In a previous article on File Transfer Automation, we explored how automating file exchanges enhances business productivity across various sectors of critical infrastructure, including energy, healthcare, and the media.
As we pointed out, automation can strengthen the continuity and reliability of data transfer by reducing manual errors and ensuring the timely delivery of essential data. Unmanaged or inadequately secured file transfers are a primary vector for cyber intrusions in critical infrastructure due to their susceptibility to loss and manipulation.
In 2023, ENISA (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity) reported a significant increase in the number of cyberattacks mainly targeting the health, manufacturing, and transportation sectors in the European Union. According to the report, the estimated global average cost of a data breach in 2024 is $4.88 million.
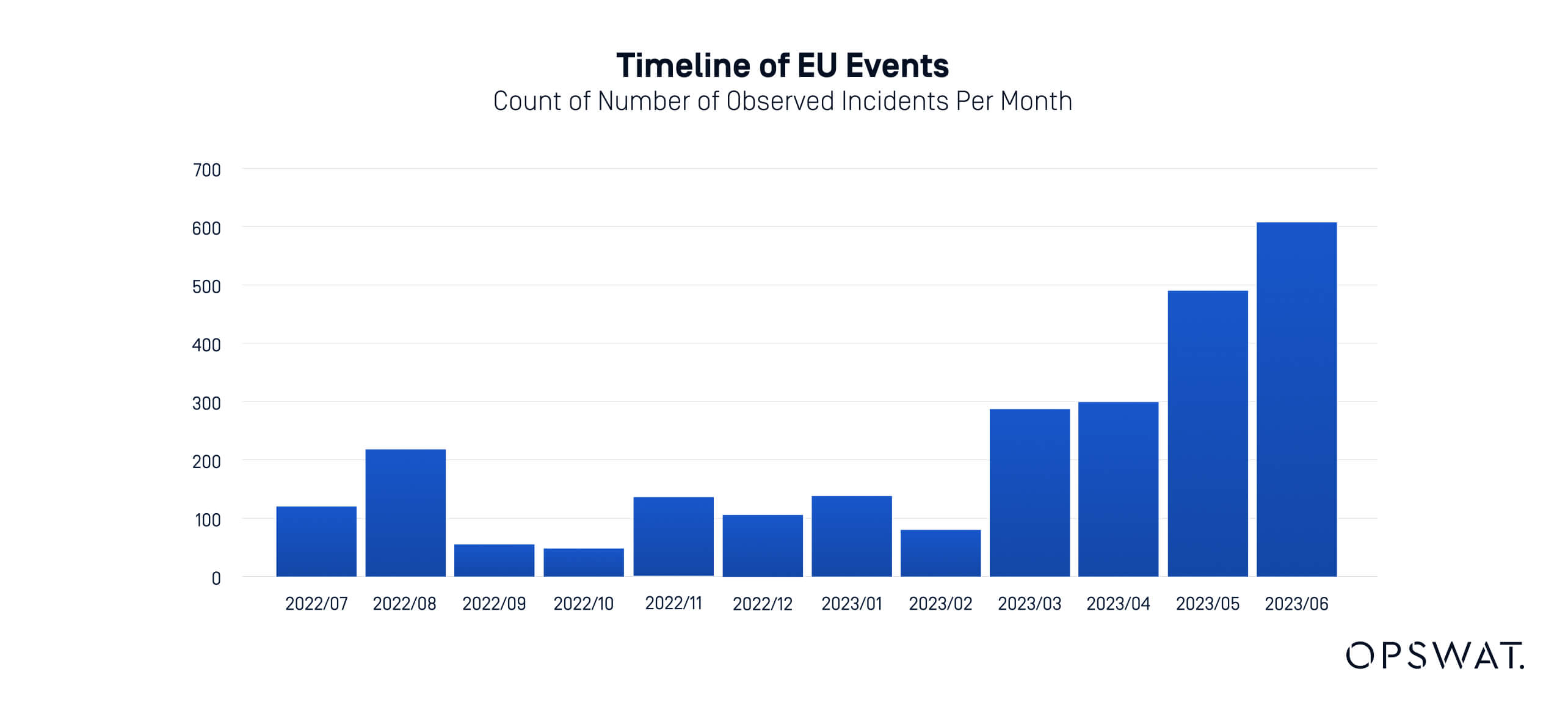
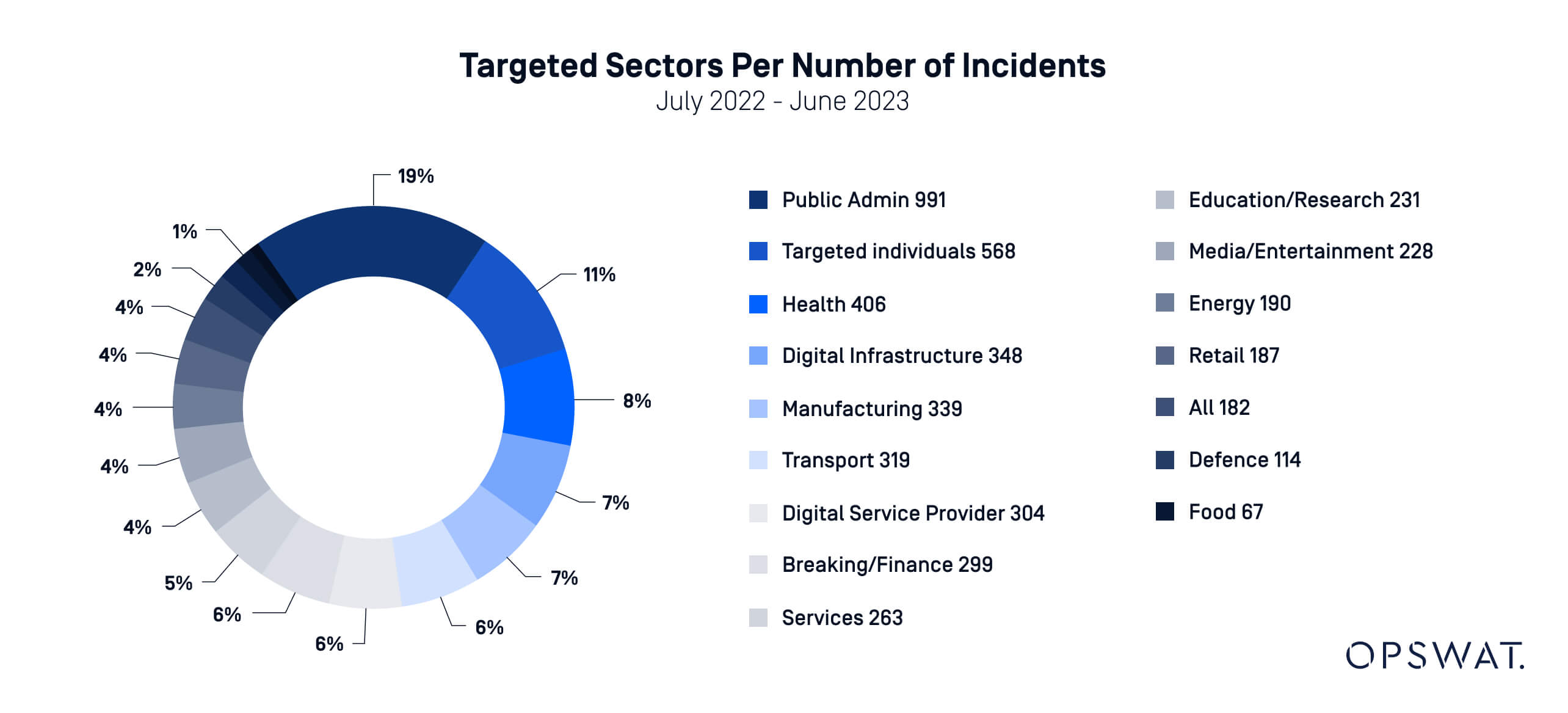
As cyberthreats continue to evolve in complexity and scale, critical infrastructure organizations must recognize that effective file transfer security must go hand-in-hand with automation.
Secure Managed File Transfer (MFT) solutions not only maintain the benefits of automation but also provide comprehensive protection against evolving file-based cyberthreats and safeguard the integrity and availability of business operations. In the following sections, we will explore the security challenges critical infrastructure sectors face concerning file-based threats and discuss how secure MFT solutions play a pivotal role in mitigating such risks.
We will also examine the differences in secure MFT adoption between advanced and developing economies and discuss strategies for bridging these gaps to enhance global cybersecurity resilience.
