker to take control of the application server due to the vulnerability in the outdated ReportLab library.
The Importance of SBOM and Proactive Security
The OPSWAT Graduate Fellows' research on CVE-2023-33733 underscores the potential security risks associated with OSS. While OSS offers undeniable benefits in terms of development efficiency and cost-effectiveness, vulnerabilities like the one found in ReportLab can leave organizations exposed to cyberattacks.
OPSWAT SBOM secures the software supply chain by providing a comprehensive component inventory for source code and containers. It supports 10+ languages, including Java, JavaScript, Go, PHP, and Python, over 5M+ third-party open-source software components, and utilizes a database of 17K+ vulnerabilities sourced from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and GitHub (GHSA).

OPSWAT MetaDefender Core, with its integrated SBOM capabilities, empowers organizations to proactively address these risks. MetaDefender Core scans software applications and dependencies, identifying the presence of known vulnerabilities like CVE-2023-33733 within the listed components. This allows developers and security teams to prioritize patching efforts and mitigate security risks before they can be exploited.
Closing Thoughts
The OPSWAT Graduate Fellows' research on the ReportLab vulnerability (CVE-2023-33733) serves as a valuable reminder of the importance of proactive security measures in the software development lifecycle. By leveraging tools like OPSWAT MetaDefender Core, organizations can gain crucial insights into their software dependencies and identify potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers.
Furthermore, OPSWAT offers a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity solutions that go beyond vulnerability scanning. These solutions provide real-time threat detection, data security, and endpoint protection, safeguarding organizations from a wide range of cyber threats. By adopting a layered security approach that includes tools like MetaDefender Core, organizations can leverage the benefits of OSS while minimizing the associated security risks.