Get the Most Out of MetaDefender Core
Performance Optimization and Fine-Tuning Guide
Customize Your MetaDefender Core Experience
Stronger Core
Resilience
Shorter Processing
and Scanning Times
Increased
Throughput
More Efficient
CPU Usage
On-Demand
Scalability
Real-World Resultsfor Cross Domain Security
A typical use-case for cross domain solutions is scanning OS patches—usually in the form of archive files (e.g. CAB, MSU, DE, etc.). In this example, see how MetaDefender Core version 5.10.0 with 20 antivirus engines ran in an optimized environment.
Throughput
150
*Scanning Windows patches totaling over 14M objects
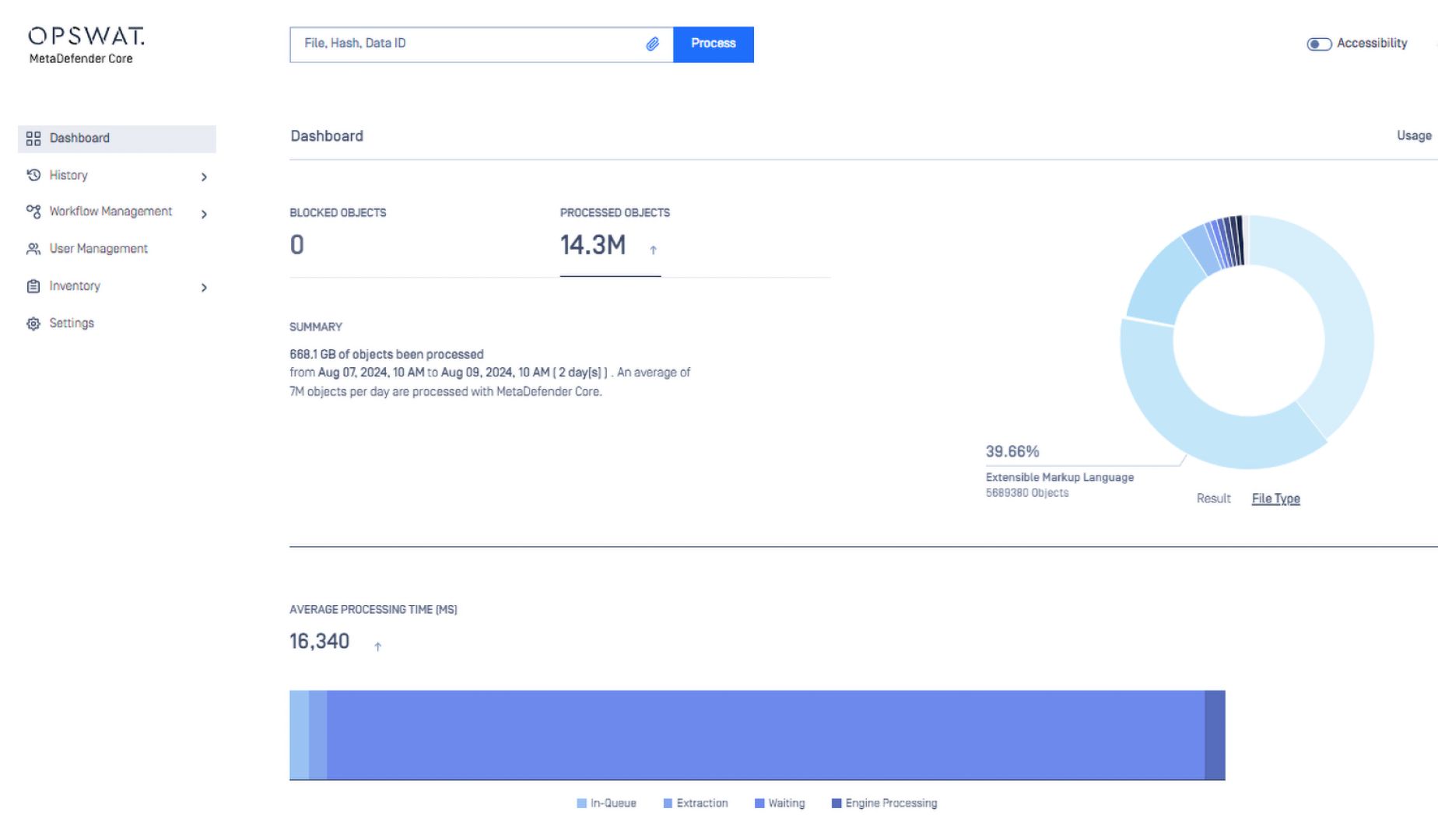
Metrics That Matter
While processing files on MetaDefender Core, the service performance is measured by various metrics, some of those commonly used to define performance level include:
- Throughput, or the number of processed objects per hour vs. number of processed files per hour
- Submission load, or the number of successful requests per second
- Average processing time per object
- Total processing time against certain data set.