File-Based Cyberthreats
Critical infrastructure sectors face a complex landscape of cybersecurity threats that can be broadly categorized into insider and outsider threats. Both pose significant risks, particularly in file-based attacks that can compromise sensitive data and disrupt essential services.
Insider threats
Insider threats involve employees, contractors, or business partners of an organization who have authorized access to sensitive files and systems. Because they already have legitimate access, these insiders can either unintentionally cause harm or exploit their position to intentionally compromise the organization’s network.
The average annual cost for companies to address insider threats is $16.2 million, as reported by the Ponemon Institute in 2023. According to the report, organizations in North America faced the highest financial losses, averaging $19.09 million, while European companies suffered the second-highest losses at $17.47 million.
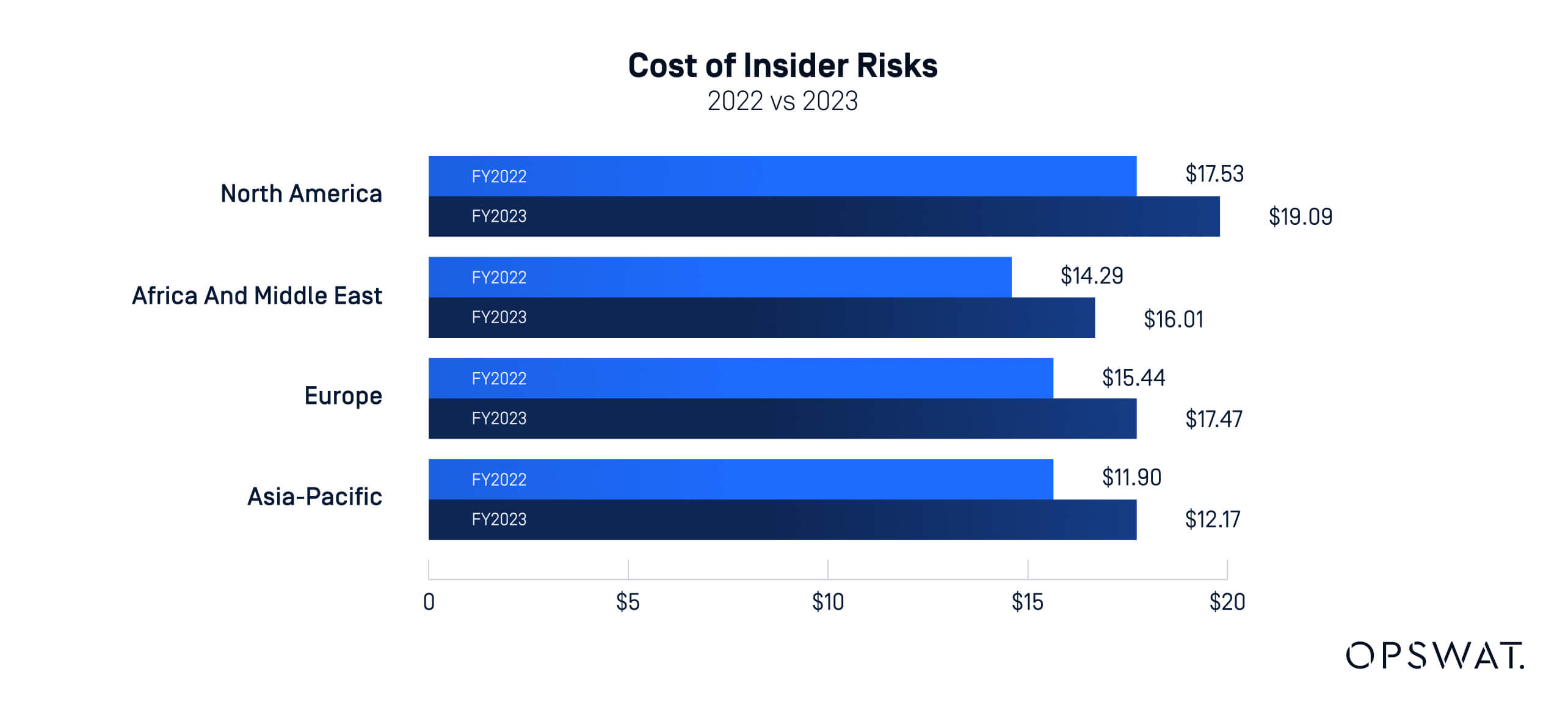
In developing economies, the risk posed by insider threats is often exacerbated by weaker enforcement of security protocols. Many developing nations lack comprehensive regulatory frameworks and robust internal controls, such as DLP (data loss prevention) or audit logs, that are standard in more developed economies.
