Metascan™ Multiscanning
Our technology uses 30+ anti-malware engines to identify both known and unknown threats while reducing false positives and minimizing exposure time.
- Maximum Threat Coverage
- Faster Incident Response
- Streamlined Integration
OPSWAT is Trusted by
30+ Anti-Malware
Engines

>99.0%
Detection Rate
Reduce False
Positives
One
License
Cloud,
On-Premises,
Air-Gapped
Signature-Based Detection
for Speed and Accuracy
Why Single-Engine AVs Aren’t Enough
Traditional antivirus solutions miss threats, have slow response times, and complicate integration.


Limited Detection Accuracy
Single-engine AVs leave gaps in threat coverage, especially for zero-day and region-specific malware.


False Negatives and Operational Risk
Missed threats lead to data breaches, downtime, and reputational damage.

Integration Complexity
Legacy AVs don’t fit modern workflows, cloud-based architectures, and air-gapped environments.
Multiscanning Redefined by OPSWAT
AI-enhanced detection analyzes structure and content to identify a file’s true type, closing gaps left by traditional verification.
How It Works
Metascan Multiscanning combines advanced multiengine scanning, normalization, and performance optimization for comprehensive file analysis.
Unmatched Detection, Performance, and Control
High Detection Accuracy
Proven to detect over 99 percent of threats when using 30+ anti-malware engines. This significantly outperforms single-engine antivirus solutions.
Low False Positives
Shared allowlists and vendor collaboration help reduce alert fatigue and improve operational efficiency.
Customizable Engine Packages
Choose from 4 to more than 30 anti-malware engines based on your risk tolerance, compliance requirements, and performance goals.
Scalable Deployment
Supports cloud, on-premises, or air-gapped environments with robust performance tuning support.
Single License Simplicity
OPSWAT bundles all antivirus engines into one license. This removes the need to manage multiple vendors and helps reduce total cost of ownership.
