In January 2025 alone, a staggering 4,085 vulnerabilities were received by NIST, creating an exceptionally high-risk start to the year as the surge in actively exploited threats escalates. Notably among them, CVE-2025-21298 is a zero-click RCE (remote code execution) vulnerability in Microsoft Windows OLE with a CVSS score of 9.8. This security flaw allows attackers to compromise systems simply by tricking users into previewing a malicious RTF email in Outlook — no clicks required.
In this blog, we dissect the technical nuances of this vulnerability, explore how OPSWAT MetaDefender Core mitigates such zero-day threats, and provide actionable recommendations for enterprises.
Understanding the Vulnerability
Leveraging a Zero-Click Attack Technique
A zero-click attack exploits software vulnerabilities to launch an attack without any user interaction. This means malware can be installed or other malicious actions carried out on a user's device without the target ever clicking a link, opening a file, or taking any action—making it especially dangerous and difficult to detect.
CVE-2025-21298 Attack Flow
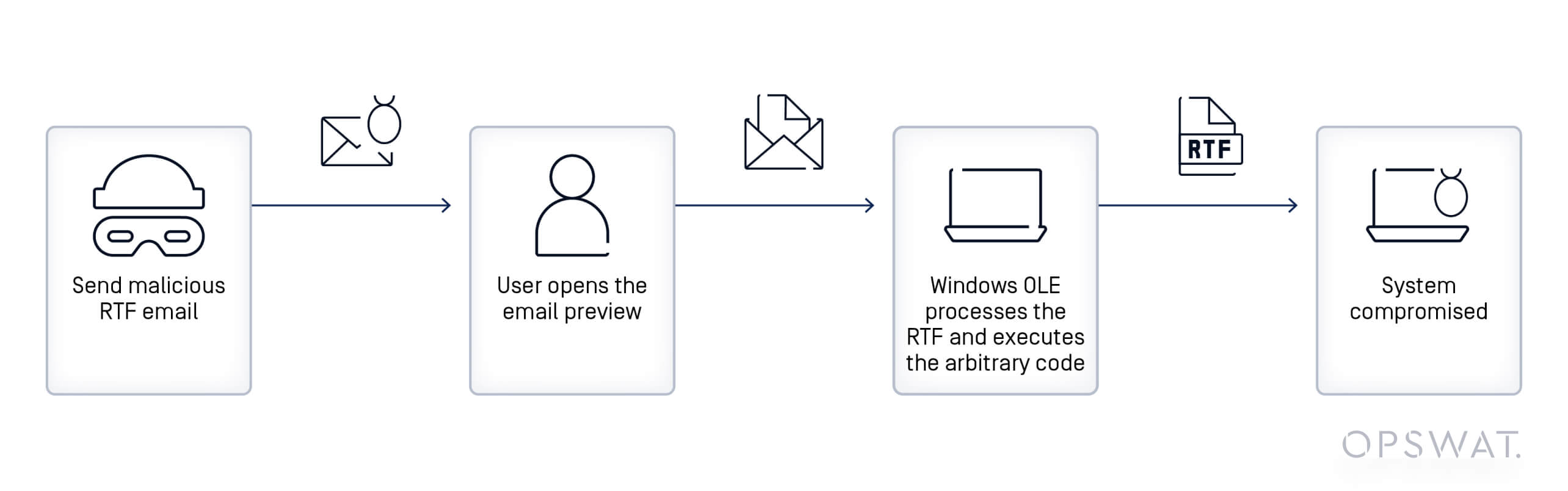
The vulnerability exists within the Windows OLE system, specifically in the ole32.dll library’s UtOlePresStmToContentsStm function. This function handles the conversion of data within OLE storage structures but contains a memory corruption issue that attackers can exploit to execute arbitrary code.
The attacker delivers a specially crafted RTF document containing malicious OLE objects via email. Upon reaching the victim’s system, the email client processes the attachment when the recipient opens or previews the message in Microsoft Outlook. The Windows OLE system engages with embedded objects, utilizing the vulnerable UtOlePresStmToContentsStm function for OLE processing.