This gap allows insider threats to flourish, as many employees in these countries do not receive adequate cybersecurity training. Moreover, without regular training, they may not be aware of the consequences of malicious actions or may not take security policies seriously, which can result in potential data breaches, or, in case of ransomware, even severe financial losses and reputational damage.
Outsider threats
Outsider threats, on the other hand, are typically posed by cybercriminals or state-sponsored actors who attempt to infiltrate critical systems. These attackers often use advanced techniques such as file-based zero-day exploits or unknown malware to breach defenses.
File-based malware attacks often start with a seemingly harmless file that, once opened, unleashes malware capable of bypassing traditional security measures such as firewalls or antivirus software. Cybercriminals use this tactic to gain unauthorized access to critical infrastructure networks and systems.
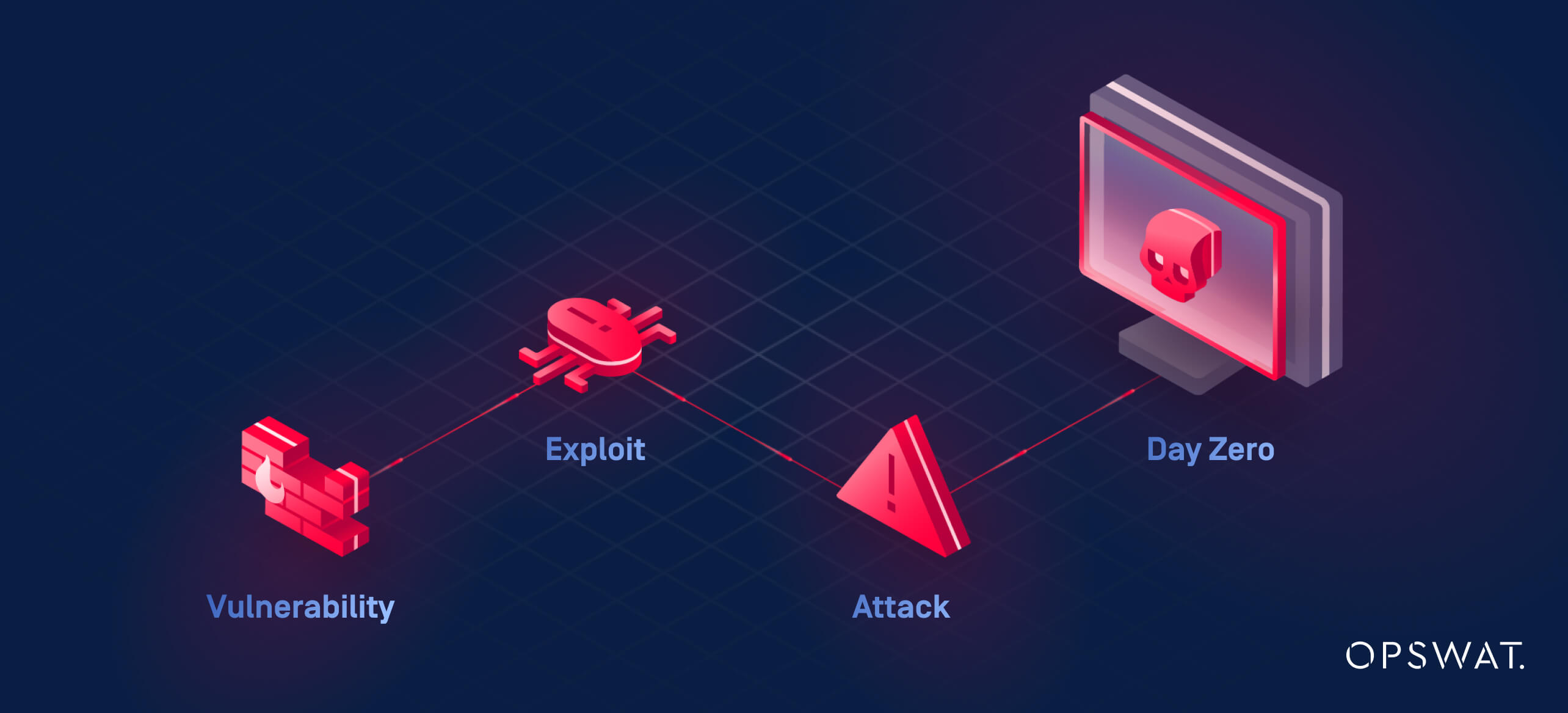
- Zero-day exploit: A type of cyberattack targeting vulnerabilities that have not yet been discovered or patched by the software developer, making it an accessible entry point for attackers. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities immediately after discovery or even before they become widely known, making them particularly dangerous as they bypass traditional defenses that rely on known threat signatures.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities: Attackers can embed exploits targeting zero-day vulnerabilities within files, such as PDFs, documents, or even media files. When these files are transferred without proper security controls, they can bypass traditional defenses and execute malicious code when opened by the recipient. For instance, if an organization lacks advanced malware scanning capabilities or fails to sanitize files from active components before allowing them into their network, it becomes significantly easier for attackers to deliver zero-day exploits.
