- What Is Sandbox-Based Threat Intelligence Automation?
- What Is a Malware Analysis Sandbox?
- What Are Sandbox Environments?
- Sandboxing in Security Operations Centers (SOC)
- How Sandbox-Based Threat Intelligence Automation Works
- Implementation Approaches for Automated Threat Intelligence
- Benefits and Challenges of Sandbox-Driven Threat Intelligence
- Automated Malware Sandboxing vs. Parallel Concepts
- Key Features to Look for in Threat Intelligence Sandboxing Solutions
- Conclusion: From Isolation to Action
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Act I: Static vs. Dynamic Defense
Cybersecurity has evolved. Traditional, signature-based detection systems have served us well in identifying known threats. But as malware authors began employing advanced obfuscation techniques and rapidly morphing code, those systems became less effective. Static analysis alone cannot adequately detect new variants or zero-day threats. What was needed was a dynamic approach—an automated system that could analyze suspicious files and behaviors in real time.
This shift in approach parallels the transition from studying microbes in petri dishes to analyzing how infections spread in real populations. It’s one thing to see what malware looks like on paper; it’s another to observe its behavior in a live environment. OPSWAT’s sandbox-based threat intelligence automation provides that live environment, safely isolating threats and observing their behavior before they can reach your network.
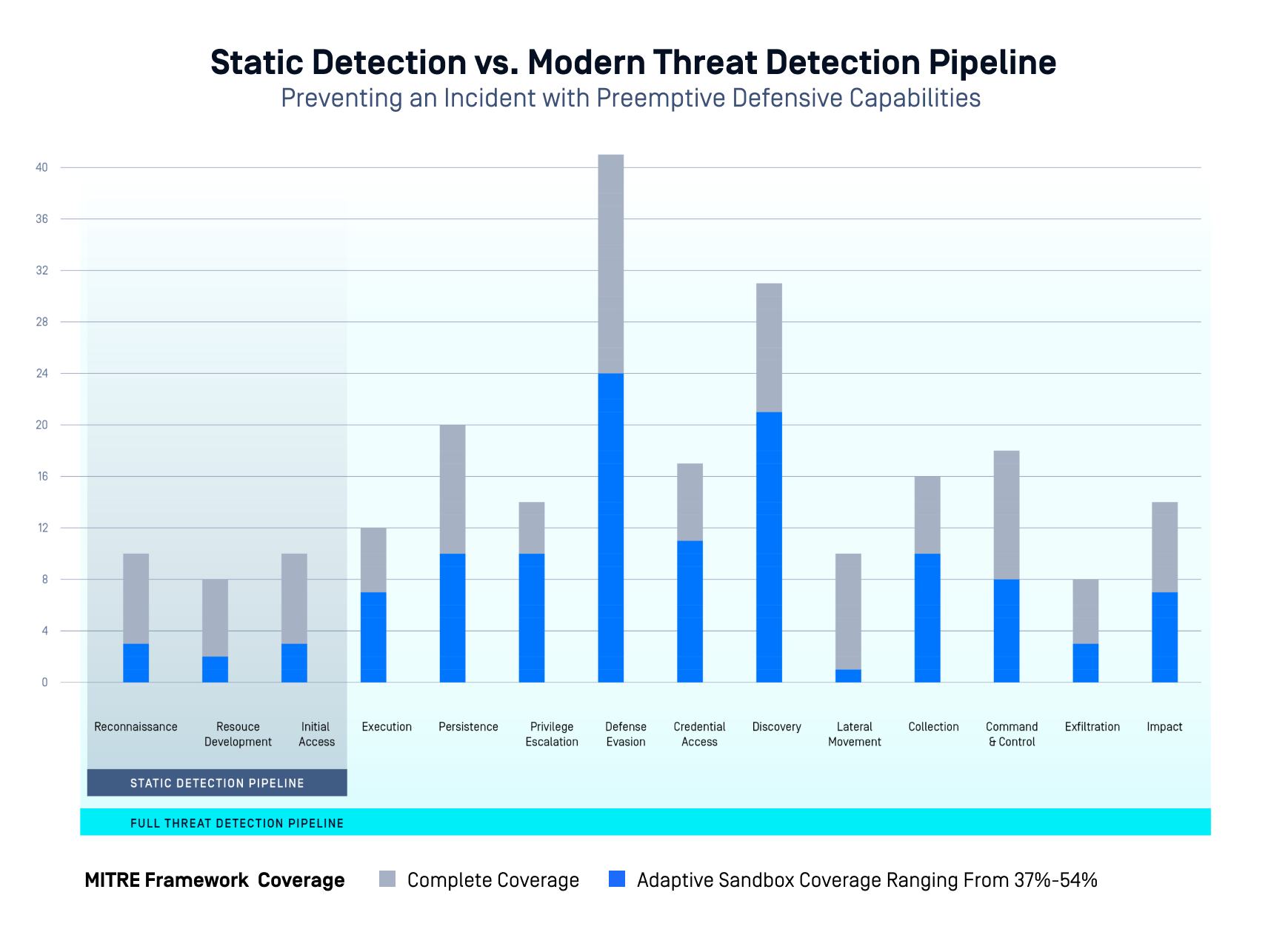
What Is Sandbox-Based Threat Intelligence Automation?
