- Understanding File Transfer Risks Unique to Healthcare and HIPAA Compliance
- Key Features Every Managed File Transfer Solution Needs for HIPAA Compliance
- How Managed File Transfer Solutions Enable Efficient HIPAA Audits and Compliance Reporting
- Best Practices for Secure File Transfer in Healthcare Organizations
- Comparing Managed File Transfer Solutions: Healthcare-Specific vs. Generic Platforms
- Implementation Steps for Deploying HIPAA-Compliant Managed File Transfer in Healthcare
- Measuring the Value of Managed File Transfer for Healthcare Compliance and Patient Data Protection
- FAQs
Understanding File Transfer Risks Unique to Healthcare and HIPAA Compliance
Healthcare file transfers expose PHI (protected health information) to data breaches, regulatory penalties, and operational disruption because files move constantly between departments, clinicians, partners, and systems.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) raises the stakes by requiring consistent protection, auditability, and control for every file transfer. Generic file-sharing tools rarely meet these expectations because they lack the governance (enforced encryption policies), validation (automated access verification), and visibility (comprehensive audit trails) that PHI handling demands.
HIPAA mandates specific requirements, including documented audit trails (auditability), encryption standards (protection), and access restrictions (control), for every file transfer containing PHI.
What Security Threats Are Most Common in Healthcare File Transfers?
Healthcare file transfers (the electronic movement of PHI between systems, departments, and external partners) are most commonly targeted by ransomware, data theft, and account compromise, where attackers intercept PHI in transit or abuse weak access controls.According to Healthcare IT News, the 2024 Change Healthcare ransomware attack confirmed exposure of data on approximately 192.7 million individuals, demonstrating how a single compromised clearinghouse can become the largest healthcare data breach in U.S. history.
Common security threats in healthcare file transfers include:
Data interception: Unencrypted or weakly protected file transfers via email or legacy protocols remain prime targets.
Unauthorized access: Shared accounts, broad permissions, or unsecured partner connections expose PHI internally and externally.
Insider misuse: Accidental mis-sending, use of personal devices, or intentional exfiltration frequently drive reportable breaches.
Third-party compromise: PHI often flows to labs, billing firms, and specialty providers that may not enforce adequate controls.
Operational failures: Breakdowns in ad-hoc transfer workflows lead to lost files, delays, or missing documentation.
How Do HIPAA Rules Shape Electronic File Transfer Requirements?
HIPAA’s Privacy Rule requires that any PHI shared internally or externally be disclosed only to authorized parties with a legitimate purpose, while the Security Rule mandates administrative, physical, and technical safeguards that protect electronic PHI during transmission.
ogether, they require covered entities and business associates to ensure that every file transfer preserves confidentiality (through encryption), verifies user authorization (via multi-factor authentication), and maintains integrity (using checksums or digital signatures) throughout the exchange.
HIPAA requires covered entities to safeguard PHI data in transit through:
- Confidentiality controls that protect data from interception
- Access verification ensuring only authorized users and systems exchange PHI
- Integrity protections confirming files are not altered during transit
- Full auditability documenting who sent what, when, and to whom
- Consistent policies and risk management governing all file transfer workflows
Why Are Traditional File Sharing Methods Inadequate for HIPAA Compliance?
Legacy or consumer-grade tools fall short because they lack enforceable controls, monitoring, and audit trails. These methods depend on user behavior rather than enforced safeguards, creating predictable compliance failures and elevating breach risk.
Legacy File Sharing Methods and Compliance Requirements
| Method | Core Issues | HIPAA Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Mis-sending, inconsistent encryption | No reliable access control or end-to-end protection | |
| FTP/SFTP | Static credentials, limited visibility | Insufficient auditing and role-based control |
| Consumer cloud tools | Public links, user-managed permissions | No enterprise governance for PHI |
| Manual/ad hoc methods | USB drives, unapproved apps | No visibility or policy enforcement |
Based on HIPAA Security Rule § 164.312(e) Transmission Security requirements and HHS guidance on electronic PHI protection.
Key Features Every Managed File Transfer Solution Needs for HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA-ready MFT (managed file transfer) platform must enforce consistent protection (encryption), verification (access authentication), and visibility (audit logging) across every PHI transfer. The core features map directly to required safeguards: encryption, access control, integrity validation, audit logging, policy enforcement, and third-party governance.
Healthcare-specific MFT solutions strengthen these controls with capabilities tailored to high-volume PHI exchange, clinical workflows, and complex vendor ecosystems beyond what generic systems can reliably deliver.
Which Encryption Standards Are Required for HIPAA-Compliant File Transfers?
HIPAA expects PHI in transit to be protected with strong, industry-standard encryption. In practice, this means:
- AES-256 for file-level and at-rest encryption
- TLS 1.2 or higher for data-in-transit protection
- Cryptographic modules aligned with NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology)-recommended algorithms
- Consistent enforcement across all internal, external, automated, and ad-hoc transfers
According to HHS HIPAA Security Rule guidance on transmission security (§ 164.312(e)), encryption is viewed as a primary safeguard for preventing unauthorized access during transmission. An MFT solution should guarantee that encryption requirements are built into policy controls and role-based configurations, preventing users from sending PHI through unprotected channels.
How Do Access Controls and User Authentication Prevent Unauthorized PHI Access?
Access to PHI must be limited to individuals and systems with a documented, job-related need (the minimum necessary principle under HIPAA Privacy Rule § 164.502(b)). An MFT platform should enforce this through:
- Granular RBAC (role-based access control) that limits visibility and transfer rights
- MFA (multi-factor authentication) for both internal users and external partners
- Strong system-to-system authentication, replacing static credentials with certificates or tokens
- Policy-based restrictions governing who can send, receive, approve, or retrieve PHI-bearing files
These measures reflect HIPAA’s core Security Rule expectations: verify identity, authorize appropriately, and prevent unauthorized disclosure.
What Audit Trails and Reporting Capabilities Are Essential for HIPAA Audits?
Auditors expect complete traceability for every PHI transfer. Without this visibility, organizations cannot demonstrate HIPAA compliance during audits and may face enforcement actions, including civil monetary penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation.
An MFT solution must capture:
- Who accessed or transmitted PHI
- What file moved, to whom, and through which workflow
- Timestamped events showing send, receive, failure, and deletion actions
- Integrity checks confirming files were not altered in transit
- Administrative activity logs for changes to settings, policies, and permissions
Additionally, healthcare programs benefit from:
- Real-time monitoring and alerts for anomalous transfers or policy violations
- Retention policies that ensure logs remain available for investigation or audit
- Exportable, audit-ready reports tailored to HIPAA inquiries

How Do MFT Solutions Support Secure Collaboration with Third-Party Vendors?
“MFT solutions support secure third-party collaboration by enforcing controlled onboarding, isolated transfer channels, and policy-driven governance for every vendor connection. Healthcare relies on an extensive network of labs, billing firms, imaging centers, and specialty providers. A compliant MFT platform must make external data exchange both secure and governed.
Key capabilities of MFT
- Controlled external user onboarding with predefined roles, approvals, and expiration
- Isolated, policy-enforced transfer channels for each partner
- Secure portals that eliminate email attachments and unmanaged links
- Automated enforcement of encryption and access controls regardless of partner technology
- Centralized visibility into all third-party transfers, including failures or unapproved workflows
HIPAA also requires that any vendor handling PHI operate under a BAA (Business Associate Agreement). An MFT solution should streamline partner onboarding with BAA alignment and documentation in order to ensure that contractual obligations match technical safeguards.
How Managed File Transfer Solutions Enable Efficient HIPAA Audits and Compliance Reporting
A well-designed MFT platform centralizes evidence, enforces policy, and provides continuous visibility into PHI movement. These capabilities can dramatically simplify HIPAA audits. Instead of manually gathering logs, screenshots, or access records from disparate systems, an MFT solution consolidates all file-transfer activity into a single, searchable source of truth. This reduces audit preparation time, improves documentation accuracy, and supports higher audit pass rates.
Healthcare-focused MFT products also align with HIPAA expectations around transmission security, access control, and auditability as outlined in the HIPAA Security Rule. Their built-in controls match what auditors look for: consistent safeguards, complete records, and proof that PHI transfers are governed.
What Documentation and Evidence Do Auditors Require from MFT Systems?
HIPAA auditors typically request evidence that demonstrates:
- Who accessed or transmitted PHI
- What files moved, to whom, and under which policy
- When each transfer occurred, including success, failure, and retries
- How integrity and encryption were enforced
- Administrative changes, such as permission updates or workflow modifications
MFT platforms automate the collection and retention of this information. For example, the detailed audit logs and reporting capabilities of OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Managed File Transfer™ capture user activity, file lifecycles, system events, and job execution from a centralized view. This directly aligns with HIPAA’s expectation that covered entities maintain complete audit trails for all PHI-involving systems.
How Can MFT Platforms Reduce the Time and Cost of HIPAA Audit Preparation?
MFT platforms reduce audit preparation time and cost by centralizing evidence, automating compliance workflows, and providing ready-made reporting. Manual audit preparation often requires days or weeks of reconstructing transfer histories, validating encryption settings, and tracking down missing evidence across siloed systems.
MFT platforms reduce that overhead through:
- Pre-built compliance reports summarizing access, transfers, failures, and policy enforcement
- Centralized dashboards that present PHI transmission activity in a single pane of glass
- Workflow automation that ensures required safeguards (encryption, authentication, approvals) are applied consistently and documented
- Searchable logs that eliminate manual data retrieval across multiple tools
MetaDefender Managed File Transfer supports policy-based automation, supervisory approval flows, and visual orchestration, enabling teams to standardize how PHI moves and how compliance is recorded. These efficiencies translate into measurable reductions in audit prep time and fewer remediation steps.
What Features Support Ongoing Compliance Monitoring and Risk Reduction?
MFT solutions support ongoing HIPAA compliance by continuously monitoring file activity, detecting anomalies, and enforcing policy controls across all transfers. HIPAA compliance isn’t evaluated only during audits, but rather it must be maintained continuously.
MFT solutions strengthen ongoing compliance with:
Real-time alerts: Flag unusual transfers, unauthorized access attempts, or deviations from approved workflows.
Anomaly detection and integrity checks: Identify suspicious file behavior or unexpected changes that could indicate misuse or compromise.
Policy enforcement at every transfer: Ensure encryption, authentication, and approval requirements are applied consistently, eliminating manual errors and ad hoc workarounds.
Centralized visibility: Monitor file movement across internal systems and external partners. MetaDefender Managed File Transfer delivers full visibility into transfers, access, and system events.
Advanced threat prevention: Healthcare auditors increasingly examine whether PHI is protected from malware or tampering. OPSWAT’s MFT technologies, such as multiscanning, content disarm and reconstruction, and vulnerability assessment, significantly reduce the risk of file-borne threats.
Together, these capabilities support proactive compliance: spotting issues before they become reportable events, reducing the likelihood of PHI exposure, and providing auditors with authoritative evidence of continuous monitoring.
Best Practices for Secure File Transfer in Healthcare Organizations
For Compliance and Risk Officers, securing PHI transfers requires more than a strong MFT platform. It requires disciplined processes, clear policies, and consistent user behavior. HIPAA’s safeguards emphasize administrative controls just as much as technical ones, meaning organizations must pair technology with governance, training, and monitoring. The goal is to ensure every PHI transfer follows a predictable, enforceable, and auditable path.
What Are the Steps to Develop a HIPAA-Compliant File Transfer Policy?
A file transfer policy should define how PHI is moved, who is authorized to move it, and what controls must be applied at every step. A clear, enforced policy reduces PHI exposure risk and aligns staff behavior with HIPAA’s administrative safeguard expectations.
A strong policy should:
- Define Acceptable Use: Specify when PHI may be transferred, what methods are approved, and which systems (including MFT) must be used.
- Establish User and System Authorization Rules: Detail role-based access, required authentication mechanisms, and approval workflows for file transfers.
- Require Encryption and Integrity Protections: Mandate the use of approved encryption standards and verification steps that align with HIPAA transmission safeguards.
- Document Retention and Disposal Requirements: Set retention schedules for logs, evidence, and transferred files, consistent with organizational and HIPAA expectations.
- Outline Escalation and Incident procedures: Define reporting steps for failed transfers, suspected breaches, policy violations, and partner issues.
- Integrate Third-party Governance: Require Business Associate Agreements and define onboarding/offboarding steps for external partners.
- Review and Update Regularly: Policies should be reviewed at least annually or even sooner if workflows, systems, or regulations change.
How Should Healthcare Staff Be Trained on Secure File Transfer Protocols?
Training ensures that technical safeguards are used correctly and consistently.
Effective programs cover:
Core training topics
- Approved file transfer tools and workflows
- How to verify recipient identity and authorization
- Avoiding unapproved methods (email attachments, personal cloud tools, USB drives)
- Recognizing and reporting failed or suspicious transfers
- Understanding PHI and minimum-necessary principles
Frequency
- Initial onboarding
- Annual refreshers
- Just-in-time training when systems, workflows, or policies change
Assessment methods
- Short quizzes or scenario-based exercises
- Simulated errors (e.g., misaddressed transfers) to reinforce expectations
- Targeted follow-up for users with repeated mistakes
Common user errors to address
- Sending to the wrong recipient
- Using unencrypted or unapproved channels
- Uploading the wrong file
- Mishandling files on personal or shared devices
Training should emphasize accuracy, verification, and the consistent use of the MFT platform so staff avoid practices that circumvent required controls.
What Are the Key Metrics to Track for Ongoing File Transfer Security?
Healthcare organizations should track specific metrics to monitor secure file transfer performance. Continuous monitoring supports proactive HIPAA compliance and operational stability. Key KPIs include:
Failed or incomplete transfer rates: High failure volumes may indicate system issues, process gaps, or partner problems
Access anomalies: Unexpected users, off-hours activity, or repeated failed authentications may signal unauthorized access attempts
Policy violations: Transfers that bypass required encryption, approvals, or workflows should be tracked and investigated
Third-party performance: Monitor partner success rates, delays, and security exceptions to ensure contractual and HIPAA obligations are met
Audit findings and remediation cycle time: Track recurring issues and how quickly they are resolved to maintain compliance readiness
Threat detection events: If advanced threat prevention technologies (e.g., malware scanning, CDR, vulnerability assessment) flag issues, recurring patterns may indicate underlying risk
These metrics drive continuous improvement: identifying process weaknesses, validating policy effectiveness, prioritizing training needs, and ensuring consistent alignment with HIPAA’s expectations for monitoring and risk management.
Comparing Managed File Transfer Solutions: Healthcare-Specific vs. Generic Platforms
Compliance and Risk Officers evaluating MFT options should distinguish between platforms that are merely “HIPAA-capable” and those designed for high-volume PHI workflows. HIPAA expects consistent safeguards for file transfer security, access control, and auditing across all systems that handle PHI.
Healthcare organizations seeking scalable, reliable, and industry-trusted solutions benefit from platforms engineered specifically for PHI workflows. Healthcare-specific MFT solutions embed these requirements along with advanced threat prevention and clinical integrations into the product by default.
How Do Leading HIPAA-Compliant MFT Solutions Compare on Security and Compliance Features?
Leading HIPAA-compliant MFT platforms differ in enforcement strength, audit depth, automation, and threat-prevention capabilities. Below is a simplified comparison between generic “HIPAA-ready” MFT platforms and healthcare-specific MFT solutions such as MetaDefender Managed File Transfer, which leverages advanced threat prevention technologies from MetaDefender Core™.
Unlike traditional MFT solutions that secure only the file transfer channel, MetaDefender Managed File Transfer secures the file itself with multi-layered threat prevention, CDR, vulnerability assessment, and sandbox analysis.
HIPAA-ready vs Healthcare-specific MFT solutions
| Capability | Generic MFT (“HIPAA-ready”) | Healthcare-Specific MFT (e.g., MetaDefender MFT) |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption in transit & at rest | Standards-based encryption, often configurable | Strong, enforced encryption policies across all workflows with minimal user choice |
| Access control & approvals | Basic RBAC, optional approvals | Granular RBAC, supervisory approval flows, and policy-based routing for PHI |
| Audit logging & reporting | Standard activity logs | Detailed audit trails for users, files, jobs, and system events, plus exportable reports for compliance |
| Threat prevention | Antivirus or none | Multi-layered file security: multiscanning, content sanitization, and vulnerability assessment |
| Integration & automation | Connectors for common IT tools | Policy-driven workflows, visual orchestration, and integrations |
| Deployment options | Often cloud-first | Flexible on-premises and hybrid deployments for regulated and offline environments |
What Are the Pros and Cons of SFTP, MFT, and Cloud-Based File Sharing for Healthcare?
SFTP, cloud file-sharing tools, and MFT platforms each offer distinct benefits and limitations in the context of HIPAA compliance. For most hospitals and health systems, a security-first MFT platform should be the standard for PHI-bearing transfers, while SFTP and cloud tools are limited to tightly scoped, low-risk use cases.
Pros and cons of SFTP, cloud tools, and MFT platforms
| Approach | Pros | Cons in Healthcare / HIPAA Context | Best Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFTP | Widely supported; better than FTP; can encrypt data in transit | Limited visibility and reporting; static credentials; manual workflows; weak governance for PHI | Point-to-point system integrations where volume is low and governance is handled elsewhere |
| Generic cloud file sharing | Easy to use; quick collaboration; mobile-friendly | User-managed permissions, public links, unclear data residency, limited PHI governance | Non-PHI collaboration; not recommended as a primary PHI transfer mechanism |
| MFT [managed file transfer] | Central control, policy-based automation, integrated encryption, auditing, and access control | Requires implementation effort and process alignment | Primary vehicle for PHI transfers, especially where HIPAA audit readiness and multi-party workflows are priorities |
Which Managed File Transfer Vendors Offer the Best Support for Healthcare Compliance Audits?
Vendors that serve healthcare well typically provide:
- Healthcare-aware support models: 24/7 support, SLAs aligned to clinical operations, and staff familiar with HIPAA expectations
- BAA-ready contracting: Standard BAAs, clear delineation of responsibilities, and documentation that maps product controls to HIPAA safeguards
- Audit-readiness services: Pre-built compliance report templates, guidance on configuring policies, and assistance in producing evidence during audits
- Security-first roadmap: Ongoing investments in advanced threat prevention, vulnerability detection, and integration with SIEM and SOC workflows
OPSWAT distinguishes itself with a security-first MFT product that combines:
- Multi-layered security through advanced threat prevention technologies such as multiscanning, content sanitization, vulnerability assessment, and sandboxing
- Policy-based file transfer automation, supervisory approvals, and centralized visibility and control tailored to regulated environments
- Compliance-focused logging and reporting that simplify HIPAA audits by providing end-to-end traceability of file movements and access
For Compliance and Risk Officers, vendors with this combination of security depth, audit-ready evidence, and healthcare-aware support are best positioned to reduce audit friction and strengthen HIPAA compliance over the long term.
Implementation Steps for Deploying HIPAA-Compliant Managed File Transfer in Healthcare
Deploying a security-first MFT solution in a healthcare environment requires structured planning, alignment with HIPAA safeguards, and coordination across clinical, IT, compliance, and vendor teams. The objective is to replace inconsistent, high-risk file transfer practices with standardized, auditable workflows that integrate tightly with existing systems while minimizing operational disruption.
What Are the Key Steps to Implement a Managed File Transfer Solution in a Hospital Setting?
As part of early planning, teams should conduct a formal risk assessment to map current vulnerabilities and ensure the MFT design aligns with HIPAA’s administrative and technical safeguard expectations.