- Unknown malware: Malicious software that has not yet been identified or cataloged by cybersecurity tools. Traditional antivirus solutions rely on known signatures to detect threats, but unknown malware can evade these defenses.
Unsecure file transfers facilitate the spread of such malware because the files are not adequately scanned or sanitized. This can occur, for example, when employees share files through unsecured channels, such as personal email accounts, unencrypted messaging services, or outdated file transfer protocols.
The Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024 by IBM illustrates the cost and frequency of various types of cyberattacks, including insider and outsider attacks.
Mitigating the Challenges
- Lack of robust IT infrastructure: Cloud-based MFT systems can be deployed with minimal upfront costs while ensuring the same level of security as traditional systems. This allows organizations with limited IT resources to still benefit from secure and reliable file transfer mechanisms, without needing to invest heavily in physical infrastructure.
- Rising cyberattacks: Secure MFT solutions offer advanced encryption protocols (SSL, AES, and SSH) and secure transfer mechanisms (HTTPS) that protect data both in transit and at rest. This is crucial for critical infrastructure organizations dealing with valuable data such as energy grids or healthcare records. Furthermore, MFT systems provide monitoring and audit trails that allow organizations to detect and respond to attacks more swiftly.
- Compliance and regulatory gaps: Secure MFT solutions are designed to comply with international standards and data protection regulations. By integrating these systems, organizations can ensure they adhere to industry norms, such as HIPAA (for healthcare) or GDPR (in regions where it's applicable), reducing the risk of regulatory penalties.
Secure MFT in Developed and Emerging Markets
The digital transformation across critical infrastructure industries has raised awareness about the importance of secure managed file transfer solutions in both advanced and developing economies.
