Introduction
Since 2021, we have seen an increase in HTML smuggling cyber attacks targeting banking and financial sectors across Latin America. Threat actors continue to use this evasion technique in large-scale malware campaigns to spread trojans such as Mekotio, /style, Trickbot, and QakBot. The unique challenges of detecting obfuscated HTML smuggling make it a persistent and pervasive threat vector.
HTML smuggling uses a variety of deception techniques to deliver malicious payloads to victims’ endpoints. Threat actors often disguise malicious scripts in email attachments or share documents infected with malware. One particularly elusive approach is to use Base64 encoding to hide malicious code within HTML content.
This article details Base64 encoding as a technique to obfuscate HTML smuggled payloads. We examine the difficulties inherent in detecting Base64-encoded threats and how organizations can implement robust defenses against this tactic using OPSWAT advanced threat prevention solutions.
The Deception of Base64 Encoding
Base64 encoding is a method of converting binary data to text and is widely used for a variety of legitimate purposes including file transmission and email attachments. However, it can also be exploited for malicious purposes through techniques like smuggled payload obfuscation, where attackers hide malicious data in seemingly innocuous files.
Instead of complex obfuscation, this approach embeds a Base64-encoded payload directly into an HTML tag like <img>

Malware evades filters looking for malicious binaries by encoding executable files as benign text. The target browser can decode the script and assemble the payload on the host. Base64 encoding enables powerful attacks even when using common images.
- Hidden into EXIF data using steganography.
- Embedded in pixels as noise.
- Appended to the end of an image file.

The Base64 Attack Flow

Challenges Detecting Encoded Threats
Traditional antivirus solutions that heavily rely on signature-based detection regularly miss new malware variants obfuscated by Base64 encoding, and social engineering tactics are often successfully used to deliver Base64-encoded payloads to unsuspecting end users.
A more advanced deception like steganography hides malware within benign images and media files. Base64 encoding can disguise malicious code as noise that is imperceptible to humans. While Base64 encoding has legitimate uses for data transfers, it's important to be cautious with images containing Base64-encoded strings, particularly if they arrive from unknown sources.
Other challenges that hinder the detection of Base64-encoded threats include:
- Encoding of the payload that is split into multiple files and reassembled locally.
- Morphing malware that bypasses static signature databases.
- Insertion of extra spaces or characters that corrupt the signature.
- Insertion of unusual file types rarely checked by traditional antivirus programs.
- Rapid distribution of new variants before signatures are updated.
Uncover Smuggled Payloads with OPSWAT MetaDefender Core
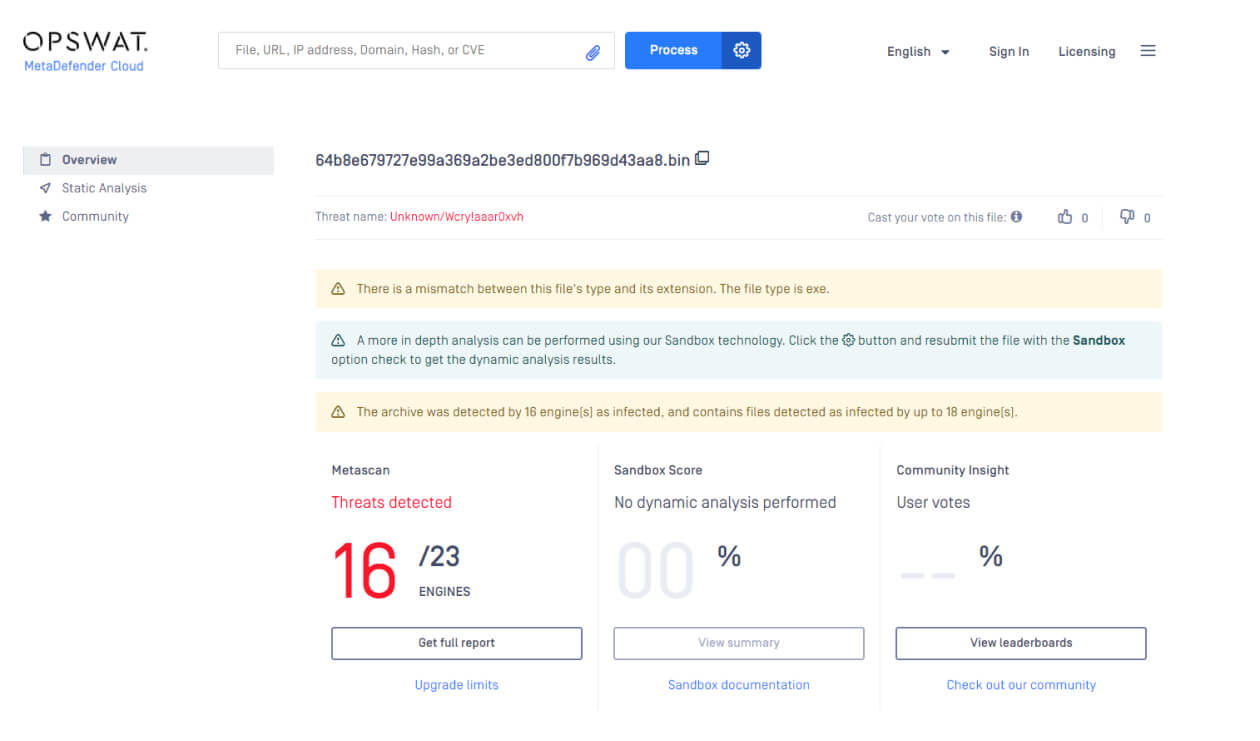
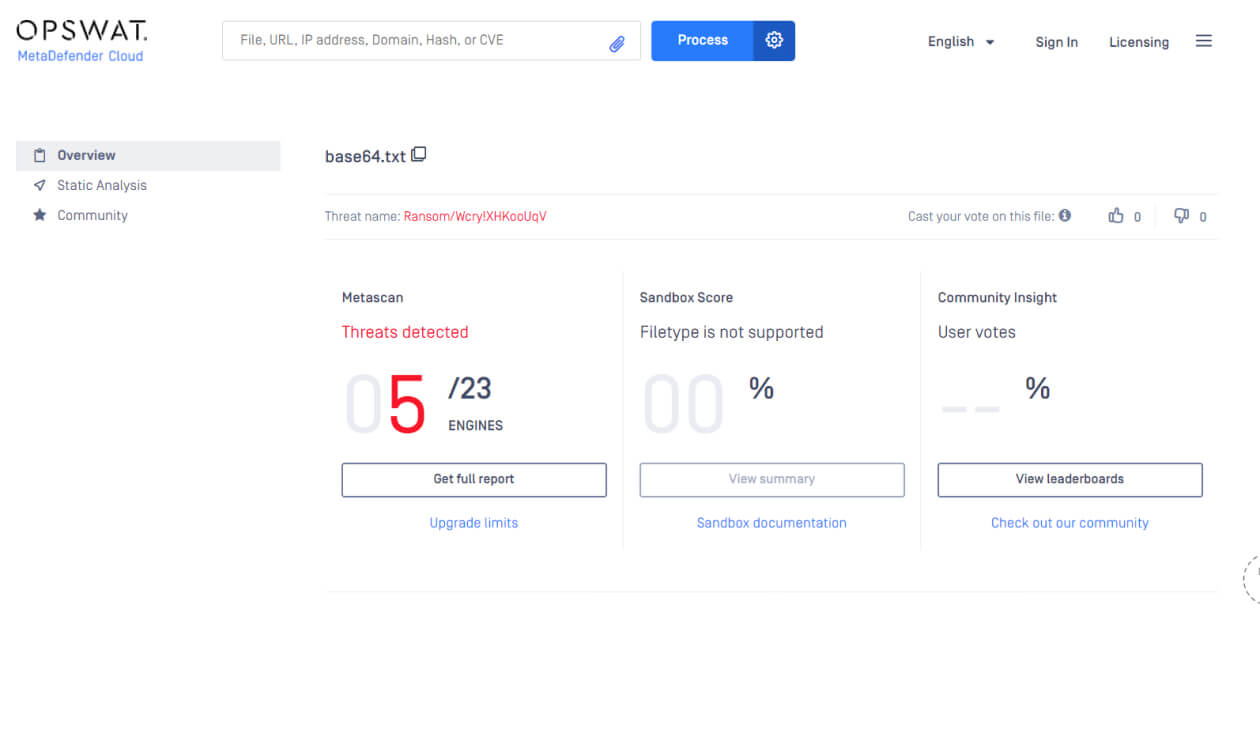
While single antivirus engines have limited effectiveness against emerging threats, combining multiple engines can significantly increase malware detection rates. OPSWAT MetaDefender Core leverages over 30 anti-malware engines to detect up to 99.2% of known and zero-day malware.
Improving static signature databases to detect new malware is a good start, but it's still possible for smuggled payloads to slip past antivirus software. Businesses need a strong defense-in-depth strategy with multiple layers of security to prevent zero-day attacks. This includes the use of dynamic protection technologies such as Multiscanning, Deep CDR (Content Disarm and Reconstruction), and Adaptive Sandbox. These technologies can help detect and block malware attacks early on (especially those that use HTML to smuggle in links and attachments) and protect sensitive data.
See a sample result at metadefender.opswat.com.
Proactive Detection with Deep CDR and Adaptive Sandbox
Deep CDR prevents Base64 encoding schemes from executing by deconstructing and regenerating sanitized files free from any potentially malicious code. For file types such as images embedded within HTML files, Deep CDR performs decoding, threat removal, and reconstruction to ensure the sanitized image is securely restored.