During this phase, the function attempts to convert data within OLE storage structures, resulting in memory corruption. This memory corruption enables RCE, granting attackers the ability to execute arbitrary commands on the compromised system with the same privileges as the current user.
A proof-of-concept exploit for CVE-2025-21298 has already published on GitHub to reproduce this attack.
Preventing Zero-Day Vulnerability with OPSWAT MetaDefender Core
Zero-day vulnerabilities represent the most challenging threats in modern cybersecurity, as they emerge unexpectedly and can be exploited before vendors have time to release patches. These critical flaws often enable immediate system compromise, giving defenders minimal time to react. CVE-2025-21298 is a particularly dangerous zero-day vulnerability.
OPSWAT MetaDefender Core is positioned at the forefront of advanced threat detection and prevention, offering a multi-layered approach to security that is particularly effective against zero-day attacks like CVE-2025-21298. It leverages Metascan™ Multiscanning, Deep CDR™ and Adaptive Sandbox to detect and neutralize threats before they can reach critical systems.
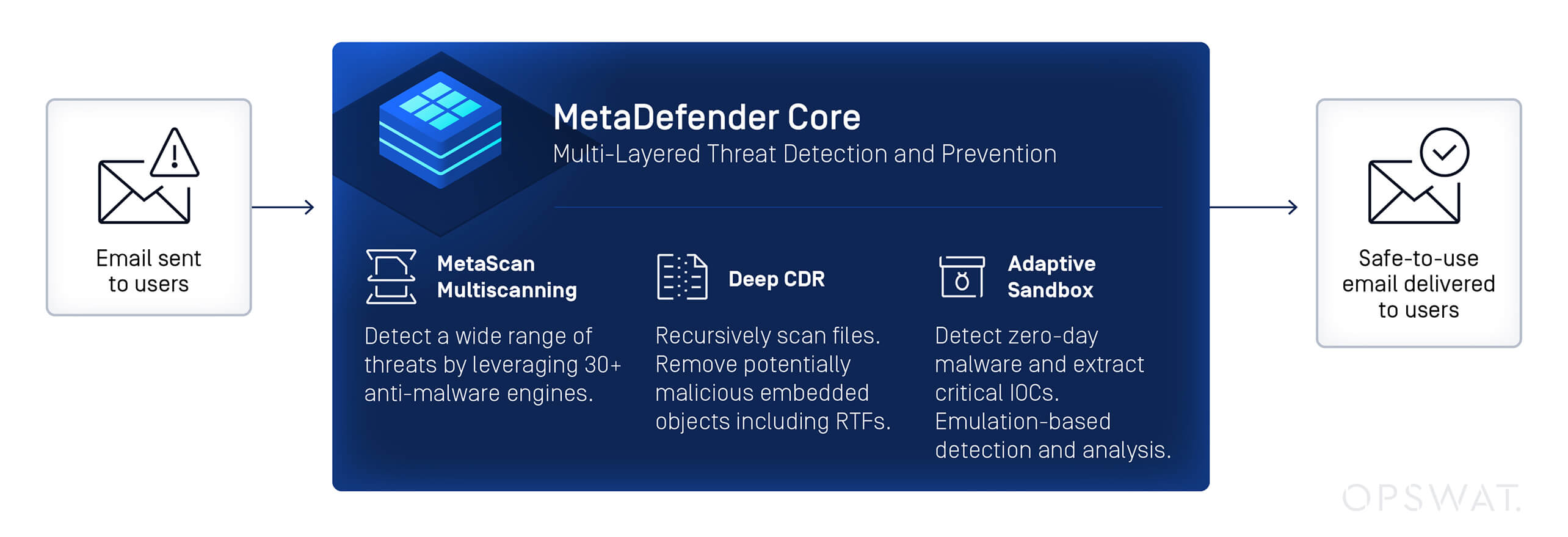
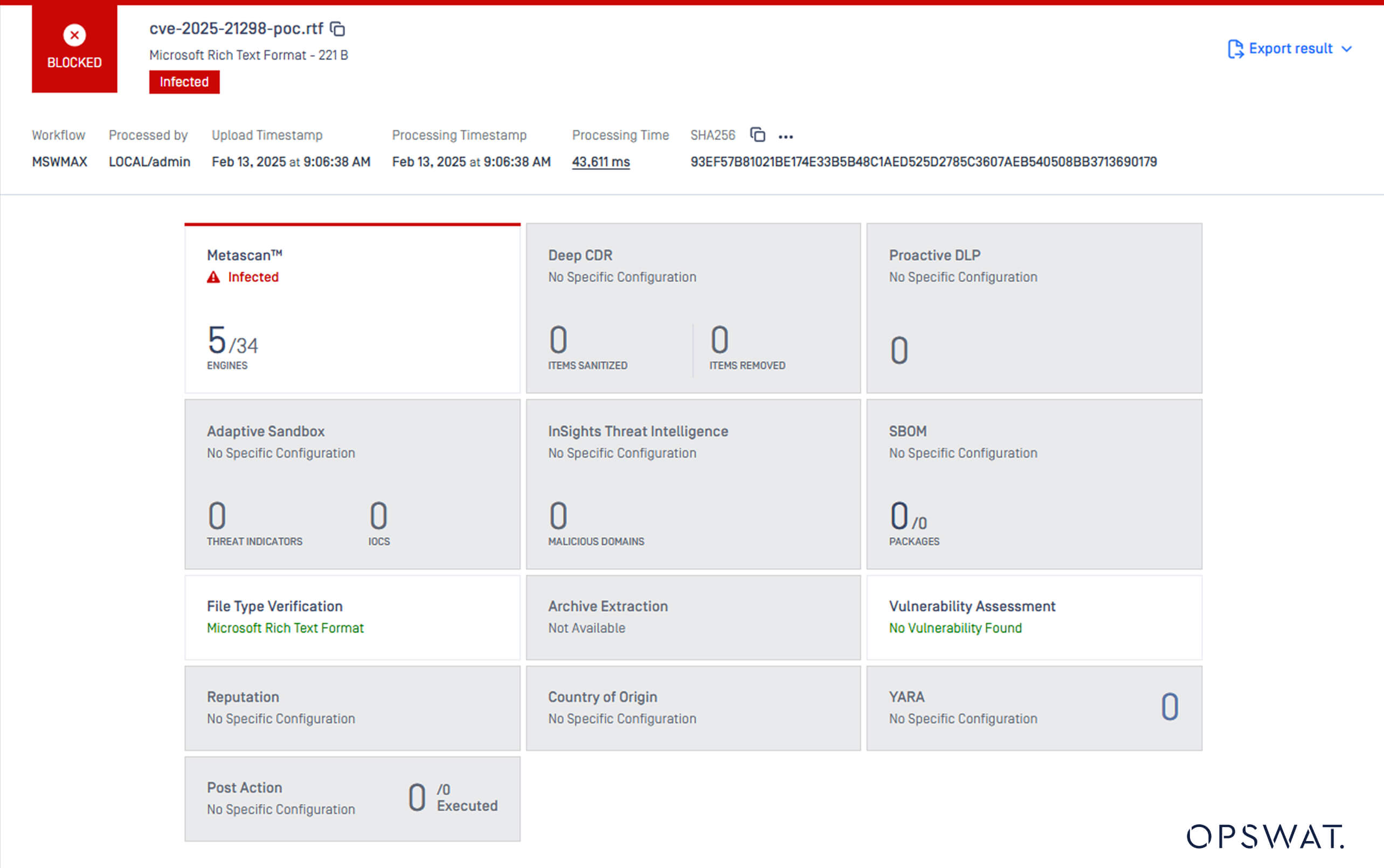
As the first line of defense, Metascan Multiscanning scans the email attachment that contains the malicious RTF file. Five out of 34 engines can detect CVE-2025-21298.
