The critical manufacturing sector has become the backbone of global economies, providing essential goods and services that power industries from healthcare to technology. This encompasses the production of vital goods like engines, electrical components, medical equipment, vehicles, and many others. Disruptions in this area can have cascading effects across various industries and regions. However, as manufacturing becomes increasingly digitalized, the sector faces a range of cybersecurity challenges, including technological vulnerabilities and the potential for significant disruptions stemming from local incidents.
The Cyberthreat Landscape in Manufacturing
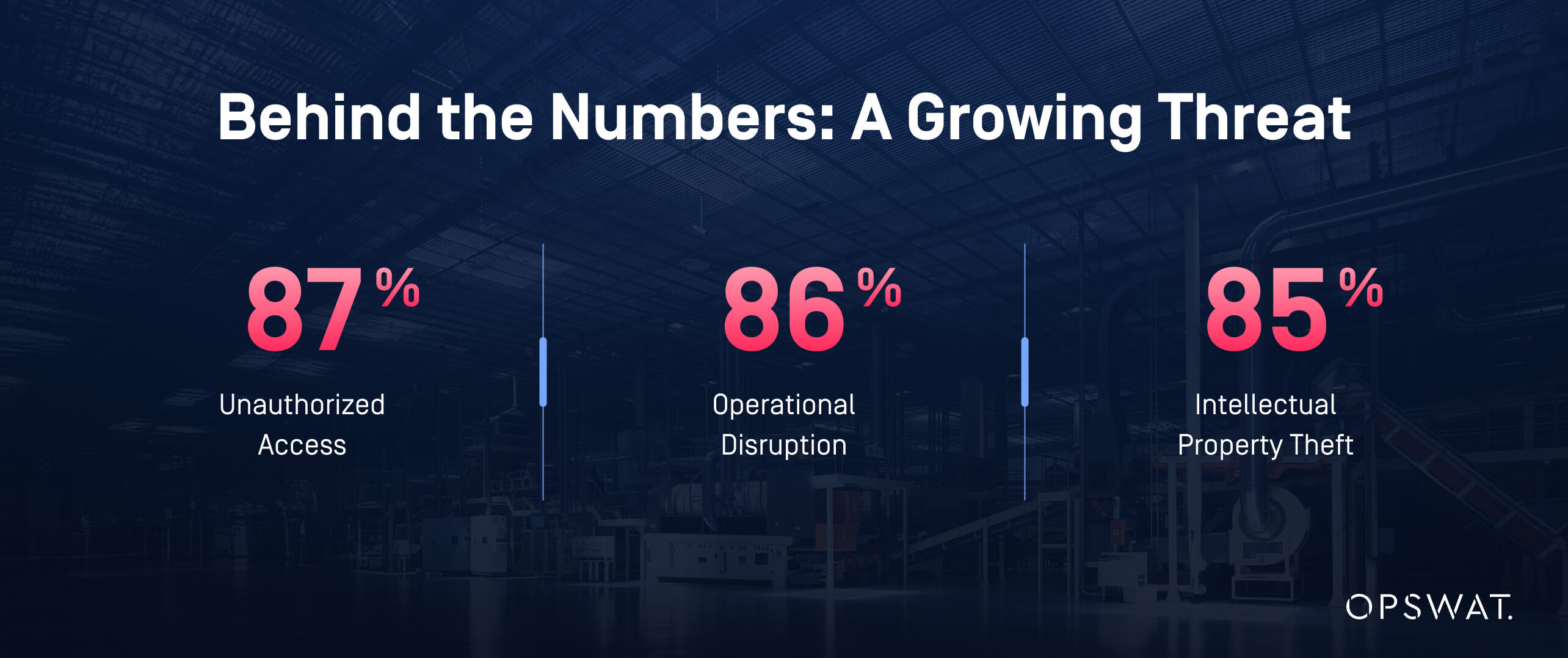
The threat landscape has been growing and evolving for both IT and OT industries. In 2023, manufacturing accounted for nearly one-fourth of all cyberattacks worldwide. Additionally, the cost of attacks on the manufacturing sector has been increasing at an exponential rate of 125% each year, making it one of the prime targets for cybercriminals. The reasons include:
- Legacy Systems: Many manufacturing processes depend on outdated or unpatched systems, creating vulnerabilities.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Competitors, cybercriminals, or disgruntled ex-employees may attempt to steal product designs, formulas, and process patents.