Sandbox-based threat intelligence automation uses automated malware sandboxes to analyze suspicious files or URLs in isolated environments. It combines sandboxing security automation with threat intelligence platforms to detect, analyze, and respond to threats in real time. This approach enables dynamic analysis, behavioral analysis, and indicator of compromise (IOC) extraction for advanced threat detection.
What Is a Malware Analysis Sandbox?
A malware analysis sandbox is a controlled, isolated virtual environment where suspicious files or URLs can be executed safely to observe their behavior. By allowing malware to run in this quarantined space, security systems can detect malicious activities that static analysis would miss, including runtime behavior, attempts at evasion, and command-and-control communications.
What Are Sandbox Environments?
Sandbox environments in cybersecurity serve as a simulation of real operating environments. These are crucial for dynamic analysis, as they allow the system to safely monitor and log actions performed by suspicious files or executables. Such environments are instrumental in threat intelligence operations, enabling analysts to observe malware behavior without risk to production systems.
Sandboxing in Security Operations Centers (SOC)
In Security Operations Centers (SOCs), sandboxing is critical to streamlining workflows. It reduces false positives, supports prioritization, and allows analysts to spend less time reviewing inconsequential alerts. By integrating sandbox-based automation, SOCs can automate the detonation and behavioral analysis of potentially malicious files and extract actionable intelligence in near real time.
Act II: The Evolution of Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is not static—it evolves with the threat landscape. Initially, security teams relied on simple threat feeds and reactive intelligence. But as threats became more adaptive and evasive, the need arose for threat intelligence platforms (TIPs) that could ingest, correlate, and enrich large volumes of data.
Sandbox-based detection plays a critical role in this evolution. It goes beyond threat feeds by providing real behavioral evidence and context. For example, OPSWAT's sandbox not only detonates files but also maps behaviors to ATT&CK techniques, enabling more accurate threat classification and adversary attribution.
How Sandbox-Based Threat Intelligence Automation Works
The process begins when a suspicious file or URL is submitted to the sandbox environment. The sandbox detonates the file in a secure, isolated environment, monitoring all system-level activity: file changes, process creations, network traffic, registry modifications, and more. This is known as dynamic analysis.
Once the malware has been executed, the system performs behavioral analysis to identify patterns consistent with known malicious actions. Indicators of compromise (IOCs) such as IP addresses, domains, and file hashes are automatically extracted. These are then enriched and correlated against existing threat intelligence feeds, providing real-time updates to security systems.
Dynamic Analysis and Malware Detonation
Dynamic analysis is the heart of sandbox-based automation. By executing files in real time, analysts and automated systems can see how a file behaves under different conditions. OPSWAT’s Adaptive Sandbox captures every nuance, from privilege escalation attempts to evasive behaviors triggered by certain environments.
Behavioral Analysis and IOC Extraction
Behavioral analysis observes the malware's actions:

Threat Intelligence Enrichment and Feeds
The extracted IOCs are not valuable on their own unless contextualized. OPSWAT integrates sandbox results into broader threat intelligence platforms (TIPs), where behaviors are mapped to known tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). This enables organizations to identify adversary campaigns and proactively defend against future threats.
Together, dynamic analysis, behavioral observation, IOC extraction, and enrichment form a cohesive loop that transforms raw execution data into actionable intelligence. Dynamic analysis provides the foundation by executing potentially malicious content in a secure, emulated environment—uncovering runtime behaviors that static techniques might miss.
Behavioral analysis then translates these actions into meaningful patterns: privilege escalation attempts, evasive techniques, lateral movement behavior, and more. Finally, the extracted indicators—IP addresses, file hashes, domains, registry keys—are enriched by correlating them with external feeds, adversary tactics (via MITRE ATT&CK), and internal telemetry.
Within OPSWAT’s integrated threat detection pipeline, the adaptive sandbox plays a pivotal role in stage two of a broader, multi-layered defense strategy. In the Threat Intelligence Pipeline, files are first processed through Reputation Services which checks the reputation of hashes, IPs, Domain, and URLs. When no definitive verdict is returned - or when high-risk heuristics are flagged—the file is passed to the sandbox for dynamic detonation and behavior logging.
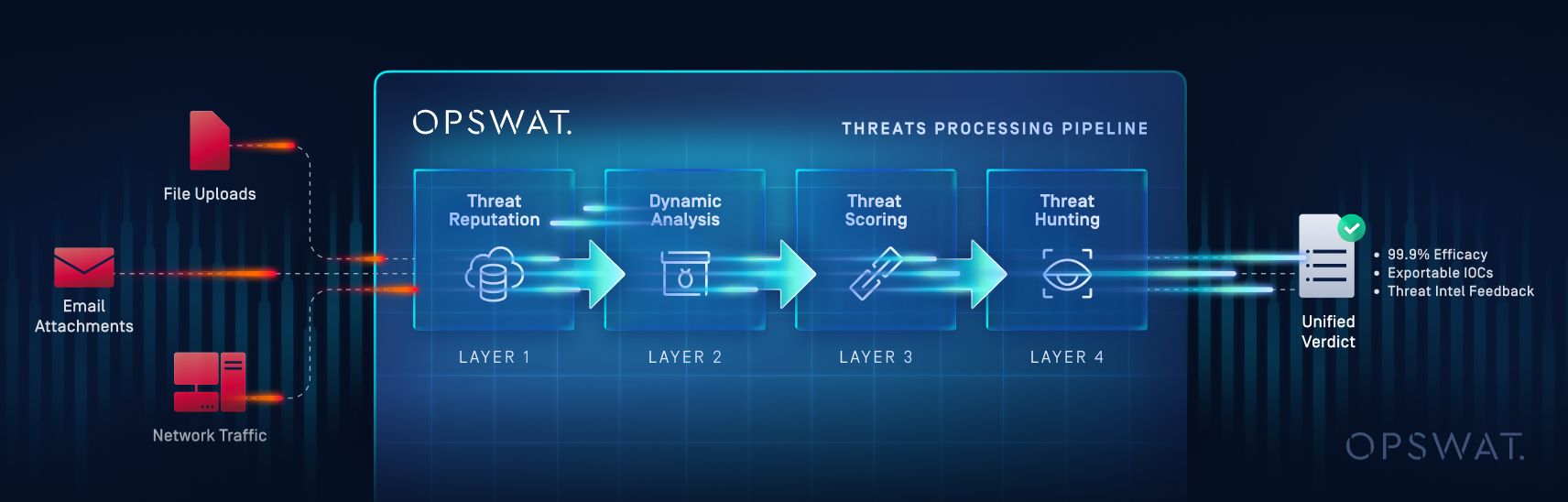
From there, results feed into OPSWAT’s threat scoring and machine learning correlation engine. This is where sandbox-extracted IOCs are compared to existing threat intelligence data, enabling not just detection but classification and attribution, identifying malware families, associated campaigns, and even likely threat actors. This integration allows for real-time, adaptive protection, helping security teams respond faster, prioritize alerts more effectively, and hunt down threats with richer context.
Act III: Automation Meets Expertise
Automation is not a replacement for human expertise; it is an augmentation. The challenge is scaling human decision-making in environments flooded with alerts. OPSWAT's sandbox helps bridge that gap. By automating early-stage threat detection and correlation, human analysts are freed to focus on deeper investigation and response.
