What is CI/CD Security?
CI/CD security is the distribution of security practices and measures throughout the continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline. It focuses on protecting the automated processes used in software development to ensure the integrity, safety, and reliability of code changes from development through deployment.
Continuous Integration (CI) involves frequently merging code into a central repository and integrating third-party tools to automate application build tasks such as testing, development, and repository management. Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD) extends this by automating the deployment of those changes to production or other environments.
When implemented effectively, CI/CD increases development speed, consistency, and delivery reliability. But without proper security controls, these pipelines can introduce vulnerabilities, expose sensitive data, and compromise application integrity.
Effective CI/CD security ensures that code changes are safe, access is controlled, and the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC) is safeguarded from potential threats and malicious activity.
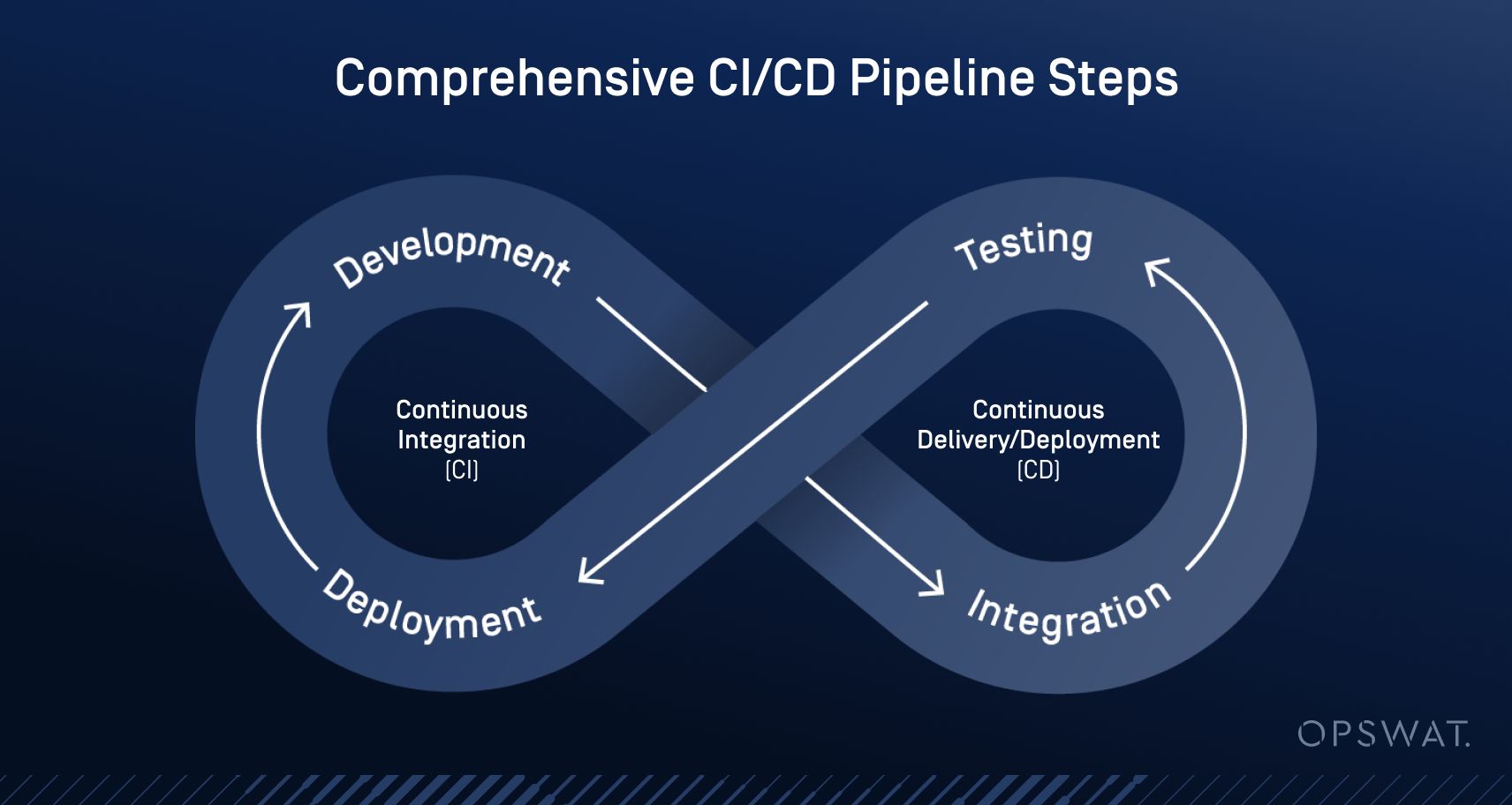
CI/CD Pipeline Explained
The CI/CD pipeline covers integration and deployment of new code into an existing codebase, which could be added features, quality-of-life improvements, or security and bug fixes. For most organizations, a robust CI/CD pipeline would include most or all of the following steps:
CI/CD Security Pipeline Risks
Having a streamlined CI/CD pipeline without proper security measures means threat actors can exploit steps in that process to compromise the entire codebase. Some of the most common CI CD security risks include:
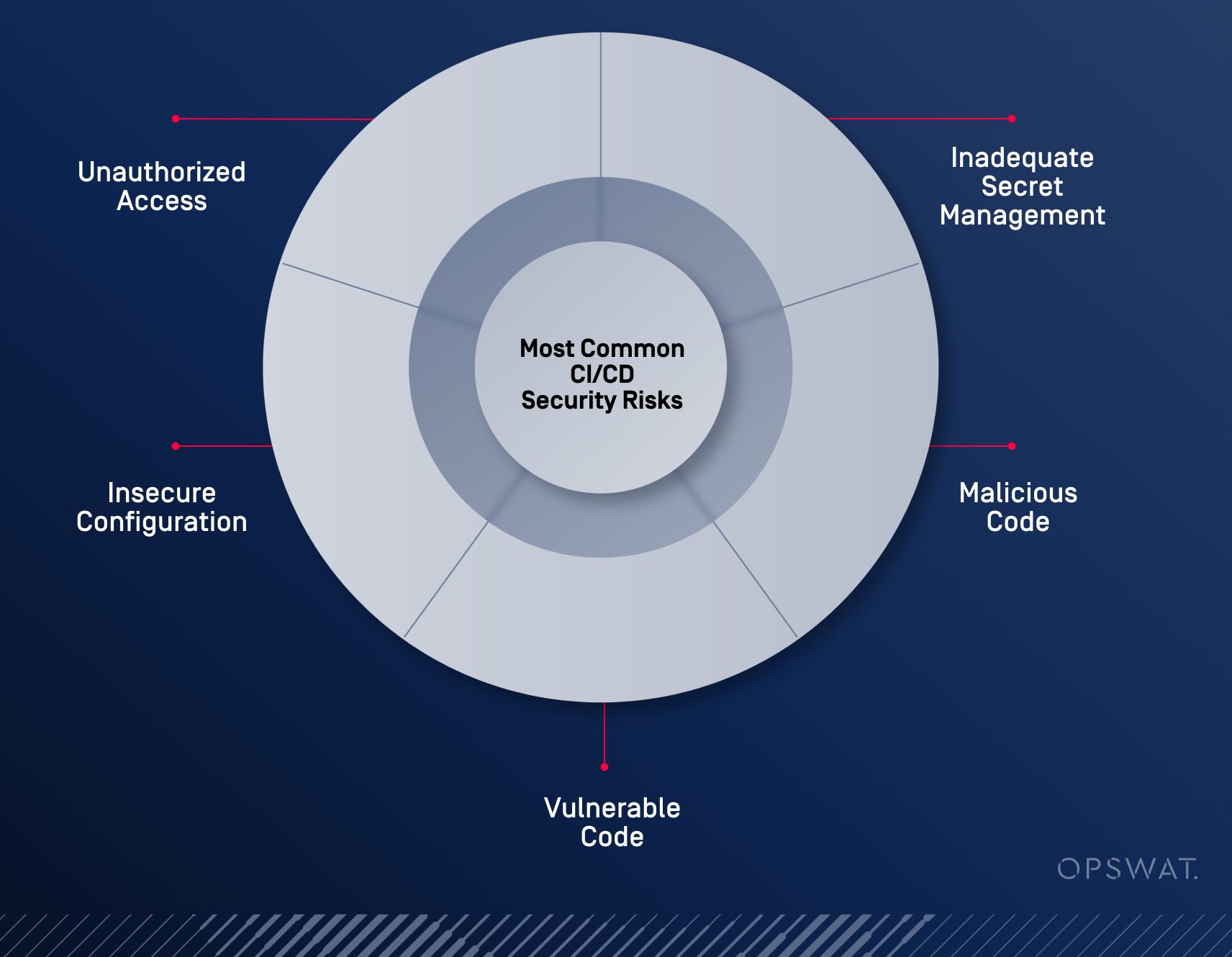
Unauthorized individuals gaining access to the CI/CD pipeline can inject malicious code or access sensitive information.