- Insider Threats: Authorized personnel can misuse their access privileges, causing damage to proprietary data or controls in critical manufacturing operations.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The reliance on extensive supply chains, which run most manufacturing facilities, increases exposure to cyberattacks.
- Cascading Effects from Other Sectors: Cyber incidents in interconnected sectors like IT, financial services, and communications can spill over, impacting manufacturing operations.

How Can Manufacturers Safeguard Their Critical Operations?
Strategy 1: Implement Robust Network Segmentation
One of the first steps in securing a manufacturing environment is network segmentation. By dividing the network into distinct zones and conduits, manufacturers can isolate critical systems from less secure ones, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Implementation Approach:
- Create distinct network zones based on security requirements
- Deploy firewalls between IT and OT networks to protect sensitive manufacturing systems
- Establish secure communication protocols between segments
- Monitor traffic between zones to detect potential threats
- Implement strict access controls for cross-segment communication
Strategy 2: Strengthen Endpoint Security
Endpoints, such as workstations and machines, are common entry points for cyber threats. These vulnerabilities become particularly critical when systems are outdated or unpatched, potentially giving attackers control over essential manufacturing processes.
Implementation Approach:
- Deploy advanced Endpoint Detection and Response solutions
- Conduct regular deep packet inspection
- Integrate threat intelligence feeds
- Perform systematic vulnerability assessments
- Implement continuous monitoring for anomalous behavior
- Maintain rigorous patch management protocols
Strategy 3: Secure Supply Chains with Risk Management
Modern manufacturing relies heavily on complex, interconnected supply chains that create multiple points of vulnerability. A single cyberattack on a supplier could compromise production and intellectual property across the entire manufacturing operation.
Implementation Approach:
- Develop robust third-party risk management frameworks
- Conduct regular cybersecurity audits of suppliers
- Enforce compliance with industry standards (NIST CSF, IEC 62443)
- Implement supply chain security monitoring tools
- Establish clear security requirements for all partners
- Perform regular security assessments of third-party integrations
Strategy 4: Incident Response and Business Continuity Plans
The ability to detect, respond, and recover from cyber incidents is critical in minimizing downtime and mitigating damage in the event of an attack. Manufacturers with limited preparedness often face extended disruptions and higher recovery costs.
Implementation Approach:
- Create and maintain detailed incident response plans
- Implement SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises and penetration testing
- Develop comprehensive disaster recovery strategies
- Establish clear communication protocols for incident response
- Regular testing and updating of recovery procedures
Strategy 5: Cybersecurity Awareness and Training
Human factors often represent the weakest link in cybersecurity, with insider threats and human error remaining significant challenges in manufacturing environments. Even the most advanced technical controls can be compromised by uninformed or untrained employees.