Deep CDR maintains image fidelity when sanitizing Base64 injection attempts. Users can view safe, decoded images with potential threats seamlessly neutralized in the background. This provides robust protection without workflow disruption.

MetaDefender Sandbox is an emulation-based malware analysis technology that scans thousands of files for malware quickly and uncovers every layer of obfuscation simultaneously to identify valuable Indicators of Compromise (IOCs).
When analyzing files that leverage obfuscation techniques like Base64-encoded payloads or HTML smuggling, MetaDefender Sandbox thoroughly inspects files, extracts JavaScript, and emulates their behavior to closely monitor for any suspicious activity. This adaptive analysis capability allows MetaDefender Sandbox to identify malicious actions, such as attempts to decode and execute Base64-encoded malware or run hidden scripts embedded within HTML content.

Going Beyond Perimeter Defenses
The covert threat posed by Base64 attacks underscores why companies must extend their defenses beyond safeguards against unknown outside sources. It is crucial to anticipate that malicious files could breach your internal endpoints despite strong network security. As an additional layer of defense, robust endpoint protection is indispensable. OPSWAT MetaDefender facilitates proactive file security by scanning incoming files with multiple anti-malware engines. This helps identify obfuscated zero-day threats that may evade perimeter defenses.
Remediation technologies like Deep CDR take it a step further by disarming, neutralizing, and reconstructing potentially malicious files before they compromise endpoints. Implementing such comprehensive file security measures limits the damage caused by threats that breach your perimeter and reduces reliance on perimeter security as the sole line of defense.
OPSWAT enables organizations to deploy multi-layered endpoint security, serving as a critical defense against evolving threats in today's landscape.