File spoofing remains one of the most effective techniques attackers use to bypass traditional security controls. Last year, OPSWAT introduced an AI-enhanced File Type Detection engine to close the gaps left by legacy tools. This year, with File Type Detection Model v3, we have advanced that capability by focusing on the file types where accuracy matters most, and where traditional logic-based systems consistently fall short.
OPSWAT File Type Detection Model v3 is designed to address a specific challenge of the reliable classification of ambiguous and unstructured files, especially text-based formats such as scripts, configuration files, and source code. Unlike generalized classifiers, this model was purpose-built for cybersecurity use cases, where misclassifying a shell script or failing to detect a document containing embedded macros, such as a Word file with VBA code, can introduce significant security risk.
Why True File Type Detection Is Critical
Most detection systems rely on three common approaches:
- File Extension: This method checks the file name to determine its type based on the extension, such as .doc or .exe. It is fast and broadly compatible across platforms. However, it is easily manipulated. A malicious file can be renamed with a safe-looking extension, and some systems ignore extensions entirely, making this approach unreliable.
- Magic Bytes: These are fixed sequences found at the beginning of many structured files, such as PDFs or images. This method improves accuracy over file extensions by examining actual file content. The drawback is that not all file types have well-defined byte patterns. Magic bytes can also be spoofed, and inconsistent standards across tools may lead to confusion.
- Character Distribution Analysis: This method analyzes the actual content of a file to infer its type. It is particularly helpful for identifying loosely structured text-based formats, such as scripts or configuration files. While it provides deeper insight, it comes with higher processing costs and may produce false positives with unusual content. It is also less effective for binary files that lack readable character patterns.
These methods work well for structured formats but become unreliable when applied to unstructured or text-based files. For example, a shell script with minimal commands can closely resemble a plain text file. Many of these files lack strong headers or consistent markers, making classification based on byte patterns or extensions insufficient. Attackers exploit this ambiguity to disguise malicious scripts as harmless documents or logs.
Legacy tools such as TrID and LibMagic were not designed for this level of nuance. While effective for general file categorization, they were optimized for breadth and speed, not for specialized detection under security constraints.
How File Type Detection Model v3 Works
The File Type Detection Model v3 training process consists of two stages. In the first stage, domain-adaptive pre-training is performed using Masked Language Modeling (MLM), allowing the model to learn domain-specific syntax and structural patterns. In the second stage, the model is fine-tuned on a supervised dataset in which each file is explicitly annotated with its true file type.
The dataset is a curated mix of regular files and threat samples, ensuring a strong balance of real-world accuracy and security relevance. OPSWAT maintains control over the training data, allowing continuous refinement for formats that matter most to security operations.
The AI component is applied with precision, not broadly. File Type Detection Model v3 focuses on ambiguous and unstructured file types that traditional detection methods cannot handle effectively such as scripts, logs, and loosely formatted text where structure is inconsistent or absent. The average inference time remains below 50 milliseconds, making it efficient for real-time workflows across secure file uploads, endpoint enforcement, and automation pipelines.
Benchmark Results
We benchmarked the OPSWAT File Type Detection Engine against leading file type detection tools using a large and diverse dataset. The comparison included F1 scores across 248,000 files and approximately 100 file types.