Implementation Approach:
- Implement regular security awareness training programs
- Conduct spear phishing simulations with real-time feedback
- Establish clear cybersecurity policies and procedures
- Train employees on RBAC (role-based access control)
- Develop proper data handling protocols
- Regular assessment of employee security awareness levels
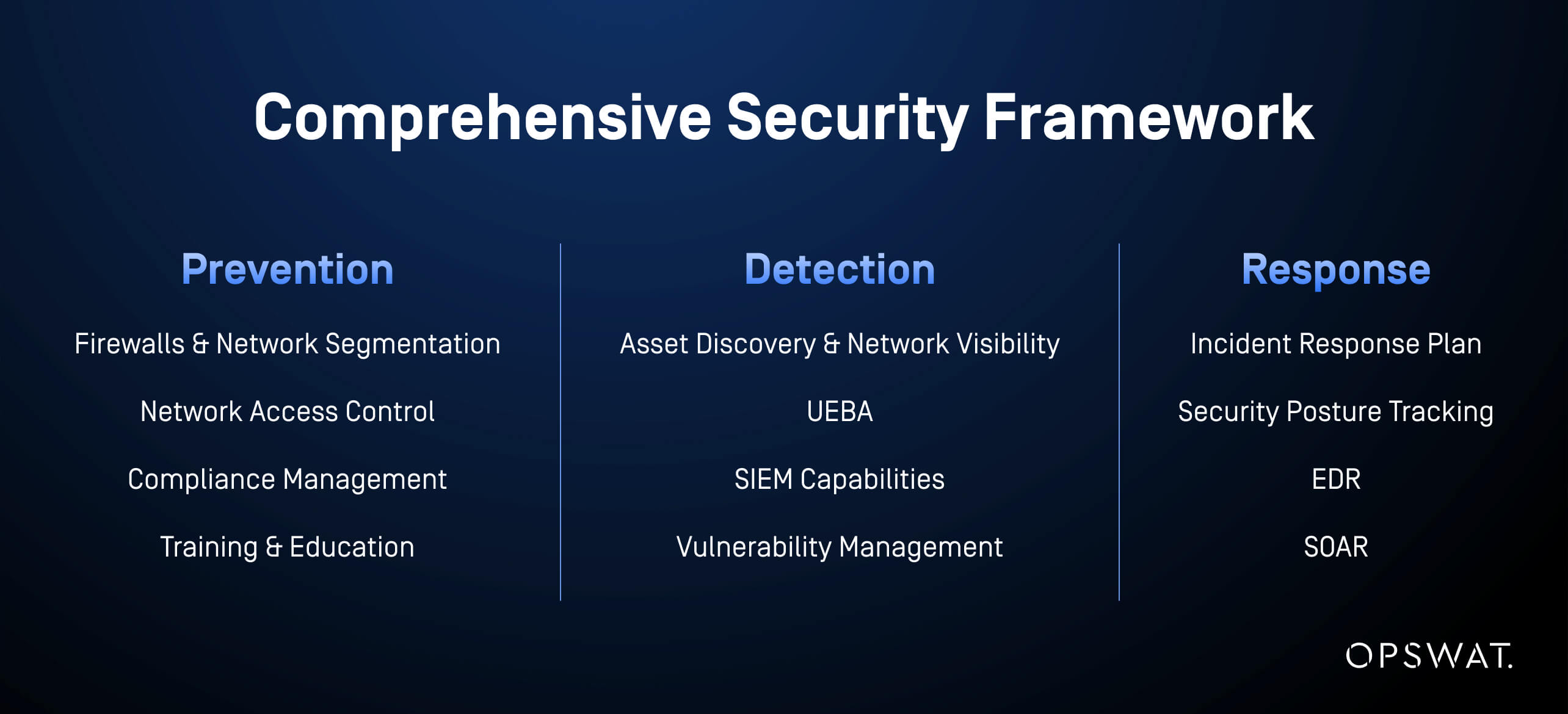
A Three-Pillar Defense Strategy
Protecting critical manufacturing environments requires a strategic, multi-layered approach to security. Our strategies work together to create a comprehensive and resilient security three-pillar framework that addresses the complex challenges faced by modern manufacturing facilities.
Ready to Strengthen Your Manufacturing Security?
As the manufacturing sector continues to embrace digital transformation, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. Implementing strategies such as network segmentation, strengthening endpoint security, securing supply chains, developing incident response plans, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness are necessary steps in safeguarding critical manufacturing environments against evolving cyber threats.
MetaDefender OT Security is designed to address these unique challenges faced by the manufacturing industry. With advanced features for threat detection, network monitoring, and compliance management, MetaDefender OT Security helps organizations protect their critical infrastructure and maintain operational continuity.