Global Market Overview
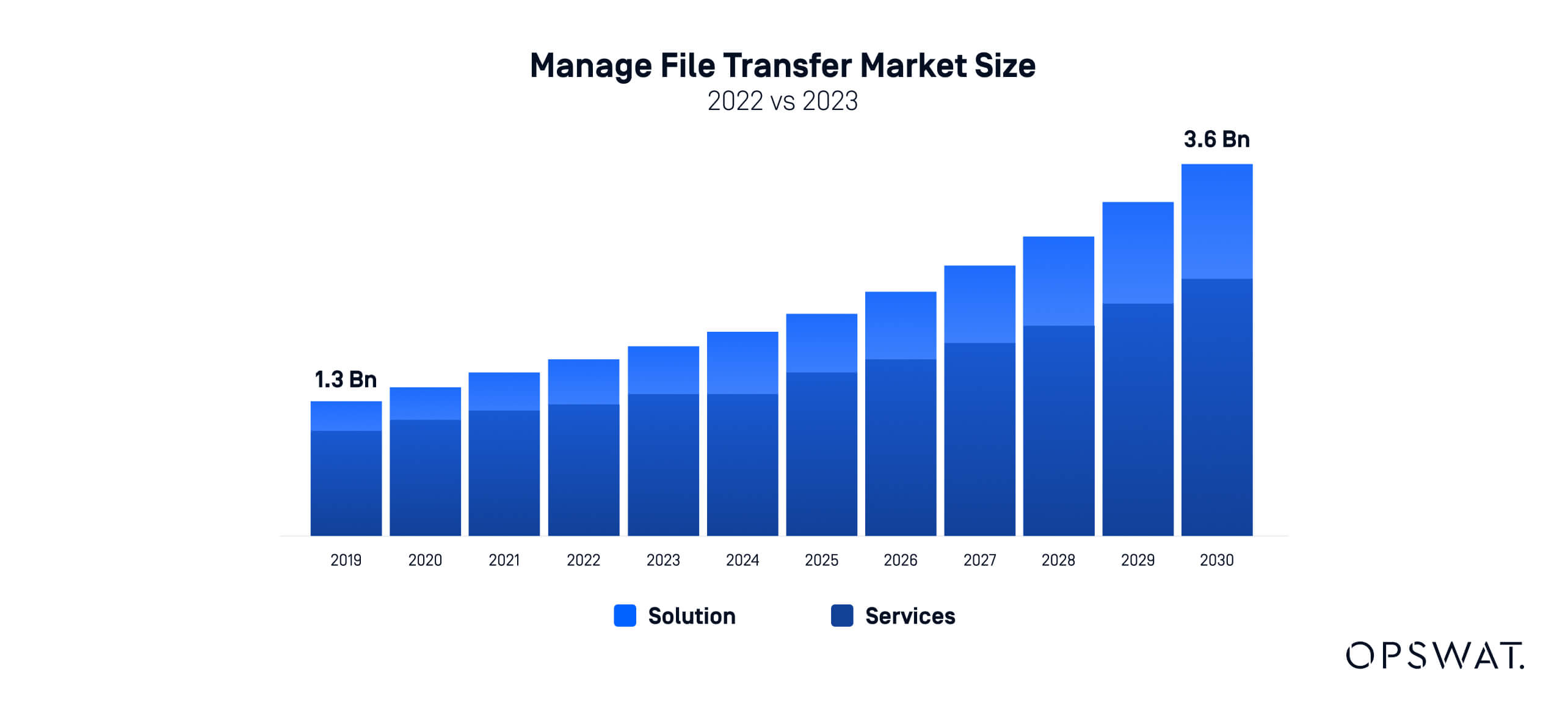
The managed file transfer market has experienced significant growth globally. According to KBV Reseaarch, the global MFT market is expected to reach $3.6 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 10.2% during the forecast period.
Adoption of MFT in Advanced Economies
In advanced economies, the adoption of secure MFT solutions in critical infrastructure is primarily driven by stringent regulatory requirements and higher penetration rates of digital technologies, cloud infrastructure, and cybersecurity measures.
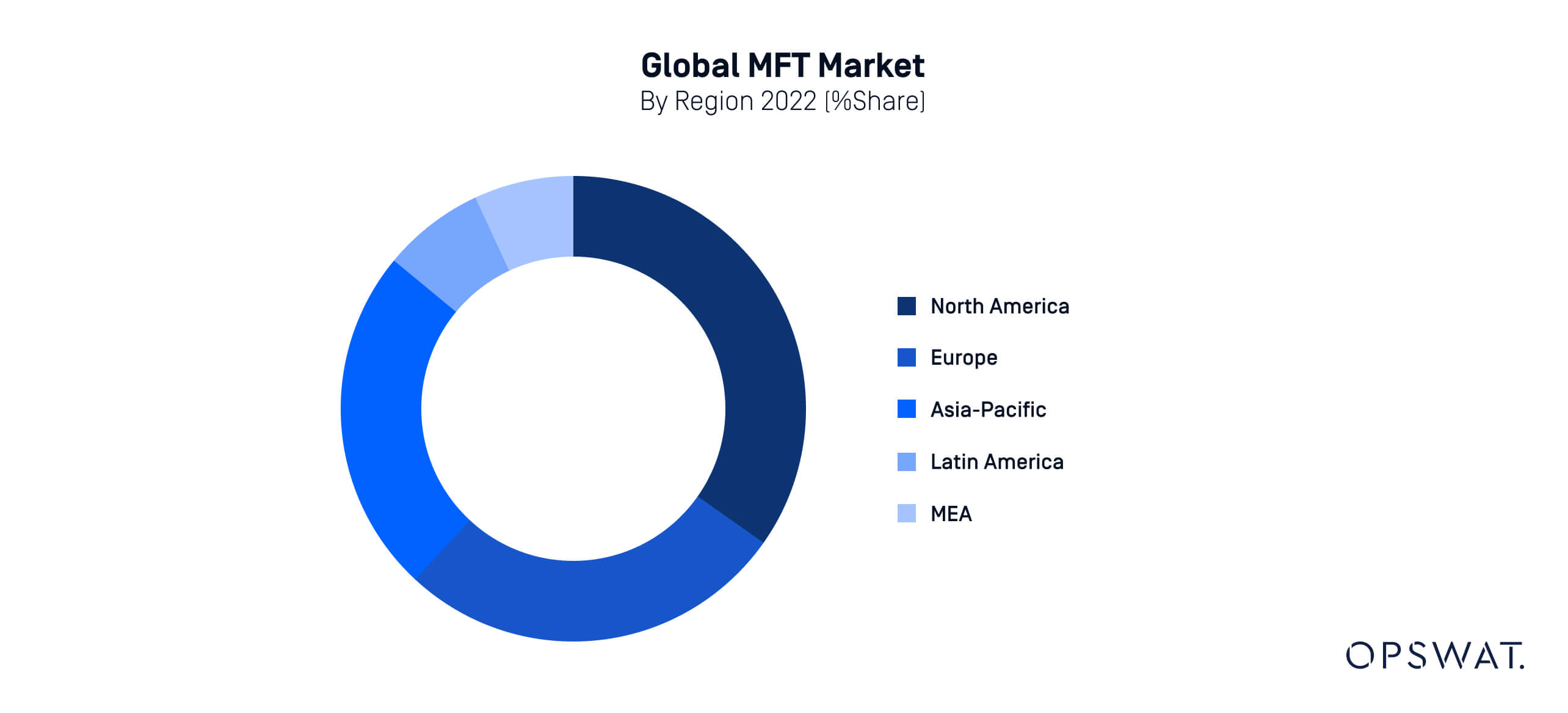
Countries in North America and Europe are at the forefront of implementing secure MFT solutions, with industries such as finance, healthcare, and government being key adopters due to the highly sensitive nature of the data they handle.
North America, for example, holds a dominant share of the global MFT market, and will most likely maintain its dominance in the future, with a market value reaching $1.2 billion by 2030.
In Europe, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has pushed organizations to adopt MFT solutions to ensure compliance with data protection norms.
https://www.acumenresearchandconsulting.com/managed-file-transfer-mft-market
Developing economies are witnessing growing adoption of MFT solutions, albeit at a different pace and under different market conditions. Regions such as Latin America, Africa, and parts of Asia are experiencing digital transformation and modernization of their IT infrastructure, which is creating a demand for secure file transfer solutions.
According to KBV Reseaarch, the MFT market in Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (LAMEA) is expected to see notable growth during the forecast period as governments and businesses in these regions focus on improving cybersecurity and data protection measures.
Comparative Challenges and Opportunities
The major difference between advanced and developing economies in terms of MFT adoption lies in the maturity of their IT infrastructure and regulatory environments.