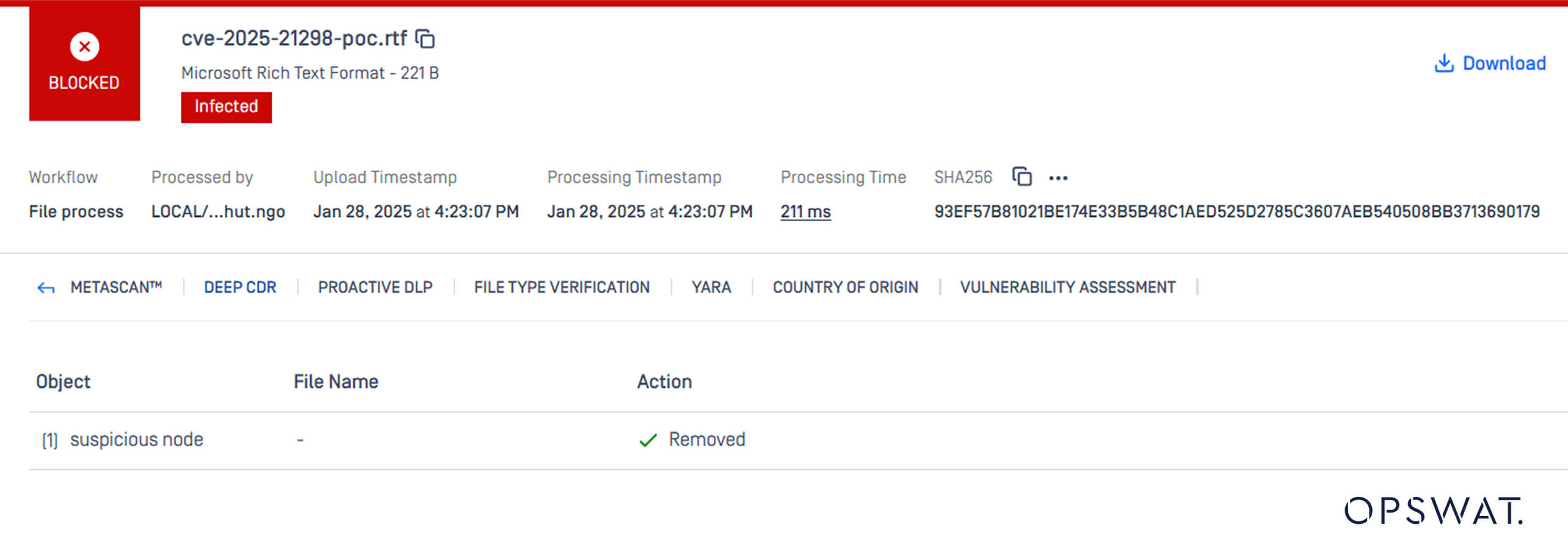
Next, Deep CDR proactively sanitizes files by removing potentially malicious elements while preserving the file's usability. To mitigate the risks associated with CVE-2025-21298, we first enable “Remove Embedded Object” for RTF under the Deep CDR configuration pane.
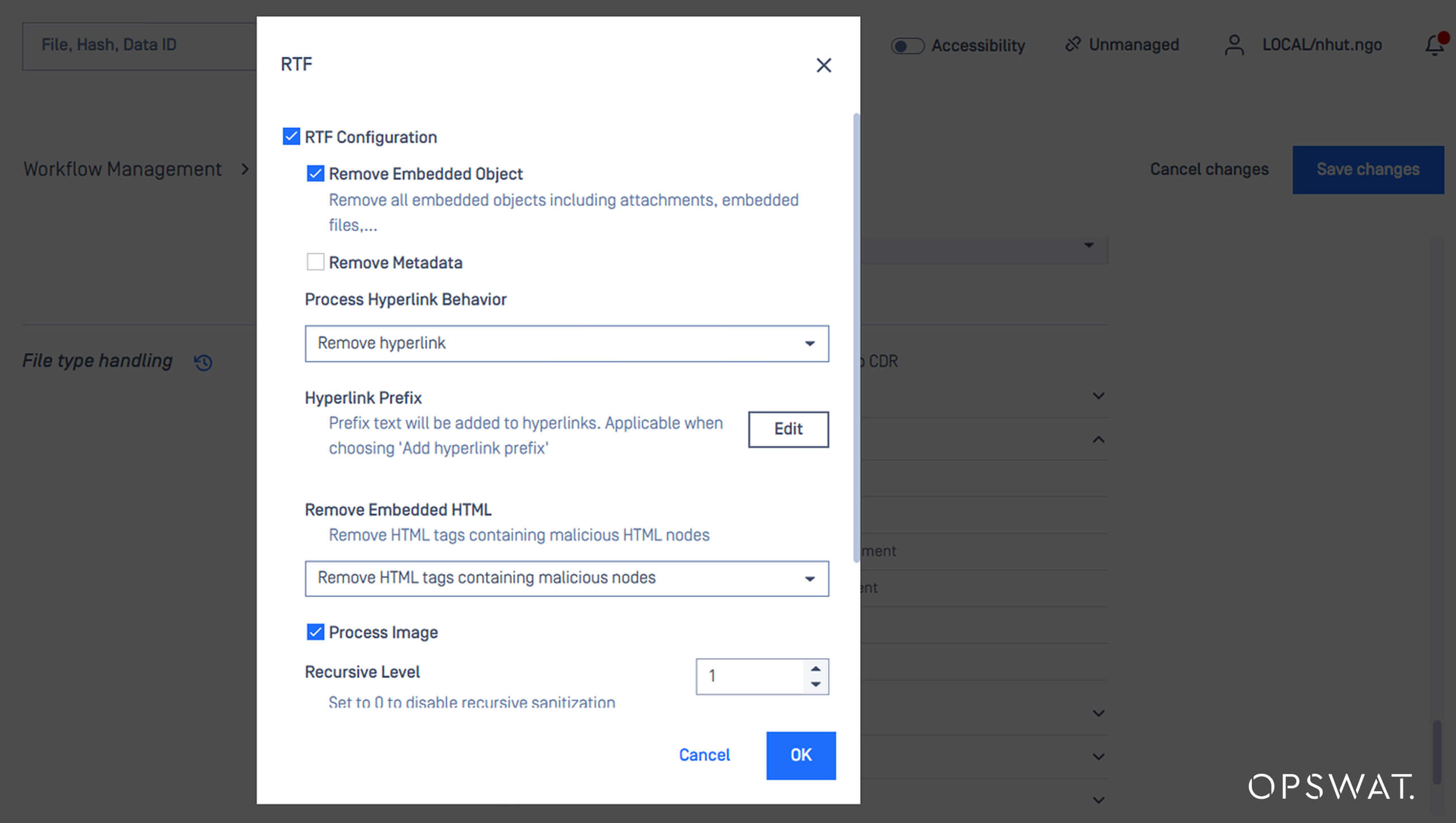
Once enabled, Deep CDR identifies this embedded object as a suspicious node and removes the RTF.
While Deep CDR focuses on malicious object removal and file sanitization, Adaptive Sandbox provides an additional layer of protection by using emulation-based detonation to analyze malicious behaviors and IOCs (indicators of compromise).
Implementation Recommendations
- Deploy Deep CDR at email gateways to sanitize all incoming files with embedded RTFs.
- Configure Adaptive Sandbox to safely detonate suspicious files before delivery.
- Implement comprehensive monitoring for potential exploitation attempts.
Why Business Trust OPSWAT for Advanced Threat Detection and Prevention
Organizations across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure, rely on OPSWAT MetaDefender Core for:
- Industry-Leading Zero-Day Protection: Advanced security measures like Deep CDR and Adaptive Sandbox provide unparalleled defense against emerging threats.
- Regulatory Compliance Support: OPSWAT solutions aid compliance with security standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST by ensuring strict file sanitization policies.
- Seamless Integration with Existing Security Infrastructure: MetaDefender Core integrates with SIEMs, firewalls, and endpoint protection platforms for comprehensive threat detection and prevention.
- Scalability for Enterprise Environments: Designed to handle high volumes of data, ensuring security without compromising performance.
Closing Thoughts
CVE-2025-21298 represents a serious threat to organizations, but with proactive security measures, businesses can prevent catastrophic breaches. OPSWAT MetaDefender Core, with its Deep CDR, Metascan Multiscanning, and Adaptive Sandbox capabilities, provides cutting-edge protection against zero-day exploits. By implementing multi-layered security strategies and leveraging OPSWAT’s advanced threat prevention technologies, organizations can effectively neutralize emerging cyberthreats and safeguard their critical assets.



