- What You Need to Know About the Future of Secure File Transfer
- How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Threat Detection in Managed File Transfer
- What Quantum Computing Means for the Security of Enterprise File Transfers
- How Quantum-Safe Encryption and Quantum Key Distribution Are Shaping the Next Generation of File Transfer Security
- Why Zero Trust Is Essential for Secure File Transfer in the Age of AI and Quantum Threats
- How CISOs Can Future-Proof Managed File Transfer Against AI and Quantum Threats
- What Compliance and Regulatory Considerations Matter When Adopting Quantum-Safe and AI-Driven File Transfer Solutions
- FAQs
- Is Your Organization Prepared for the Future of Secure File Transfers?
What You Need to Know About the Future of Secure File Transfer
Secure file transfer is entering one of the most disruptive technological eras since the introduction of public key cryptography. As AI accelerates the speed and sophistication of cyberattacks, and quantum computing prepares to break widely used encryption systems, CISOs must rethink how they protect data in motion.
Until the mid-2010s, security professionals operated under the assumption that encrypted file transfers using RSA and AES were inherently secure against all known attack vectors. This assumption is no longer applicable in the age of quantum computing and AI-driven threats.
Attackers are weaponizing AI-driven malware, behavioral mimicry, and automated credential attacks. Meanwhile, nation-state actors are already harvesting encrypted data today with the intention of decrypting it once quantum computing reaches maturity, known as the “harvest now, decrypt later” threat.
This convergence of AI, quantum computing, and increasingly distributed architectures has made secure file transfer a strategic priority for CISOs. According to Gartner's 2024 CISO Survey, 68% of security leaders identified quantum-resistant file transfer as a top-three infrastructure priority for the next 24 months. Those who act now can future-proof their data exchange environments.
Why Traditional File Transfer Security Is No Longer Enough
Since the 1990s, secure file transfer has relied heavily on encryption algorithms including RSA (introduced in 1977) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography, standardized in the early 2000s), perimeter-based authentication, and static trust models.
Legacy encryption algorithms, once thought unbreakable, are now vulnerable to quantum algorithms such as Shor’s algorithm. Authentication methods that depend on static credentials can be bypassed through AI-driven credential stuffing or synthetic identity attacks. Perimeter-based models, designed for centralized networks, offer no meaningful protection in multi-cloud and remote environments.
As threat actors continue to evolve, CISOs can no longer rely on traditional MFT assumptions. They must transition to architectures that assume compromise, validate continuously, and remain resilient even when encryption standards shift.
How AI, Quantum, and Zero Trust Are Reshaping File Transfers
AI is transforming both attack and defense capabilities. AI enables real-time anomaly detection, content classification, and predictive threat scoring, significantly enhancing file-level inspection. Conversely, attackers use AI to disguise malware, generate polymorphic payloads, and mimic user behavior.
Quantum computing introduces a second and more consequential shift. Once quantum computers achieve approximately 4,000 stable logical qubits (a threshold researchers estimate could arrive within 10-15 years) they will be able to break 2048-bit RSA and 256-bit ECC encryption using Shor's algorithm. Post-quantum (quantum-safe) cryptography and QKD (quantum key distribution) represent the needed evolutionary step.
Zero Trust ties these elements together by enforcing continuous verification, least privilege access, and micro-segmentation across file transfer workflows. It is the architectural backbone required to withstand both AI-driven and quantum-enabled threats.
How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Threat Detection in Managed File Transfer
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing threat detection across MFT environments by enabling deeper visibility, faster response times, and far more accurate detection of sophisticated attacks. Where traditional tools rely on static signatures, AI analyzes behavior, content structure, and cross-environment patterns to identify anomalies.
For CISOs, AI provides tangible operational advantages:
- Real-time identification of abnormal file behavior
- Predictive threat scoring to assess file transfer risk before delivery
- Content classification that reduces exposure in regulated workflows
- Automated response actions that isolate, quarantine, or block malicious transfers
- Visibility across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, where perimeter monitoring fails
What Are the Latest AI Techniques for Detecting File Transfer Threats?
AI-driven threat detection within MFT environments now incorporates three core categories:
- ML (Machine Learning) – Detects deviations from known file transfer baselines, flagging anomalies such as unusual file sizes, transfer times, or destinations.
- Behavioral Analytics – Monitors user, system, and file behavior over time to detect insider threats, compromised accounts, and suspicious workflows.
- Deep Learning Models – Identify complex malware patterns buried within documents, media files, compressed archives, or encrypted payloads, including those designed to evade AV engines.
According to a 2024 study by the SANS Institute, AI-driven detection systems improved accuracy by 43% when analyzing unknown or polymorphic threats compared to signature-based detection methods, reducing false negatives from 28% to 16%.
How Can AI-Powered Security Tools Be Integrated with Managed File Transfer Platforms?
CISOs evaluating AI-enhanced file transfer solutions should ensure that AI integrates across every stage of the workflow:
- Pre-transfer scanning using ML-based threat scoring
- Real-time behavioral monitoring integrated with SIEM/SOAR
- Post-transfer validation to detect latent or evolving threats
- Policy automation that adapts based on risk signals
- Zero Trust identity signals to enhance access control decisions
Integration best practices include:
- Selecting MFT platforms with built-in AI or native integration options
- Ensuring APIs support automation, behavioral telemetry, and security event correlation
- Aligning AI tools with IAM, DLP, and SIEM ecosystems
How Does AI Help Secure File Transfers in Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments?
Cloud architectures complicate traditional monitoring, but AI offers a scalable solution. Modern AI-driven analytics:
- Detect anomalous file movements between cloud tenants
- Identify compromised API keys or service accounts
- Monitor lateral movement across cloud resources
- Enforce contextual access policies based on user behavior and device identity
- Enhance compliance logging by providing real-time insights across distributed systems
MetaDefender Managed File Transfer™ (MFT) supports secure and compliant file movement across complex, multi-cloud architectures by embedding intelligence and Zero Trust controls into file exchange workflows.
What Quantum Computing Means for the Security of Enterprise File Transfers
Quantum computing represents the single greatest cryptographic disruption in decades. While still emerging, quantum systems will eventually break the asymmetric cryptography that underpins secure file transfer today.
Even if practical quantum attacks are years away, threat actors are already capturing encrypted data for future decryption. The U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) and the UK's National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) have both issued public warnings about nation-state actors conducting 'harvest now, decrypt later' campaigns targeting encrypted communications and file transfers. Any sensitive data transferred today using vulnerable cryptography is at long-term risk.
Quantum threats make early preparation essential.
How Soon Will Quantum Computing Impact Enterprise File Transfer Security?
Although estimates vary, NIST, the Global Risk Institute, and leading quantum computing researchers from IBM and Google agree on several milestones:
- Today: Harvest-now attacks are underway, creating long-term confidentiality risks.
- Within 2–5 years: PQC standards will be widely adopted by governments and critical infrastructure sectors.
- Within 5–10 years: Quantum computers may reach the scale needed to break 2048-bit RSA encryption.
CISOs cannot rely on distant timelines; migration planning needs to begin now.

What Are the Core Vulnerabilities of Traditional File Transfer Encryption Against Quantum Attacks?
Quantum algorithms directly threaten:
- RSA encryption (factorization vulnerability)
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) (discrete logarithm vulnerability)
- Diffie–Hellman key exchange
- TLS protocols that leverage RSA/ECC-based key negotiation
Encrypted files transferred today using these algorithms could be decrypted retroactively, potentially exposing regulated, classified, or proprietary information.
How Can Organizations Assess Their Exposure to Quantum-Driven Threats?
A practical CISO-led assessment includes:
- Keeping inventory of all file transfer workflows that rely on RSA/ECC
- Identifying long-lifespan data, such as healthcare, financial, or government records
- Assessing partner ecosystems for quantum readiness
- Evaluating encryption dependencies within MFT tools, API integrations, and TLS endpoints
- Modeling “harvest now, decrypt later” risk for sensitive workloads
How Quantum-Safe Encryption and Quantum Key Distribution Are Shaping the Next Generation of File Transfer Security
Quantum-safe encryption and QKD represent the foundational technologies for future-proofing secure file transfer. They ensure long-term confidentiality even in the presence of adversaries possessing quantum capabilities.
What Are the Leading Post-Quantum Cryptography Standards for Managed File Transfer?
NIST (the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology) and ETSI (the European Telecommunications Standards Institute) are driving global PQC standardization.
Leading algorithms include:
- CRYSTALS-Kyber (key establishment)
- CRYSTALS-Dilithium (digital signatures)
- SPHINCS+ (hash-based signatures)
- Falcon (lattice-based signatures)
These algorithms are designed to resist quantum attacks while maintaining performance suitable for enterprise file transfer workloads.
How Does Quantum Key Distribution Compare to Post-Quantum Cryptography for Securing File Transfers?
QKD (Quantum Key Distribution):
- Uses quantum physics to secure key exchanges
- Detects eavesdropping in real time
- Requires specialized hardware and fiber-optic infrastructure
PQC (Post-Quantum Cryptography):
- Runs on existing hardware
- Is easier to deploy at scale
- Will become the dominant standard for enterprise MFT due to practicality
For global organizations, PQC adoption will likely precede QKD, though both may coexist in high-security environments.
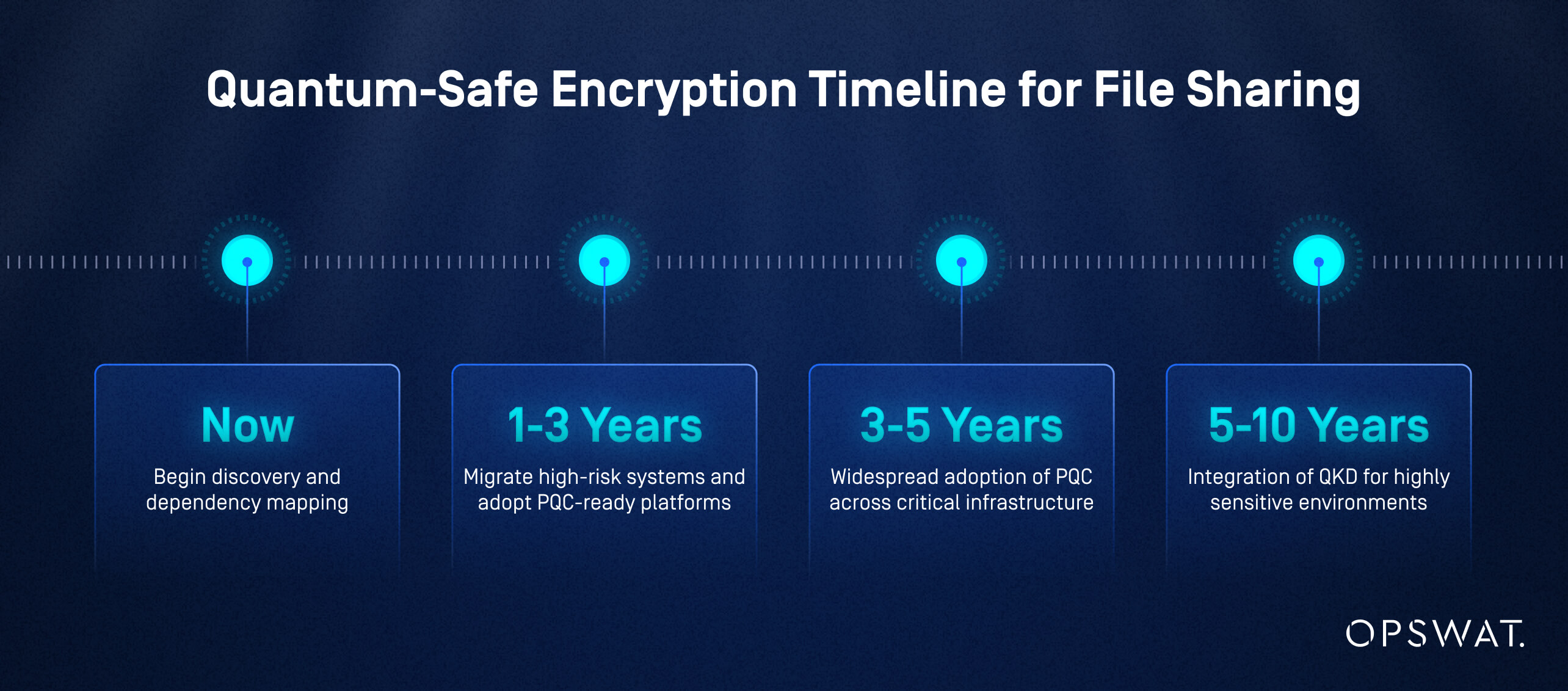
What Is the Timeline for Adopting Quantum-Safe Encryption in Enterprise File Sharing?
Based on NIST's post-quantum cryptography roadmap and industry adoption patterns observed in previous cryptographic transitions, a strategic timeline includes:
- Now: Begin discovery and dependency mapping
- 1–3 years: Migrate high-risk systems and adopt PQC-ready platforms
- 3–5 years: Widespread adoption of PQC across critical infrastructure
- 5–10 years: Integration of QKD for highly sensitive environments
Why Zero Trust Is Essential for Secure File Transfer in the Age of AI and Quantum Threats
Zero Trust is the only security architecture flexible and robust enough to withstand AI-driven threats, quantum-enabled decryption, and increasingly distributed networks.
By eliminating implicit trust and verifying every access request, Zero Trust ensures that even if encryption is broken or credentials are compromised, attackers cannot move freely or exfiltrate sensitive data.
How Is Zero Trust Evolving to Address Quantum and AI-Driven Threats in File Transfer?
Zero Trust models now incorporate:
- Continuous risk scoring informed by AI
- Identity and device trust evaluations in real time
- Encryption agility to support post-quantum protocols
- Micro-segmentation across hybrid and multi-cloud file transfer environments
- File-level inspection to validate integrity and detect concealed threats
These enhancements ensure resilience even in scenarios where AI-driven malware bypasses traditional controls or quantum threats undermine existing cryptography.
What Are the Practical Steps for Implementing Zero Trust in Managed File Transfer Environments?
CISOs can adopt Zero Trust for MFT using a phased approach:
- Map all file transfer assets (users, systems, workflows, partners).
- Enforce least-privilege access and conditional policies.
- Implement continuous verification using identity, device, and file-level signals.
- Segment file transfer environments to limit lateral movement.
- Integrate advanced threat prevention, including AI-driven inspection and CDR.
- Automate policy enforcement and monitor behavior continuously.
Success requires executive sponsorship, tight IAM integration, and a modern MFT platform designed for Zero Trust.
How Does Zero Trust Improve Compliance and Resilience in File Transfer Operations?
Zero Trust dramatically strengthens compliance by ensuring:
- Clear, immutable audit trails
- Enforced data governance controls
- Documented access restrictions
- Adaptive risk-based authentication
- Strong alignment with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX
With continuous verification and deep visibility, organizations become more resilient against breaches, misconfigurations, insider threats, and audit challenges.
How CISOs Can Future-Proof Managed File Transfer Against AI and Quantum Threats
CISOs must combine strategic planning with technology modernization to ensure their file transfer environments remain secure as threats evolve. Future proofing requires investment in AI-driven insights, post-quantum cryptography, and Zero Trust architecture.
What Are the Actionable Steps for Migrating to Quantum Resistant File Transfer Architectures?
A future-proof migration strategy includes:
- Assessment – Evaluate encryption dependencies, long-term data sensitivity, and quantum exposure.
- Prioritization – Identify high-risk or long-retention file workflows.
- PQC Readiness – Select MFT platforms that support agile cryptography.
- Piloting – Test PQC implementations in low-risk environments.
- Full deployment – Transition workflows and partners to quantum-safe protocols.
- Ongoing validation – Monitor standards updates and maintain crypto-agility.
How Can AI Be Leveraged to Detect and Mitigate Quantum-Based Threats in File Transfer?
AI enhances quantum-era security by:
- Monitoring for anomalies tied to quantum-enabled attacks
- Predicting which assets face long-term cryptographic risk
- Validating file integrity post-transfer
- Detecting unusual access patterns indicative of harvest-now campaigns
- Automating quarantine and isolation workflows
OPSWAT’s AI-based threat detection tools strengthen this model by integrating threat intelligence directly into file exchange workflows.
What Are the Best Practices for Preparing Managed File Transfer Environments for Quantum and AI-Driven Cyber Threats?
CISOs should adopt the following best practices:
- Implement crypto agility to switch algorithms rapidly
- Enforce Zero Trust principles across all file transfer workflows
- Deploy AI-driven anomaly detection and risk scoring
- Reduce reliance on vulnerable legacy protocols
- Validate partner ecosystems for PQC readiness
- Document quantum and AI-risk governance for compliance reporting
- Incorporate file-level threat prevention such as CDR and anti-malware scanning with multiple engines
What Compliance and Regulatory Considerations Matter When Adopting Quantum-Safe and AI-Driven File Transfer Solutions
Regulations are evolving quickly to account for quantum threats, AI risk, and advanced data protection requirements. CISOs must ensure that their file transfer modernization efforts align with these shifting expectations.
What Are the Key Compliance Standards for Quantum-Safe File Transfer?
Key standards and guidance come from:
- NIST PQC guidelines (Kyber, Dilithium, SPHINCS+)
- ETSI standards for QKD and PQC
- Regional mandates for crypto-agility and algorithm updates
- U.S. Executive Orders and federal guidelines on quantum readiness
These standards emphasize algorithm transitions, key management updates, audit documentation, and long-term confidentiality guarantees.
How Should Organizations Document and Report Quantum-Safe and AI-Driven File Transfer Security?
Best practices include:
- Maintaining cryptographic inventories
- Documenting algorithm transitions and key lifecycle governance
- Recording AI-driven detection events and response actions
- Capturing access control decisions within Zero Trust workflows
- Generating compliance reports aligned to GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and SOX
OPSWAT’s compliance-ready logging and reporting greatly reduce the burden on security teams.
What Are the Implications of Quantum and AI Technologies for Data Privacy and Cross-Border Transfers?
Quantum and AI create new privacy considerations:
- PQC ensures long-term confidentiality for sensitive exports
- AI inspection introduces jurisdictional concerns over data processing
- Data sovereignty laws (GDPR, CCPA, APAC regulations) demand cryptographic transparency
- Cross-border transfers require assurance that quantum-safe protections persist after data leaves the originating environment
CISOs must ensure that file transfer systems can prove encryption durability and apply AI responsibly within regulatory bounds.
FAQs
What are the leading post-quantum cryptography standards for MFT?
NIST-approved algorithms such as Kyber and Dilithium form the foundation of future PQC adoption.
How can AI-powered tools integrate with MFT platforms?
Through behavioral analytics, anomaly detection, and automated threat scoring with SIEM/IAM integration.
What is the roadmap for PQC adoption in enterprise MFT?
Begin assessment now, pilot PQC in 1–3 years, achieve full adoption in 3–5 years.
What is the risk of harvest-now, decrypt-later attacks?
Attackers can capture encrypted files today and decrypt them once quantum computers mature.
How does QKD compare to PQC?
QKD offers unparalleled security but requires specialized hardware; PQC is more practical for large-scale adoption.
How should enterprises prepare for AI and quantum threats?
Implement Zero Trust, adopt crypto-agility, deploy AI-based detection, and modernize legacy protocols.

