In high-security environments like ICS (industrial control systems) and critical infrastructure, even the most advanced firewalls and intrusion prevention systems have limitations. To truly protect sensitive networks, organizations need a solution that eliminates the possibility of external access altogether.
Data diodes are powerful, hardware-based cybersecurity barriers designed to enforce unidirectional data flow. In this guide, we’ll explore how data diodes work, why they’re essential for ICS security, and how they help organizations meet regulatory compliance.
- What is a Data Diode?
- Unidirectional Data Flow Explained
- How Does a Data Diode Work?
- Technical Architecture of Data Diodes
- Implementation in Network Security
- Data Diodes in Industrial Control Systems
- Enhancing ICS Security
- Compliance and Regulatory Standards for Data Diodes
- Meeting ISO 27001 Standards
- Comparing Data Diodes with Other Security Solutions
- Data Diode vs. Firewall
- Data Diode vs. Data Guard
- A Comprehensive Data Diode Solution
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Data Diode?
A data diode is a cybersecurity hardware device that enforces unidirectional data flow, meaning data can physically travel in only one direction—from one network to another—without any possibility of return traffic. This one-way communication is essential for protecting sensitive systems by completely isolating them from external threats.
Data diodes—sometimes referred to as optical diodes in cybersecurity—are often used in environments that manage critical infrastructure, such as ICS and SCADA networks. By preventing two-way communication, they eliminate common attack vectors like malware injection, command-and-control communication, and data exfiltration.
Unidirectional Data Flow Explained
Unidirectional data flow ensures that information can move in one direction only—typically from a high-security zone (like an operations network) to a lower-security zone (like a data historian or enterprise network). Unlike traditional bidirectional systems (e.g., TCP/IP-based communication), data diodes physically restrict reverse traffic, making them ideal for network isolation and information security.
How Does a Data Diode Work?
A data diode works by allowing one-way data transmission between two separate network segments. It typically consists of a hardware component that ensures data can leave a secure network but cannot return.
Data diodes are a critical cybersecurity barrier, preventing unauthorized access, remote command injection, and data leakage.
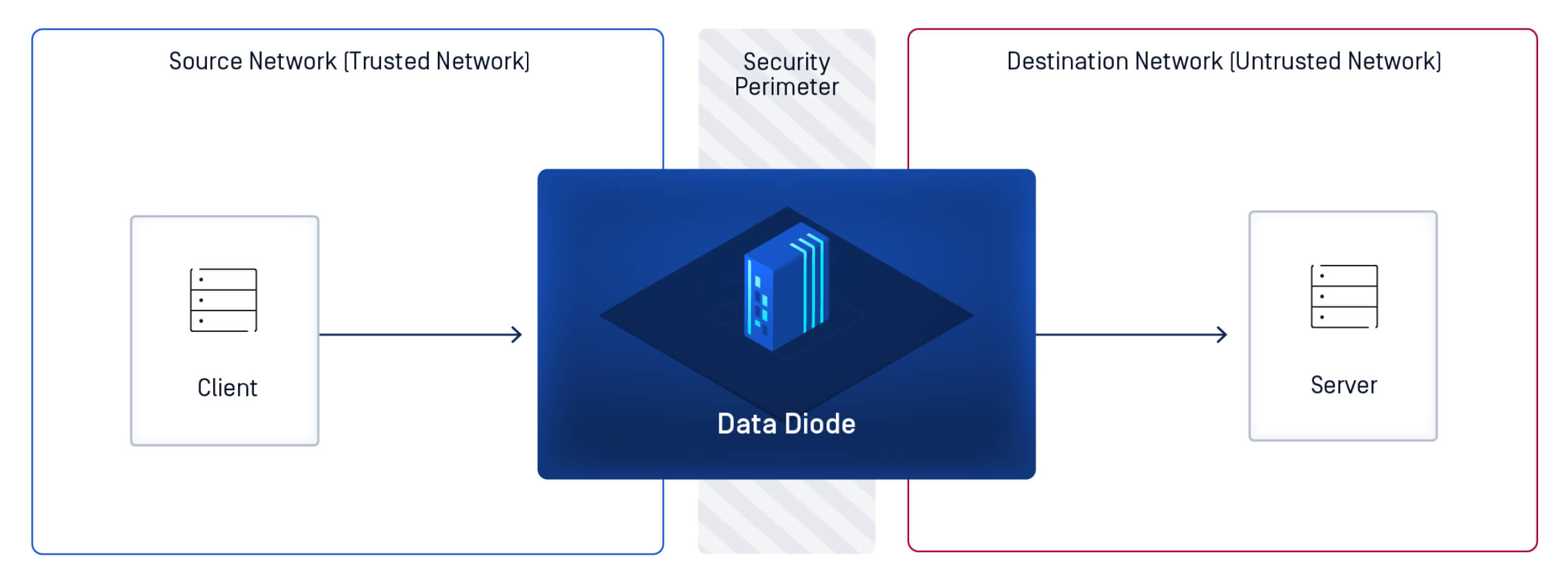
Technical Architecture of Data Diodes
At the core, a data diode’s technical architecture includes a sender and a receiver module connected by a unidirectional optical link. The hardware is physically constructed to block any return signal. In more advanced systems like OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Optical Diode, the device may include multi-scanning engines, protocol break support, and file sanitization for additional layers of protection.
