Operational Technology (OT) encompasses hardware and software systems designed to monitor, control, and manage physical processes, devices, and infrastructure across critical sectors including manufacturing, energy production, transportation networks, and public utilities. Unlike Information Technology (IT), which focuses on data processing and communication, Operational Technology (OT) manages real-world physical processes. This makes OT security essential for ensuring safety, continuity, and integrity of critical infrastructure.
In recent years, OT environments have increasingly become targets of sophisticated cyber threats. These threats commonly include ransomware, unauthorized access attempts, deliberate sabotage of critical infrastructure, and the exploitation of vulnerabilities within industrial control systems (ICS). Notable recent incidents underscore the critical nature of these threats, exemplified by the 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, which caused substantial disruptions to fuel supplies along the U.S. East Coast, and the 2022 cyberattack on Viasat's satellite networks, severely affecting communication infrastructures across Europe during intensified geopolitical conflicts. As OT systems become increasingly interconnected and integrated with IT infrastructures, they encounter unique cybersecurity threats that can lead to severe operational disruptions and substantial economic consequences.
Vulnerability Discovery in Schneider Modicon M241 PLC by OPSWAT Unit 515
Schneider Electric is a global leader in industrial automation and energy management, providing innovative solutions across diverse industries. The Modicon PLC series, specifically the Modicon M241, has become notably popular due to its capability to manage complex automation processes efficiently. Equipped with intuitive programming tools and seamless integration capabilities through Schneider's EcoStruxure platform, the Modicon M241 PLC is widely implemented in industries requiring precise and reliable automation controls.
Considering the widespread adoption and critical role of the Schneider Modicon M241 PLC in industrial operations, our Unit 515, including Loc Nguyen, Dat Phung, Thai Do, and Minh Pham, undertook a comprehensive vulnerability assessment of this device at the OPSWAT Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Lab. Our analysis uncovered a significant security vulnerability, which, if exploited, could compromise system integrity and exposure of sensitive data. Our team has proactively contacted Schneider Electric, reporting the issue to assist them in the identification and remediation planning process, with the goal of strengthening the overall security posture of OT environments.
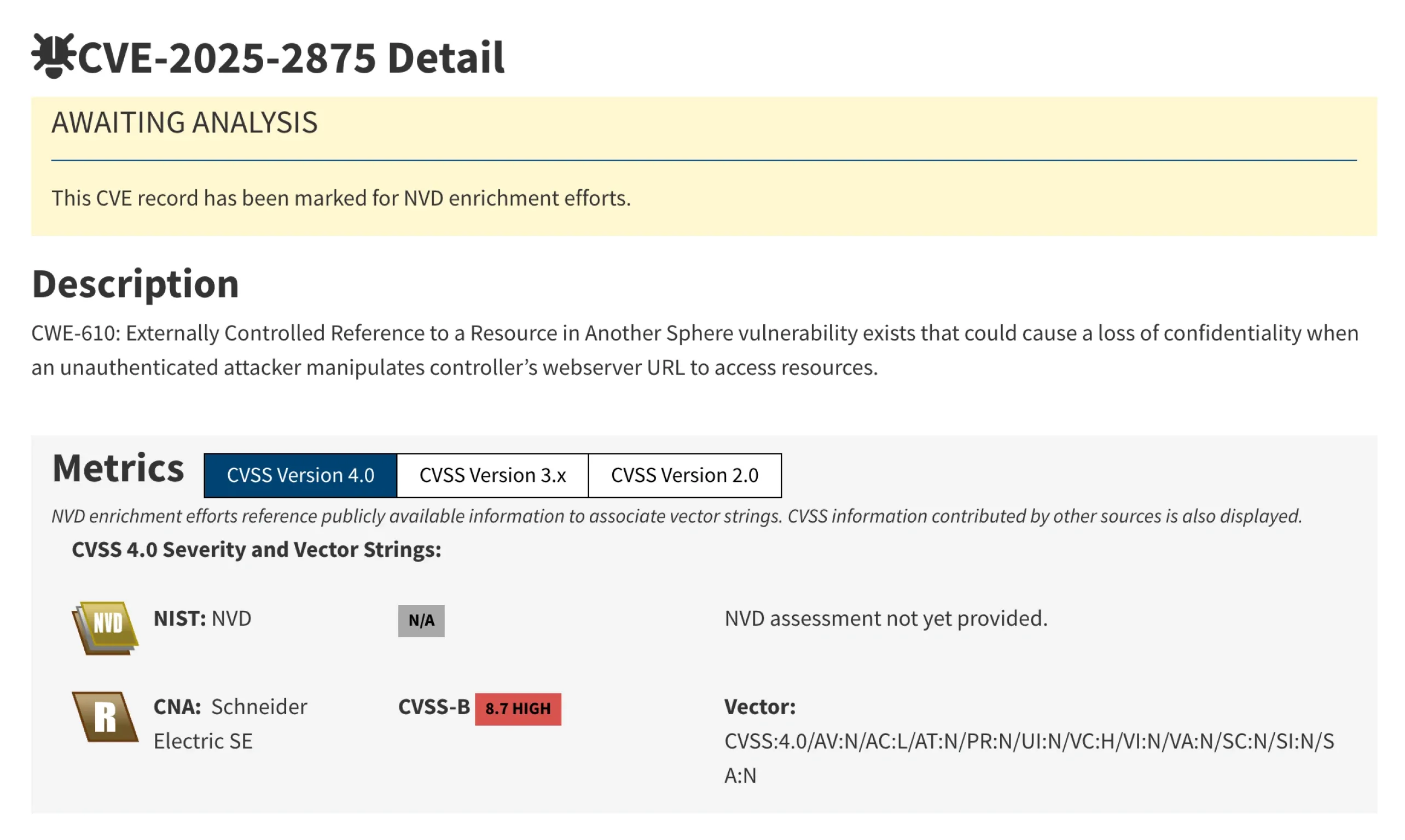
In response to our report, Schneider Electric has issued a security advisory acknowledging this vulnerability in the Modicon M241 PLC, specifically CVE-2025-2875. These advisories are intended to inform stakeholders of potential security risks and to provide clear guidance on how to implement appropriate remediation measures.