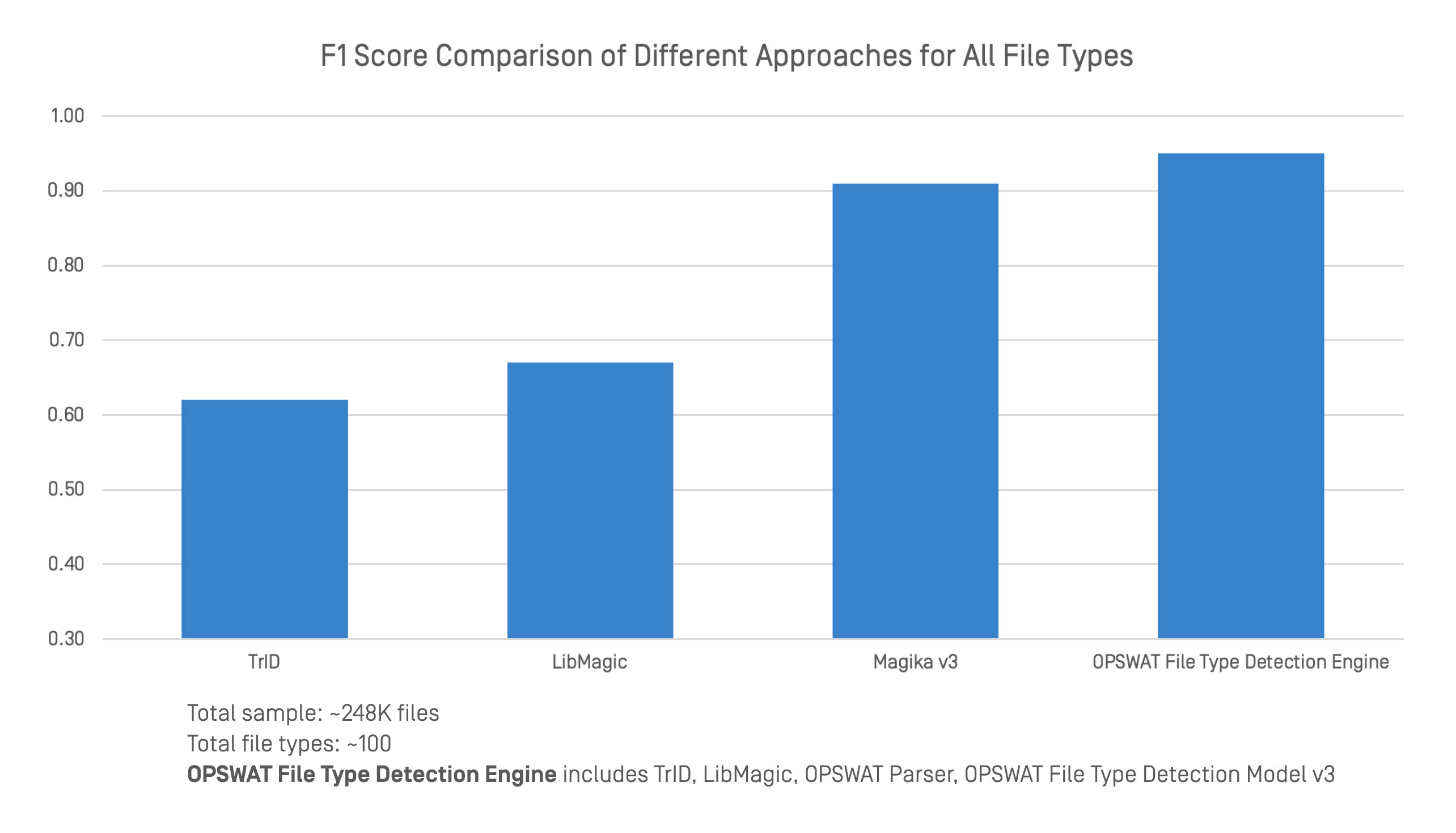
The OPSWAT File Type Detection Engine integrates multiple techniques, including TrID, LibMagic, and OPSWAT’s own technologies such as advanced parsers and File Type Detection Model v3. This combined approach delivers stronger and more reliable classification across both structured and unstructured formats.
In benchmark testing, the engine achieved higher overall accuracy than any single tool alone. While TrID, LibMagic, and Magika v3 perform well in certain areas, their accuracy declines when file headers are missing, or content is ambiguous. By layering traditional detection with deep content analysis, OPSWAT maintains consistent performance even when the structure is weak or intentionally misleading.
Text and Script Files
Text and script-based formats are often involved in file-borne threats and lateral movement. We conducted a focused test on 169,000 files across formats such as .sh, .py, .ps1, and .conf.