See Metascan Multiscanning in Action
Experience how Metascan Multiscanning identifies complex threats faster and more effectively than single-engine solutions.
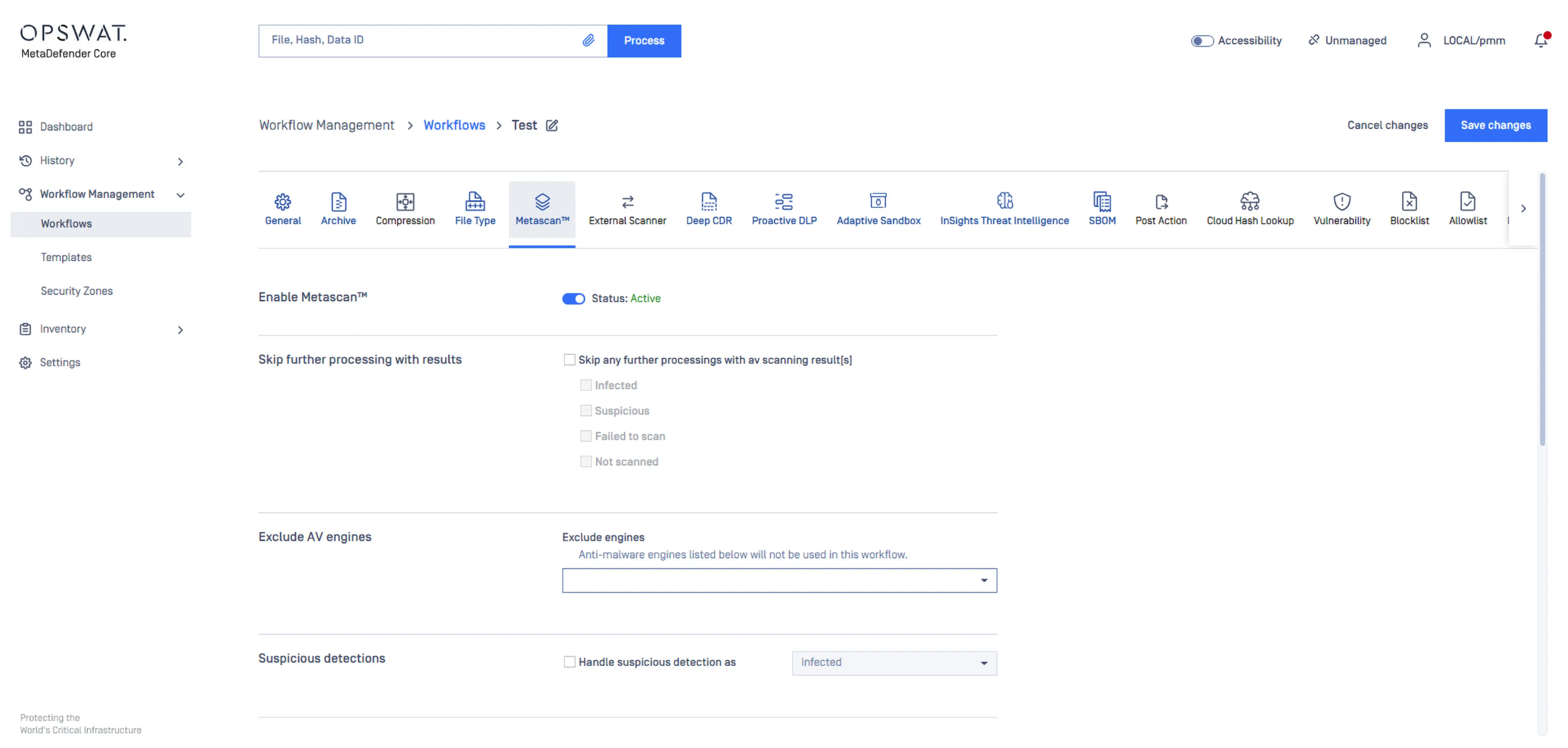
Enable multi-engine malware scanning with 30+ anti-malware using signature, heuristics and AI/ML for maximum threat protection.
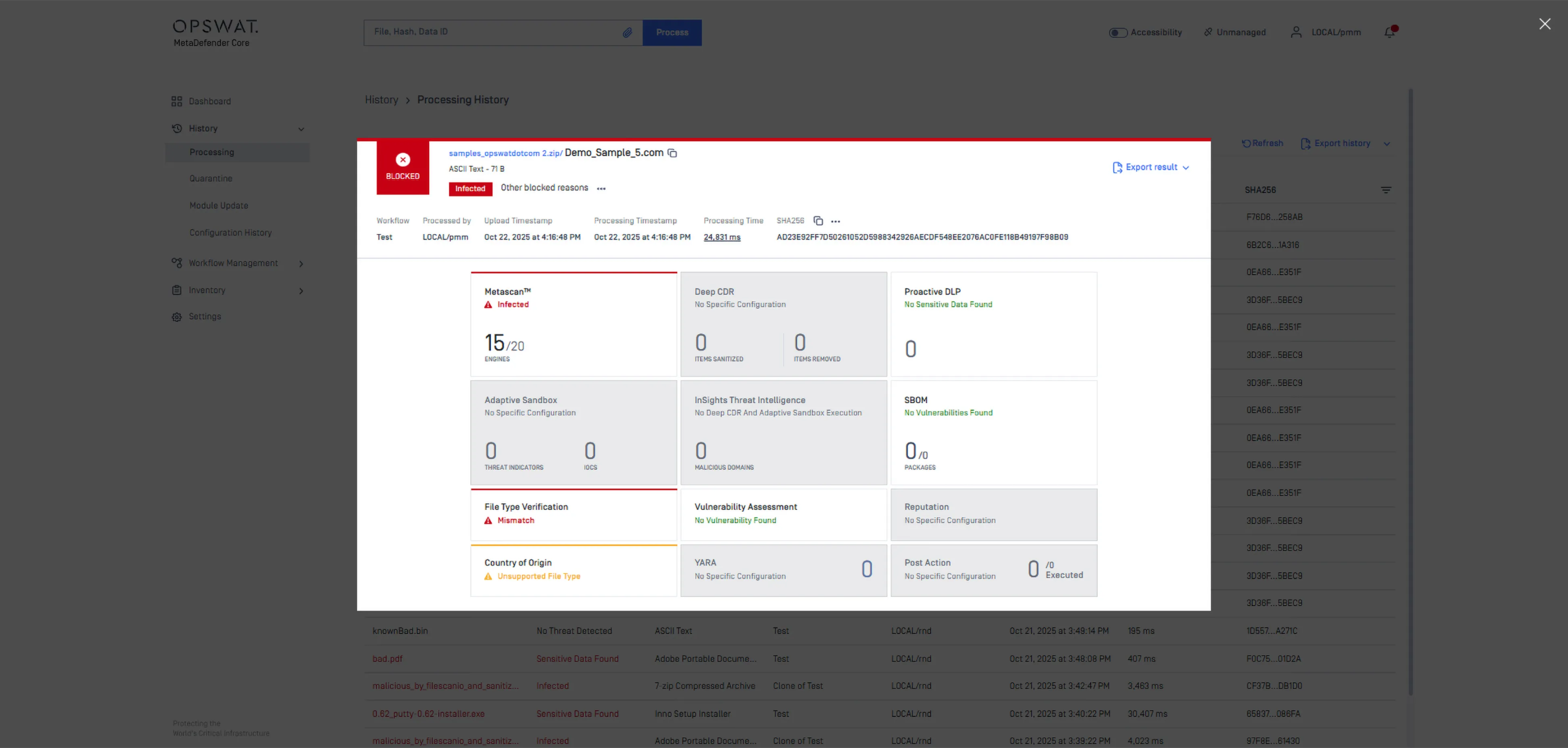
Detects malicious files using multiple anti-malware engines and provides verdicts such as Infected or Suspicious.
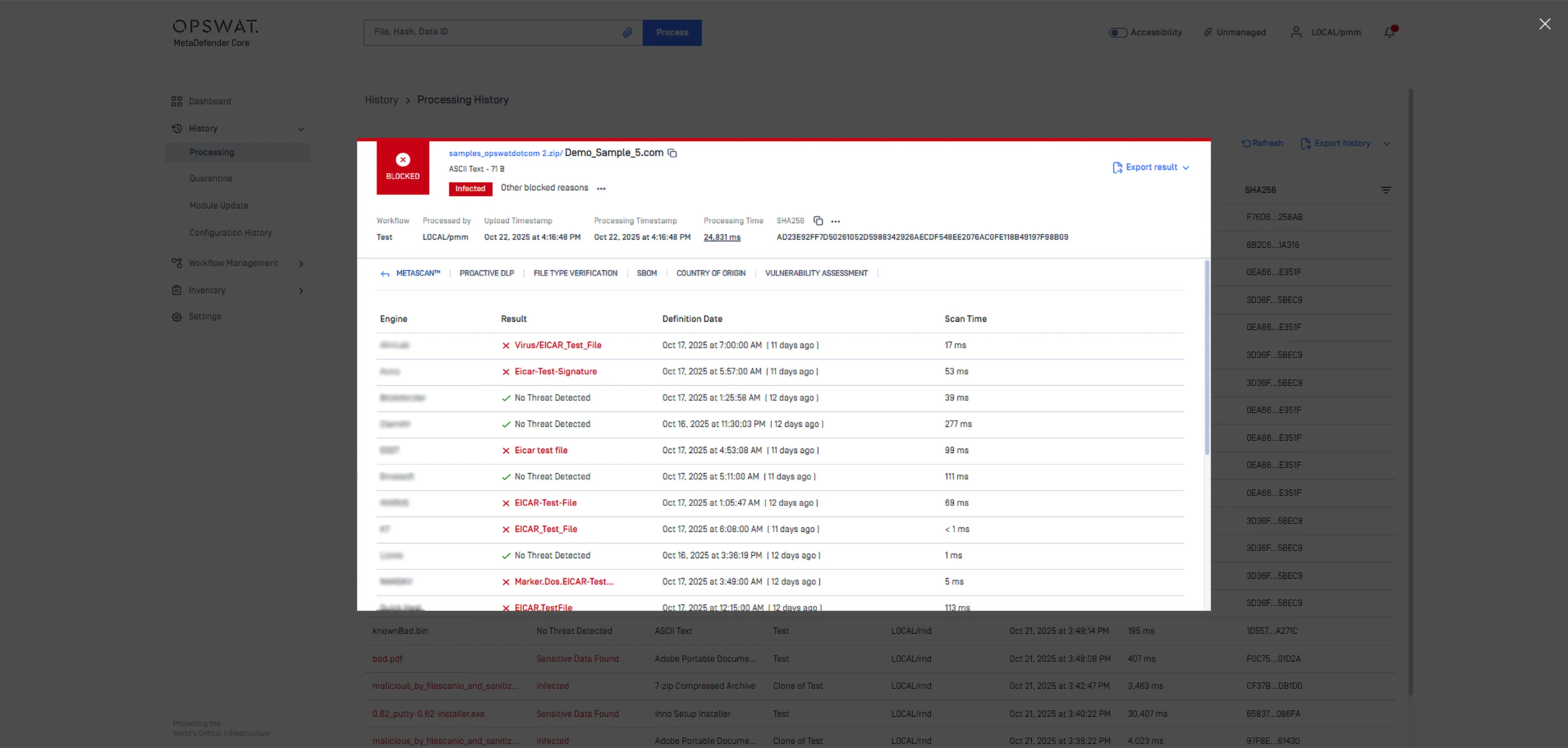
Shows detailed scan results from your enabled anti-malware engines, including malware names, database update dates and scan durations.
Deploy Anywhere, Integrate Everywhere
Scalable, comprehensive file security solution that integrates seamlessly and follows your files wherever they go.

Cloud
Scalable, managed threat detection in the cloud.
On-Premises
Full control over engines, configurations, and performance.

Air-Gapped
Isolated deployment for secure environments with no external network connectivity.