Data Diode and
Unidirectional Security Gateway Guide
Overview
Data diodes and unidirectional security gateways are cybersecurity solutions that strictly ensure one-way data transfer between two networks of different security classifications. While firewalls have long been the traditional solution to segment network traffic, they are prone to misconfigurations and exploits.
Data diodes and unidirectional security gateways have been common for decades in high-security environments, such as defense and intelligence agency facilities. Data diodes physically enforce one way data transfers by converting data to light via a hardware-enforced, one-way link, ensuring now return path exists. Modern unidirectional security gateways utilize integrated security software and protocol replication to enforce unidirectional data flows.
A Unidirectional Security Gateway builds security services and protocol handling on top of a unidirectional link, enabling more complex, reliable, and operationally usable data transfer, without breaking the one-way guarantee.
With the rise of industrial IoT and digitization, unidirectional security gateways are increasingly being deployed by private enterprises to securely transmit data generated by industrial control and safety systems. This includes nuclear power plants and other electrical power generating facilities, manufacturing facilities, and transport systems to other networks (including the public Internet) while the gateways protect the networks containing these systems from attack.
Unidirectional means data can travel in only one direction. A reasonable way to think of unidirectional security gateways is as “one-way valves for data”, allowing data to flow out, without a way back in. A common scenario is where unidirectional gateways provide one-way data transfers from a high-security network towards a network with a lower security level. Data can be transferred while the high-security network stays protected from attack using that connection. In this scenario, the technology is protecting the systems in the high-security network producing the data being transferred.
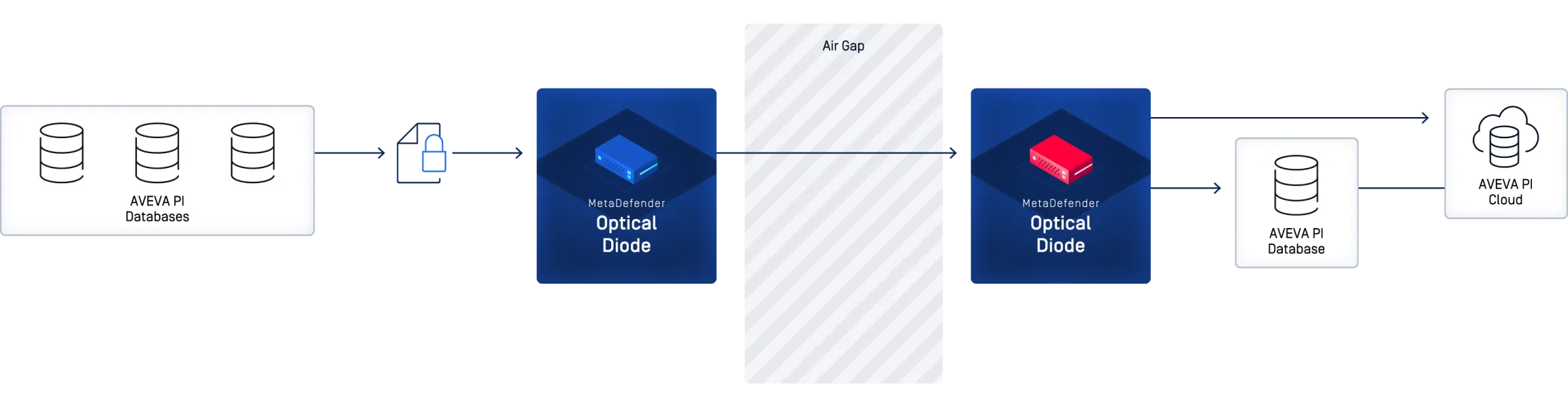
AVEVA PI Data Replication Between Three Power Generation Plants and Enterprise Historian
MetaDefender Optical Diode reliably replicates AVEVA Pi historian data using the MetaDefender AVEVA Pi Connector. Data is transferred over a non-routable protocol break enhancing security and confidentiality of the source network.
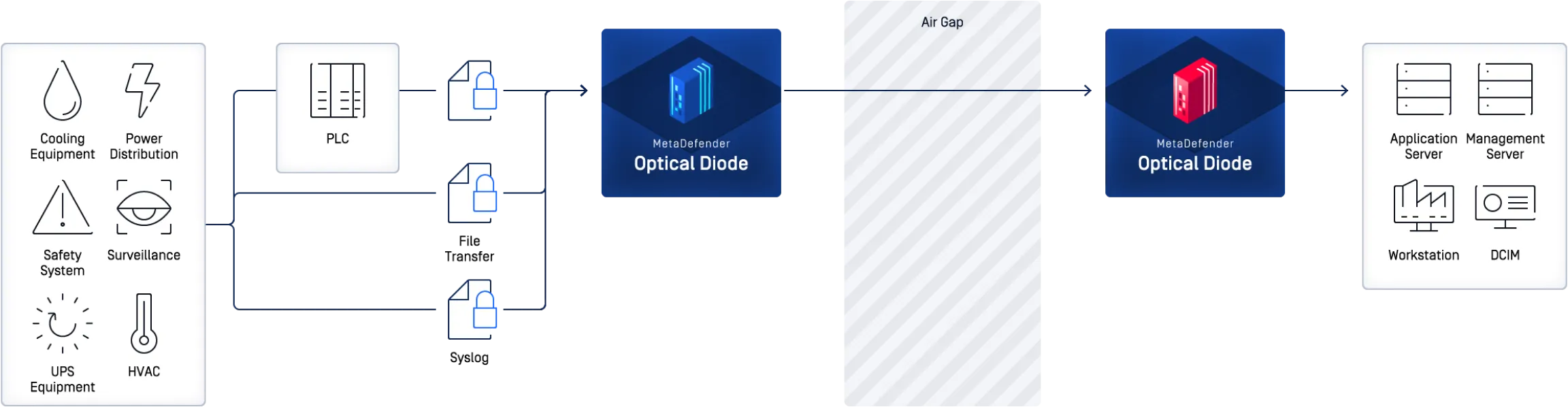
National Healthcare Provider Requires Secure Transfer of Data Center Alerts and Monitoring Data
MetaDefender Optical Diode securely transfers alerts and monitoring data to a central monitoring location. MetaDefender Modbus, SFTP and SMTP (email) connectors transfer data over an enforced one-way non-routable protocol break.
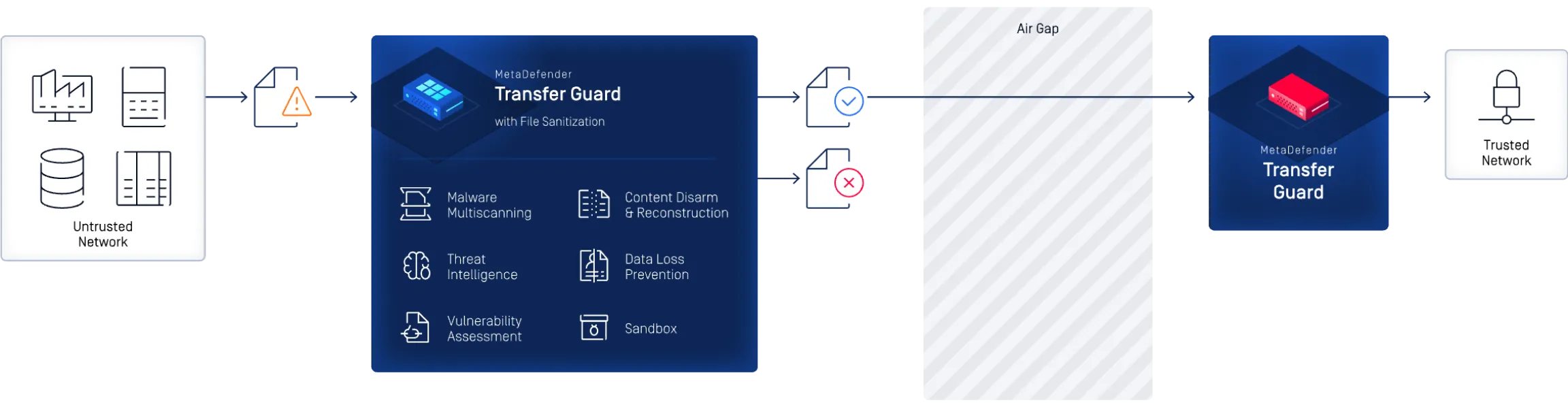
Secure Cross Domain File Transfer
MetaDefender Transfer Guard couples the air-gap level security provided by Optical Diode with OPSWAT’s award-winning MetaDefender Core file sanitization engine ensuring files are safe to transfer.
- Hardware-enforced network segmentation
- File transfer over non-routable protocol break
- Advanced threat prevention for files entering secure domain
See Comparison Table below or get the guide.