Poor handling of secrets, such as API keys and passwords, can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches.
Introduction of malicious code through dependencies or direct code injection can compromise the application and its data.
Security vulnerabilities in the codebase, as well as vulnerabilities introduced by third-party components, if not detected and addressed, can be exploited by attackers.
Misconfigured CI/CD tools and environments can open up avenues for attacks and data leaks.
There are numerous unfavorable outcomes that could unfold as a result of failure to protect the CI/CD process, including:
- A compromised CI/CD server leading to the deployment of malware in a production environment.
- Unauthorized access and exposure of sensitive data due to hardcoded credentials in the source code.
- Injection of malicious code through an unprotected third-party dependency, resulting in a supply chain attack.
OWASP Top 10
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 is a comprehensive list of the most common web application security risks, derived from extensive research and surveys. Updated regularly, it is widely recognized as an industry benchmark for secure web application development. Key risks include:
Highly configurable application servers, frameworks, and cloud infrastructure can have security misconfigurations, such as overly broad permissions, unchanged insecure default values, or overly revealing error messages, providing attackers with easy ways to compromise applications.
Poor implementation of authentication and access restrictions can allow attackers to easily access restricted resources. Unauthorized users might gain access to sensitive files, systems, or user privilege settings.
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in web applications that accept compromised data, such as SQL injection, OS command injection, and Cross Site Scripting (XSS). By injecting malicious code into input fields, attackers can execute unauthorized commands, access sensitive databases, and control systems.
Issues such as weak cryptographic keys, outdated algorithms, or hardcoded passwords can lead to the exposure of sensitive data.
Added in the 2021 OWASP Top Ten, this category focuses on fundamental design flaws and ineffective controls rather than just weak or flawed implementations.
CI/CD Security Challenges
Developers face several critical security challenges throughout the SDLC and CI CD processes.
The lack of visibility and awareness of secrets and sensitive data can lead to issues with sharing and tracking sensitive information. Effective secret management involves securely storing and handling secrets like API keys, passwords, and certificates. The frequent need to access and store this information presents a potential attack vector for threat actors.
Developers must also contend with the unexpected presence of malicious code, which can be injected either by external intervention or internally by employees who act maliciously or whose credentials are stolen and abused. This code may also originate from unverified sources or out-of-date third-party dependencies.
Continuous monitoring and scanning for known vulnerabilities in the codebase and dependencies is essential. Threat actors may take advantage of these unpatched vulnerabilities to proliferate malicious code.
Finally, the source code itself may come under threat from unauthorized access and tampering. Without regular audits and adherence to best practices in source code management, the integrity and security of the codebase could be compromised.
How to Secure a CI/CD Pipeline
To tackle these challenges in the CI/CD process, developers must implement robust security measures, including:
What are the CI/CD Security Best Practices?
While security measures are critical, developers must also adopt ongoing practices throughout the SDLC to ensure CI/CD security measures are implemented as effectively as possible.
Keep dependencies up to date to mitigate the risk of vulnerabilities. Use tools like Dependabot and Renovate to automate dependency updates.
Perform regular security audits of the CI/CD pipeline to identify and address potential risks. Security audits help in maintaining compliance and ensuring the effectiveness of security measures.
Where is CI/CD Security Most Critical?
When it comes to CI/CD security pipelines, which processes and teams are most affected? Understanding this aspect is critical to ensuring security improvements and resources are allocated to the right teams.

Integrating security practices into the DevOps process ensures a secure development lifecycle. DevSecOps emphasizes the importance of security at every stage of the CI/CD pipeline.

Protecting the software supply chain from vulnerabilities and threats involves vetting third-party dependencies and implementing security controls for the entire supply chain.
Protect your Project with CI/CD Security
Ensuring security in CI/CD pipelines is essential to protect software integrity, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate risks associated with software development and deployment. By implementing comprehensive, multi-layered CI CD security practices and using secure CI/CD tools, organizations can safeguard their CI/CD processes and deliver secure software. Effective CI/CD security measures enhance the reliability and trustworthiness of the software, ensuring that it meets both functional and security requirements.
Learn how OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Software Supply Chain secures the entire supply chain, ensuring comprehensive protection for your project.
FAQs
What is CI/CD security?
CI/CD security is the distribution of security practices and measures throughout the continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline. It focuses on protecting the automated processes used in software development to ensure the integrity, safety, and reliability of code changes from development through deployment.
What does a CI/CD pipeline include?
The CI/CD pipeline covers integration and deployment of new code into an existing codebase, which could be added features, quality-of-life improvements, or security and bug fixes. For most organizations, a robust CI/CD pipeline includes development, integration, testing, and deployment stages.
Why are CI/CD pipelines at risk?
A streamlined CI/CD pipeline without proper security measures leaves gaps that threat actors can exploit. Common risks include unauthorized access, inadequate secret management, malicious code injection, vulnerable code, and insecure configuration. These weaknesses can compromise software and expose sensitive data.
What are the most common CI/CD security risks?
- Unauthorized Access: Attackers gaining access to the CI/CD pipeline can inject code or steal information.
Inadequate Secret Management: Poor handling of API keys or passwords can cause breaches.
Malicious Code: Code injected by threat actors or dependencies can compromise apps.
Vulnerable Code: Unpatched or flawed code opens the door to exploitation.
Insecure Configuration: Misconfigured environments can lead to data leaks or control loss.
What is the OWASP Top 10 and why does it matter?
The OWASP Top 10 is a regularly updated list of the most common web application security risks. It includes issues such as security misconfiguration, broken access control, injection, cryptographic failures, and insecure design. It serves as an industry benchmark for identifying and addressing security issues.
What security challenges do developers face in CI/CD?
Developers often struggle with lack of visibility over secrets, malicious code introduced through dependencies, and unpatched vulnerabilities. Unauthorized access to source code and improper secret handling increase risks. These challenges emphasize the need for consistent security monitoring and secure development practices.
How can you secure a CI/CD pipeline?
- Secrets Management: Use encrypted vaults for storing credentials.
Automated Security Tests: Integrate tools to detect vulnerabilities early.
Source Code Security: Use code reviews and access controls.
Least Privilege Principle: Limit access to only what is necessary.
Environment Security: Isolate development and production environments with proper controls.
What are best practices for CI/CD security?
- Regularly update third-party dependencies.
Conduct security audits of the CI/CD pipeline.
Monitor the pipeline for threats using logging and alert systems.
Where is CI/CD security most critical?
CI/CD security is essential in areas such as:
DevSecOps
Application Security Testing
Container Security
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Compliance and Governance
Supply Chain Security
Patch Management
Incident Response
Microservices Security
Why is securing CI/CD pipelines important?
CSecuring CI/CD pipelines is critical to protect software integrity, prevent unauthorized access, and reduce risks throughout the software development lifecycle. Robust CI/CD security helps ensure safe, reliable, and compliant software delivery.