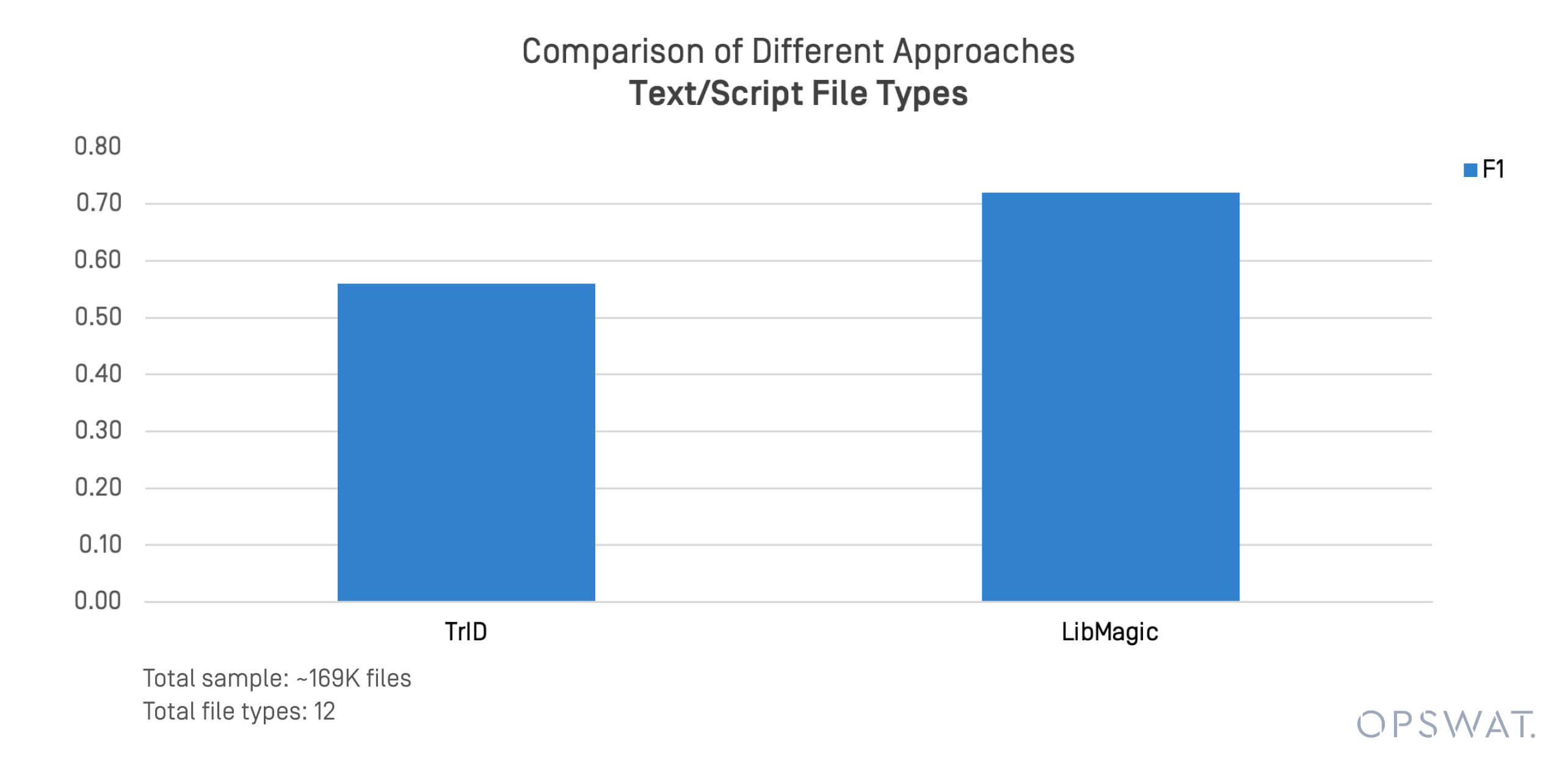
TrID and LibMagic showed limitations in detecting these unstructured files. Their performance degraded quickly when file content deviated from expected byte patterns.
File Type Detection Model v3 vs Magika v3
We evaluated OPSWAT File Type Detection Model v3 against Magika v3, Google’s open-source AI classifier, across 30 text and script file types using the same 500,000-file dataset.