Advanced economies benefit from well-established data protection regulations, which drive higher adoption rates of secure MFT solutions. Meanwhile, developing economies are still catching up in terms of infrastructure and regulatory frameworks, though their potential for rapid growth is evident as more businesses and governments embrace digital transformation.
Developing economies offer significant opportunities for MFT vendors as these markets are relatively untapped compared to their advanced counterparts. The ongoing expansion of internet access and the rise of cloud computing services in developing regions are expected to drive further demand for MFT solutions in the coming years.
International Support and Cooperation
Efforts to bridge the gap between the cybersecurity capabilities of advanced and developing regions include international cooperation, where developed nations and global organizations provide technical assistance, training, and access to secure MFT technologies. This support is crucial for helping developing countries enhance their cybersecurity posture, particularly in the protection of critical infrastructure.
Multinational companies operating in both regions face the challenge of aligning compliance with varied regulations. Implementing unified MFT platforms ensures consistent data protection and operational efficiency, fostering resilience across diverse environments.
The Path to Global MFT Adoption
Secure managed file transfer is critical in today's globalized economy. While advanced economies are leading the way in MFT adoption due to established infrastructure and regulations, developing economies present a growing market with significant potential as they continue to modernize and digitize.
Continuous improvement in MFT systems is vital for both advanced and developing economies to safeguard critical infrastructure against emerging cyberthreats and ensure the resilience of essential services.
Explore how OPSWAT's industry-leading MFT solution, MetaDefender Managed File Transfer (MFT), can protect your organization.