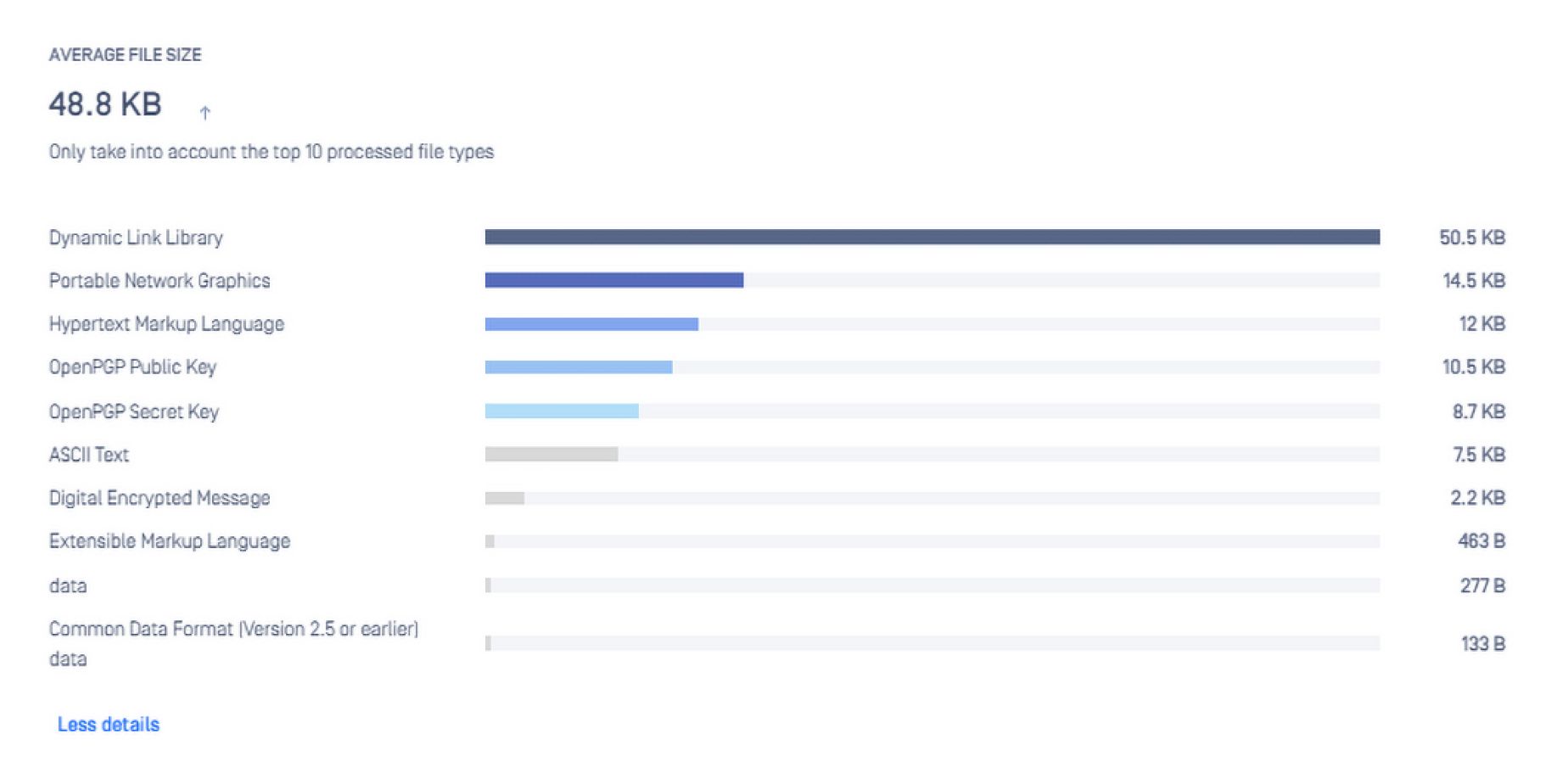
It is crucial too for any high-performance system to have monitoring mechanisms that ensure all metrics are kept in control, and if not, are identified and addressed efficiently and quickly. In the context of MetaDefender Core, these parameters can be monitored for performance measurement:
- System resources (CPU, RAM, Disk, etc.)