AI-Powered Sandboxing
OPSWAT uses machine learning models to detect patterns and behaviors indicative of malware, even when traditional signatures fail. This is particularly effective for identifying zero-day threats that have not yet been cataloged. AI also supports mapping behaviors to threat actor profiles, adding context to technical indicators.
Implementation Approaches for Automated Threat Intelligence with Sandboxing
Organizations can deploy sandboxing in multiple ways: cloud-based, endpoint-integrated, or hybrid models. OPSWAT supports flexible deployment, enabling use cases across sectors with varying compliance needs.
Cloud-Based vs. Endpoint Sandboxing
Cloud-based sandboxes are scalable and easy to manage but may introduce latency. Endpoint sandboxes offer immediate response and local isolation but require greater resource allocation. The right approach depends on the organization’s infrastructure and threat model.
Sandbox-Based Automation and Threat Intelligence Platforms
OPSWAT’s sandbox integrates tightly with SIEM, SOAR, and EDR platforms. This allows automated feedback loops, where alerts trigger sandbox detonations, and results feed back into response workflows. This kind of sandboxing security automation ensures timely action against evolving threats.
Benefits and Challenges of Sandbox-Driven Threat Intelligence
Advantages of Threat Intelligence Tools
The benefits of sandbox-based threat intelligence automation are clear: real-time detection, reduced manual workload, and faster response times. By observing actual behavior, organizations can detect threats that evade traditional defenses. Moreover, threat visibility and classification improve dramatically.
Sandbox Evasion and Limitations
Advanced malware may employ sandbox evasion techniques, such as checking for virtual environments or delaying execution. While no system is perfect, OPSWAT mitigates these limitations with advanced emulation and anti-evasion tactics. Human oversight remains essential to validate results and provide context.
Automated Malware Sandboxing vs. Parallel Concepts
Automated Malware Analysis vs. Sandbox-Based Automation
Automated malware analysis often relies on static techniques - disassembling code and inspecting strings. While useful, it can miss runtime behaviors. Sandbox-based automation offers deeper insights by capturing actions in real time, especially when paired with behavioral detection and IOC extraction.
Sandbox-Based Automation and Threat Intelligence Platforms
Traditional threat intelligence platforms consume external threat feeds and correlate data from various sensors. When enhanced with sandbox automation, these platforms gain access to firsthand behavioral data, making correlations more accurate and context rich.
Key Features to Look for in Threat Intelligence Sandboxing Solutions
Integration and Automation Capabilities
Look for sandbox solutions that support API integration with SIEM, SOAR, and TIP systems. Automation should include file detonation, IOC extraction, and report generation. OPSWAT provides full REST API access, ATT&CK technique mapping, and actor attribution, making it a comprehensive threat intelligence automation platform.
From Isolation to Action
From detecting novel malware strains to enriching global threat intelligence, OPSWAT’s sandbox-based automation is a critical component in modern cybersecurity. It represents a shift from reactive to proactive defense, giving security teams the tools to respond faster and smarter.
To learn more about how OPSWAT’s MetaDefender Sandbox™ can strengthen your threat detection and response capabilities, visit our website.
FAQs
Q: What is sandboxing?
A: Sandboxing is a technique used to run suspicious files or code in an isolated environment to safely observe behavior without risking production systems.
Q: What is a malware analysis sandbox?
A: A malware analysis sandbox is a secure virtual space used to execute and analyze potentially malicious files to detect threats based on behavior.
Q: What is threat intelligence automation?
A: Threat intelligence automation is the process of collecting, analyzing, and applying threat data using automated tools and platforms to accelerate detection and response.
Q: What are sandbox environments?
A: Sandbox environments are simulated operating systems used to safely execute suspicious code for analysis and detection of malicious behavior.
Q: What is sandboxing in AI?
A: In AI-powered cybersecurity, sandboxing enables automated systems to observe malware behavior and detect anomalies, often with the aid of machine learning.
Q: What is sandboxing in SOC?
A: In a Security Operations Center (SOC), sandboxing helps streamline alert triage and investigation by automating the detonation and analysis of suspicious files.