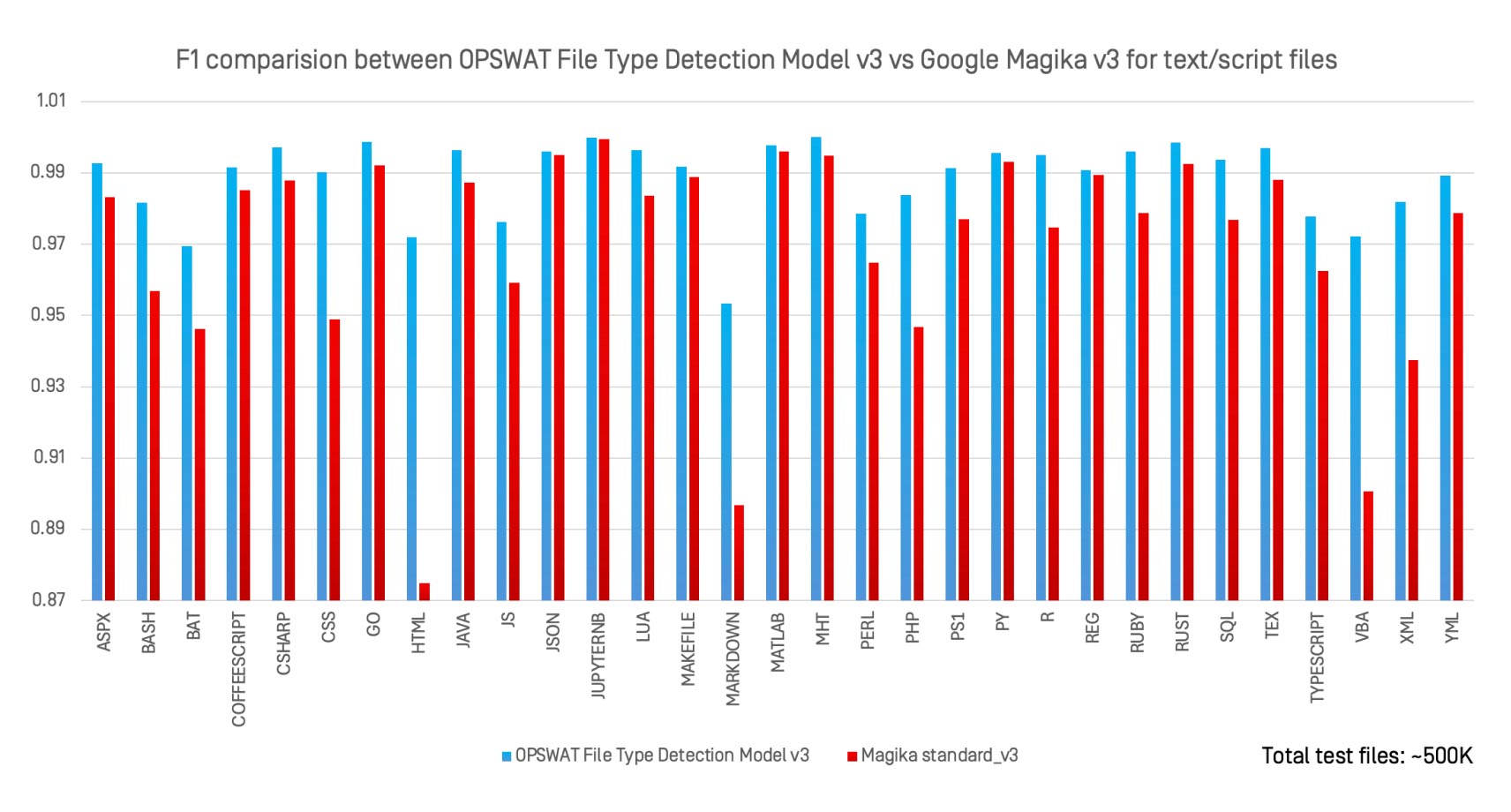
Key observations:
- File Type Detection Model v3 matched or outperformed Magika on nearly all formats.
- The strongest gains were seen in loosely defined formats such as
.bat, .perl, .html,and .xml. - Unlike Magika, which is designed for general-purpose identification, File Type Detection Model v3 is optimized for high-risk formats where misclassification has serious security implications.
Top Use Cases
Secure File Uploads, Downloads, and Transfers
Prevent disguised or malicious files from entering your environment through web portals, email attachments, or file transfer systems. AI-enhanced detection goes beyond extensions and MIME headers to identify scripts, macros, or embedded executables inside renamed files.
DevSecOps Pipelines
Stop unsafe artifacts before they contaminate your software build or deployment environments. By validating the true file type based on actual content, MetaDefender Core ensures that only approved formats move through CI/CD pipelines, reducing the risk of supply chain attacks and maintaining compliance with secure development practices.
Compliance Enforcement
Accurate file type detection is essential for meeting regulatory mandates like HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, and NIST 800-53, which require strict control over data integrity and system security. Detecting and blocking spoofed or unauthorized file types helps enforce policies that prevent sensitive data exposure, maintain audit readiness, and avoid costly penalties.
Final Thoughts
General-purpose file classifiers like Magika are useful for broad content categorization. But in cybersecurity, precision matters more than coverage. A single misclassified script or mislabeled macro can be the difference between containment and compromise.
The OPSWAT File Type Detection engine delivers that precision. By combining AI-enhanced file type analysis with proven detection methods, it provides a dependable layer of classification where traditional tools fail, especially in ambiguous or unstructured formats. It’s not about replacing everything; it’s about reinforcing the critical weak spots in your security stack with real-time, context-aware detection.