- MetaDefender Core active performance
- MetaDefender Core health check
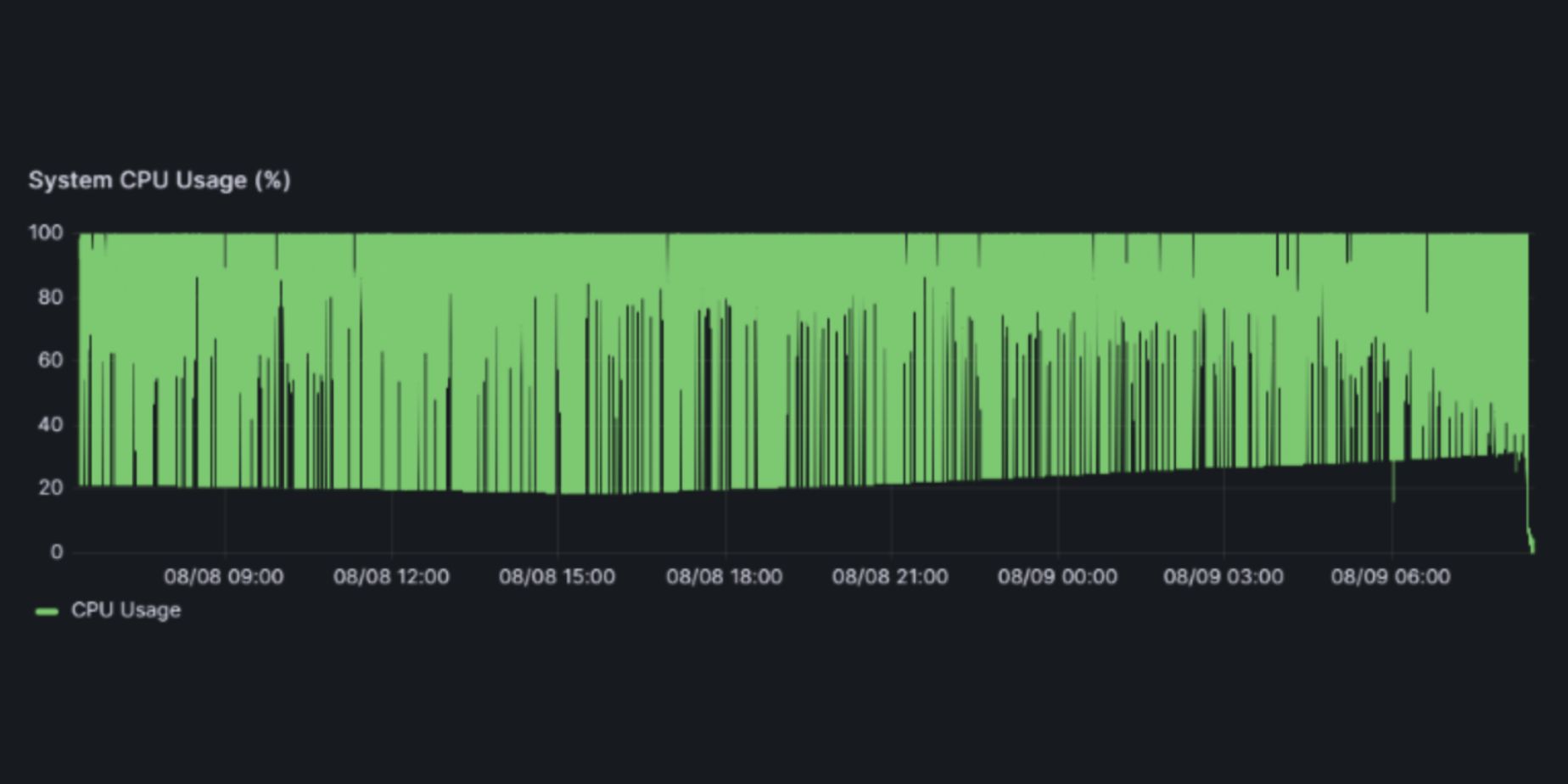
Fine-Tuning MetaDefender Core
During its operation, MetaDefender Core and its engines are expected to utilize system resources as much as possible to boost throughput while not exceeding pre-defined thresholds continuously for long periods of time.
Fine-tuning Meta Defender Core based on your use-case and system hardware can maximize overall performance with optimization broken down into two categories: System Tuning and Application Tuning.
| Factors | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| CPU |
|
| RAM |
|
| Disk |
|
| Environment |
|
| Factors | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Max file sizes setting | Larger files likely mean longer processing time, at least for temporary file creation and access, and file hash calculation. For security and performance reasons, each workflow has a default maximum file size setting for file scans. Adjust this limit as needed based on your dataset. |
| Archive settings | Large files are usually in archive compressed file format so it will require MetaDefender Core and its engines to extract and process nested files within. Increase archive settings based on your dataset. |
| File Type | File type timeout should be high enough as archive file could be large. |
| MetaDefender Core queue size | Consider increasing the MetaDefender Core queue size when scanning large quantities of archive files. |
| Engine parallel count | Increase this limit to push more tasks to engines when applicable. NOTE: increasing this limit does not always mean higher throughput produced by engines, as too many threads opened might overload engines. |
| Skip hash calculation setting | Hash calculation may require significant CPU resources and add overhead to the overall processing time—especially for large files. |
| Engine scan timeout | Lowering down this timeout threshold to seconds will help MetaDefender Core move on quickly without pending on any unexpectedly slow scanning from any engine at any time for any reason. |
| For guidance on standard settings please visit https://docs.opswat.com/mdcore/installation | |
MetaDefender Core Knowledge Base
Looking for more documentation for advanced MetaDefender Core usage? Visit our in-depth resource repository now for more information.