A practical, repeatable implementation sequence includes:
- Assess requirements and risks: Identify PHI workflows, regulatory needs, integration points, and success metrics
- Design solution architecture and align stakeholders: Choose deployment model, define governance roles, and coordinate compliance, IT, security, and clinical teams
- Configure security policies and integrations: Set routing, approvals, access controls, retention rules, and integrate MFT technologies such as Metascan™ Multiscanning and Deep CDR™
- Test workflows and train users: Validate transfers, logs, alerts, and audit readiness; train admins and end users on approved workflows
- Launch, monitor, and refine: Deploy in phases, track key performance metrics, and perform post-implementation reviews
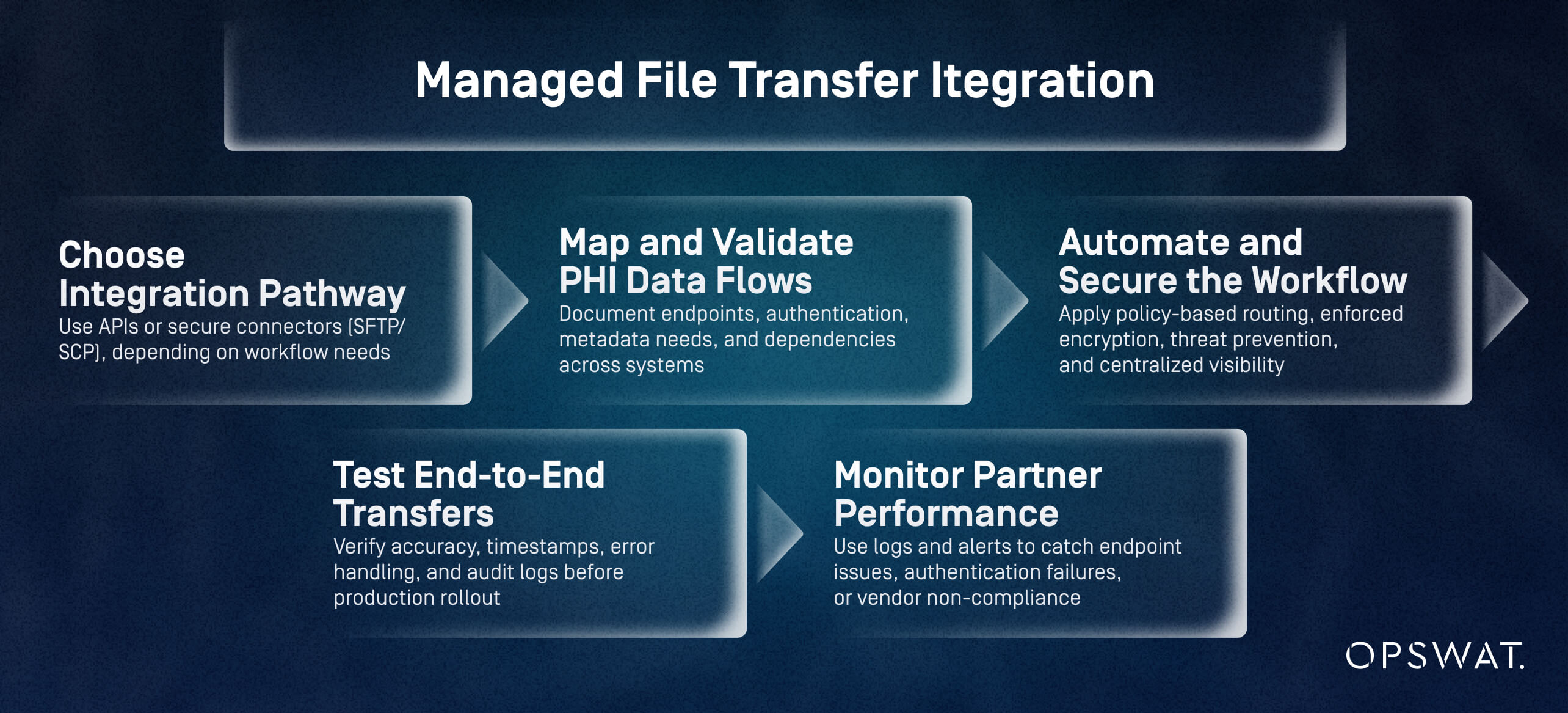
How Can Healthcare Organizations Integrate MFT with Existing EHR and Vendor Systems?
Healthcare organizations integrate MFT with EHR and vendor systems by selecting secure connection methods, mapping PHI flows, and automating file transfer policies. EHRs and adjacent vendor systems exchange vast amounts of PHI, making integration a critical success factor.
Effective MFT integration in 5 steps:
- Choose integration pathway: Use APIs or secure connectors (SFTP/SCP), depending on workflow needs
- Map and validate PHI data flows: Document endpoints, authentication, metadata needs, and dependencies across systems
- Automate and secure the workflow: Apply policy-based routing, enforced encryption, threat prevention, and centralized visibility
- Test end-to-end transfers: Verify accuracy, timestamps, error handling, and audit logs before production rollout
- Monitor partner performance: Use logs and alerts to catch endpoint issues, authentication failures, or vendor non-compliance
What Are Best Practices for Migrating from Legacy File Transfer Methods to MFT?
Best practices for migrating to MFT include assessing transfer risks, mapping workflows, validating parallel runs, and refining governance as processes transition. Most healthcare organizations migrate from a mix of email, SFTP, manual uploads, and shared folders.
A Structured Migration
- Analyze risk and prioritize workflows: Identify PHI-heavy or high-risk transfer paths (email, manual uploads, shared folders) and migrate them first
- Map data and prepare the new workflows: Define routing, naming conventions, retention rules, and system dependencies
- Migrate in phases with parallel validation: Run legacy and MFT workflows simultaneously, validating integrity, routing, and audit logs
- Optimize and update governance: Apply threat prevention, refine workflows, update policies, and train users based on lessons learned
Measuring the Value of Managed File Transfer for Healthcare Compliance and Patient Data Protection
A healthcare-ready MFT platform improves HIPAA compliance, reduces breach risk, and streamlines PHI workflows. By enforcing encryption, access control, threat prevention, and complete audit trails, organizations gain both regulatory and operational ROI.
How Does MFT Reduce the Risk of Data Breaches and Non-Compliance Penalties?
MFT directly mitigates the leading causes of PHI exposure: unencrypted transfers, unauthorized access, user errors, and insufficient logging. Healthcare-specific platforms further reduce risk using advanced threat prevention technologies.
Main risk-reduction outcomes:
- Enforced encryption and access control
- Protection against malware and zero-day threats
- Complete audit trails supporting HIPAA investigations
- Lower likelihood of regulatory penalties and remediation costs
What Are the Measurable Outcomes of Optimized File Transfer Processes?
Organizations moving from email, SFTP, and manual workflows to MFT typically see gains in:
Compliance readiness
- Faster evidence retrieval
- Comprehensive, exportable logs
Operational efficiency
- Reduced failed transfers
- Less manual intervention through policy-based automation
Error and incident reduction
- Fewer mis-sent files
- Early detection of abnormal activity through real-time alerts
Threat prevention
- Significant decrease in harmful files reaching clinical systems
How Can Compliance Officers Demonstrate the Value of MFT Investments to Stakeholders?
Stakeholders respond to risk, cost, and operational impact. Compliance leaders can articulate value through:
Key messages
- Reduced regulatory exposure through enforced safeguards
- Lower breach likelihood and response costs
- Fewer audit findings and faster audit cycles
- Improved operational reliability and vendor collaboration
Link to organizational priorities
- Patient safety: Reliable PHI movement reduces delays in care
- Financial stability: Avoided penalties and downtime protect margins
- Organizational trust: Strengthened PHI protection supports reputation and partner confidence
- Digital transformation: MFT forms a secure foundation for modernization
MetaDefender Managed File Transfer™ is OPSWAT’s managed file transfer (MFT) solution that supports regulatory compliance through encryption, access control, and detailed audit trails.
To learn how it and its advanced threat prevention technologies can strengthen HIPAA compliance, reduce PHI exposure risk, and streamline secure collaboration across your healthcare ecosystem, speak with an OPSWAT expert or request a demo today.
FAQs
What are the top managed file transfer solutions that are fully HIPAA compliant for healthcare organizations?
Solutions that enforce encryption, access controls, policy automation, and full audit trails meet HIPAA expectations. Healthcare-focused platforms, such as MetaDefender Managed File Transfer, provide additional threat prevention and compliance reporting that generic tools often lack.
What features should I look for in an MFT solution to ensure HIPAA compliance in healthcare?
Enforced encryption, granular RBAC, MFA, detailed audit logging, policy-based automation, secure third-party collaboration, and advanced threat prevention (e.g., multiscanning, CDR, vulnerability assessment).
How do different managed file transfer providers compare in terms of HIPAA compliance and security features?
Many providers cover encryption and basic logging, but healthcare-focused platforms add supervisory approvals, advanced threat detection, detailed reporting, and flexible deployment models needed for PHI-heavy environments.
What documentation or audit trails do MFT solutions provide to demonstrate HIPAA compliance during an audit?
Audit logs showing user activity, file movement, system events, approvals, encryption status, and transfer outcomes. MetaDefender Managed File Transfer provides centralized, exportable reports for compliance reviews.
How do I implement role-based access controls and encryption in a managed file transfer system for HIPAA compliance?
Configure RBAC to limit PHI access by role, require MFA, and apply enforced encryption (e.g. AES-256, TLS 1.2+) across all workflows. HIPAA transmission safeguards expect these protections by default.
Do managed file transfer vendors offer Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) and what should be included in them?
Yes. BAAs should define PHI protection responsibilities, breach notification requirements, permitted uses, and security expectations aligned with HIPAA safeguards for transmission and access control.
What are the typical costs and licensing models for HIPAA-compliant MFT solutions in healthcare?
Pricing varies by deployment (cloud, on-prem, hybrid), volume, and add-on technologies. Most vendors offer subscription or perpetual licensing; the total cost reflects compliance reporting, workflow automation, and integrated threat prevention.
What are best practices for migrating from legacy file transfer methods to an MFT platform that meets HIPAA requirements?
Assess current risks, map PHI workflows, migrate in phases, run parallel validation, and incorporate advanced threat prevention from day one. Update policies and training as workflows transition.