Key design considerations:
- Dedicated hardware to prevent tampering
- Compatible with different network topologies
Implementation in Network Security
Deploying a data diode requires strategic placement within your network architecture—typically between zones with varying trust levels. Common deployment models include:
- Between ICS networks and enterprise zones
- From a SCADA system to a remote monitoring location
- As a secure data transfer mechanism from isolated environments
Challenges may include integration with legacy systems and protocol incompatibility, but modern solutions provide protocol adapters and transfer agents to streamline implementation.
Data Diodes in Industrial Control Systems
Industrial sectors such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation increasingly depend on ICS and SCADA systems. These systems often run on outdated software and lack modern security features, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
Enhancing ICS Security
Data diodes serve as a critical safeguard for ICS networks by:
- Blocking inbound malware or ransomware threats
- Preventing exfiltration of sensitive operational data
- Allowing safe export of monitoring data without exposing control systems
Case Study Example
A large oil and gas company deployed OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Optical Diode in its refinery to isolate control networks from corporate IT. The result: uninterrupted operations and compliance with TSA cybersecurity directives.
Learn more in our blog: 3 Ways to Strengthen High Security Networks with Multi-Scanning and Data Diodes
Compliance and Regulatory Standards for Data Diodes
As governments and industry regulators push for stronger cybersecurity standards, data diodes are becoming essential for achieving compliance.
Meeting ISO 27001 Standards
Data diodes help satisfy requirements in ISO 27001 and other standards by enforcing data confidentiality, integrity, and availability in high-risk environments. They’re also referenced in regulations and guidance from:
- NIST
- NERC CIP
- TSA SD 02C
- IEC 62443
By physically enforcing network segmentation, data diodes ensure organizations meet requirements for secure air-gapped or isolated networks.
Comparing Data Diodes with Other Security Solutions
While firewalls, data guards, and intrusion prevention systems all offer protection, only data diodes offer uncompromising assurance of one-way communication at the hardware level.
Data Diode vs. Firewall
| Feature | Data Diode | Firewall |
| Data Flow | One-way only | Bidirectional (rules-based) |
| Attack Surface | Minimal | Higher (software vulnerabilities) |
| Ideal Use Case | ICS, SCADA, air-gapped networks | General enterprise environments |
Unlike firewalls that rely on rules and require frequent patching, data diodes eliminate the potential for reverse communication by design. Firewalls share routable information between networks. Data diodes ensure complete network confidentiality, leveraging a protocol break, so no routable information is shared between networks.
Data Diode vs. Data Guard
Data guards are software-based solutions that inspect, filter, and transfer data between networks. While useful, they are vulnerable to:
- Software misconfigurations
- Exploits in underlying OS
- Insider threats
Data diodes, by contrast, provide tamper-proof physical enforcement of unidirectional data flow, making them ideal for critical infrastructure environments.
Does your data diode have the right set of features? Explore our in-depth buyer's guide and find out: Read The Guide
MetaDefender Optical Diode: A Comprehensive Data Diode Solution
OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Optical Diode is engineered to meet the highest standards of network isolation, data integrity, and regulatory compliance—offering a trusted defense against modern cyberthreats targeting critical infrastructure and operational technology environments.
With the recent acquisition of FEND, OPSWAT now provides data diodes for every use case, from compact deployments at remote facilities to large-scale industrial applications. Whether you’re securing a refinery, power plant, transportation hub, or defense system, there’s a MetaDefender Optical Diode purpose-built for your environment.
Our diode offerings include:
- EAL4+ certified solutions for high-assurance security implementations
- C1D2 certified variants designed for hazardous environments like oil and gas and manufacturing
- A powerful Transfer Guard option, combining the powerful, industry-leading threat prevention technologies of MetaDefender Core enable safe and sanitized file transfers even in air-gapped systems
By combining physical unidirectional data flow with advanced threat prevention, MetaDefender Optical Diode ensures that your critical networks can communicate safely—without ever being exposed. It’s more than a cybersecurity device—it’s peace of mind for high-stakes environments.
Are you ready to explore how data diodes can ensure your secure networks stay that way? Discover more about OPSWAT’s suite of data diodes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does a data diode work with TCP?
Data diodes do not support native TCP bidirectional communication. Instead, proxy systems or retransmission protocols are used to simulate responses, enabling one-way transfers of TCP-based data like syslog or file streams.
Q: How does a data diode work?
A data diode physically enforces one-way data transmission, ensuring information can travel out of a secure system but cannot re-enter it, thereby eliminating backchannel vulnerabilities.
Q: How fast is a data diode?
Speeds vary by model, but modern data diodes like OPSWAT’s support up to 10 Gbps, depending on the supported protocols and data types.
Q: What is the difference between a firewall and a data diode?
A firewall filters bidirectional traffic based on policies; a data diode allows only one-way data flow and physically blocks any return traffic, offering stronger isolation.
Q: Who needs a data diode?
Any organization managing critical infrastructure, classified networks, or air-gapped systems should consider data diodes to ensure unbreachable boundaries.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of data diodes and firewalls?
Data diodes offer strict isolation but lack bidirectional support. Firewalls provide flexibility but require careful configuration to avoid vulnerabilities.
Q: Why do you need a data diode?
Data diodes are essential for eliminating the risk of remote exploits and data breaches in high-security networks.
Q: What is the difference between data guard and data diode?
Data guards rely on software inspection and filtering; data diodes rely on hardware-level, physical one-way communication to secure network boundaries.