In this blog, we provide a high-level summary of CVE-2025-2875, a security vulnerability identified in Schneider Electric’s Modicon M241 device. Without disclosing detailed technical information that could facilitate misuse, we highlight the nature of this vulnerability, assess its potential implications for operational technology (OT) environments, and offer practical recommendations to mitigate associated risks. This overview aims to support security professionals and asset owners in safeguarding critical infrastructure.
Modicon M241 & the Embedded Web Server
The Modicon M241, developed by Schneider Electric, is a high-performance micro programmable logic controller (PLC) engineered for demanding machine automation tasks. It is particularly well-suited for modular and complex machine architecture, offering a powerful processing core, flexible communication interfaces, and scalable configuration options to meet a wide range of industrial requirements.
One notable capability of the Modicon M241 is its embedded web server, which offers a ready-to-use interface that can be accessed directly through any standard web browser. This feature allows users to monitor, configure, and interact with the controller remotely, without the need for additional software or complex setup.

While the embedded web server greatly enhances usability, particularly in remote operations, it also introduces potential cybersecurity risks if not properly secured. Improper input validation or lack of authentication controls could expose the system to unauthorized access or manipulation.
Recognizing these potential security concerns, our Unit 515 conducted a thorough security assessment of the Modicon M241's embedded web server. The objective was to determine whether any exploitable vulnerabilities exist within this component that could compromise the integrity, availability, or confidentiality of the system.
CVE-2025-2875: Externally Controlled Reference to a Resource in Another Sphere
In alignment with this objective, the Unit 515 performed an in-depth analysis of the Modicon M241 embedded web server. This analysis revealed specific scenarios wherein the embedded web server would accept intentionally crafted file access requests, thereby bypassing intended security restrictions. Additionally, an extensive examination of the device allowed the identification of internal file paths within the PLC. Exploiting this vulnerability could potentially allow an unauthenticated attacker to access sensitive internal files on the device, significantly impacting system confidentiality.
The vulnerability was disclosed to Schneider Electric through a responsible disclosure process, and appropriate mitigations and remediations have since been made available. To safeguard Schneider’s customers and prevent potential misuse, OPSWAT has intentionally withheld detailed technical information related to this vulnerability.
CVE-2025-2875 Timeline
Consistent with responsible disclosure practices and OPSWAT’s commitment to safeguarding critical infrastructure, the Unit 515 promptly reported the vulnerability to Schneider Electric through their official security contact channel to assist with the investigation and remediation planning:
- February 20, 2025: The Unit 515 submitted a vulnerability report to Schneider Electric detailing the vulnerability in the Modicon M241 device.
- February 21, 2025: Schneider Electric acknowledged receipt of the report and initiated an internal investigation. A case tracking ID was assigned for follow-up coordination.
- March 20, 2025: Following a detailed analysis, Schneider Electric confirmed the validity of the vulnerability and began developing a remediation plan.
- May 13, 2025: Schneider Electric published a public advisory along with remediation guidance for the identified issue. A CVE identifier, CVE-2025-2875, was assigned to this vulnerability.
Remediation
We strongly recommend that organizations utilizing Schneider Electric Modicon M241 PLC devices follow the official guidance provided by Schneider Electric to remediate this vulnerability, available here: Schneider Security Advisory Document.
To effectively mitigate vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-2875, organizations should adopt a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy, which includes:
- Vulnerability detection via continuous CVE scanning: Regularly scanning networks for vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-2875
- Monitoring for anomalous behaviors: Flagging unusual increases in frequency in communication to the Schneider Modion M241 PLC, which could suggest an ongoing unauthorized data exfiltration attempt
- Identifying unauthorized device connections: the system should detect when a rogue/ unauthorized device connects to the PLC
- Network segmentation: Isolating affected devices can help prevent the lateral spread of attacks, thus minimizing impact.
- Intrusion Prevention: immediately identifying and blocking malicious/ unapproved commands to the PLC, then effectively protect normal operations of the PLC
OPSWAT’s MetaDefender OT Security addresses these needs by detecting CVEs, continuously monitoring the network for unusual behaviors and identifying unauthorized connections. Using AI, it learns normal traffic patterns, establishes baseline behavior, and implements policies to alert anomalies. This allows instant, informed responses to potential threats.
In the case of an attack exploiting CVE-2025-2875, MetaDefender OT Security integrates with the MetaDefender Industrial Firewall to detect, alert and block suspicious communications based on set rules. MetaDefender Industrial Firewall uses AI to learn regular traffic patterns and enforce policies to prevent unauthorized connections.
The following video illustrates how OPSWAT’s MetaDefender OT Security and MetaDefender Industrial Firewall proactively mitigates this vulnerability and prevents unauthorized access within OT environment:
Beyond prevention, OPSWAT’s MetaDefender OT Security also empowers organizations to monitor signs of exploitation in real time through continuous asset visibility and vulnerability assessment. By leveraging advanced asset inventory tracking and vulnerability assessment capabilities, our platform provides proactive threat detection and facilitates rapid, effective remediation actions.
The following video demonstrates how MetaDefender OT Security efficiently identifies vulnerable devices and rapidly provides remediation for identified vulnerabilities:

