Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Why Does My MD Core Deployment on Kubernetes Lose Data After a Restart?
This article applies to all MetaDefender Core releases deployed through OPSWAT MetaDefender Helm Chart on Kubernetes.
PostgreSQL behaviour on Kubernetes
This behavior is typically related to the deployment configuration and how MetaDefender Core manages data persistence in a Kubernetes environment. By design, Kubernetes Pods are stateless. Each time the Core Pod is stopped, restarted, or rescheduled, a new Pod instance is created—with a different name and a fresh container environment. As a result, any data not stored on a persistent volume is lost during this process.

Pod name before restart

Pod name changed after restart
Due to this behavior, all files stored within the Core Pod are lost after a Pod restart. If you are using the bundled PostgreSQL database included with the Core Helm chart, it is essential to configure persistent storage for the PostgreSQL Pod.
This can be achieved by mapping a Persistent Volume to the path specified by the persistentDir value in the postgres-core section of the Core Helm chart. This ensures that database data is retained across Pod restarts or re-creations.
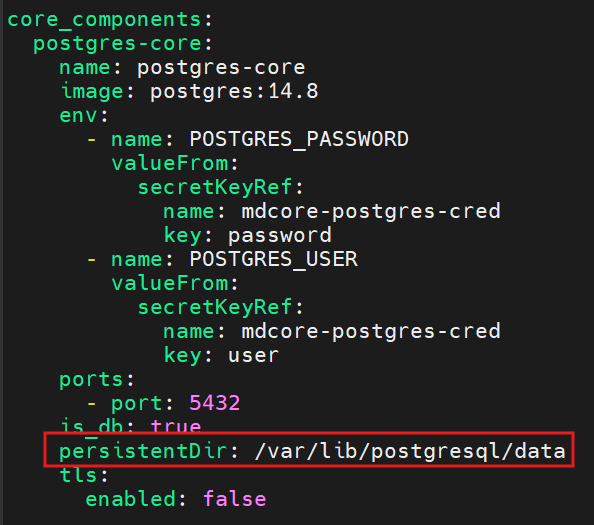
A sample config for Persistent Volume Mount can be found on our MD Core Documentation Page:
Storage Configuration on K8S - MetaDefender Core
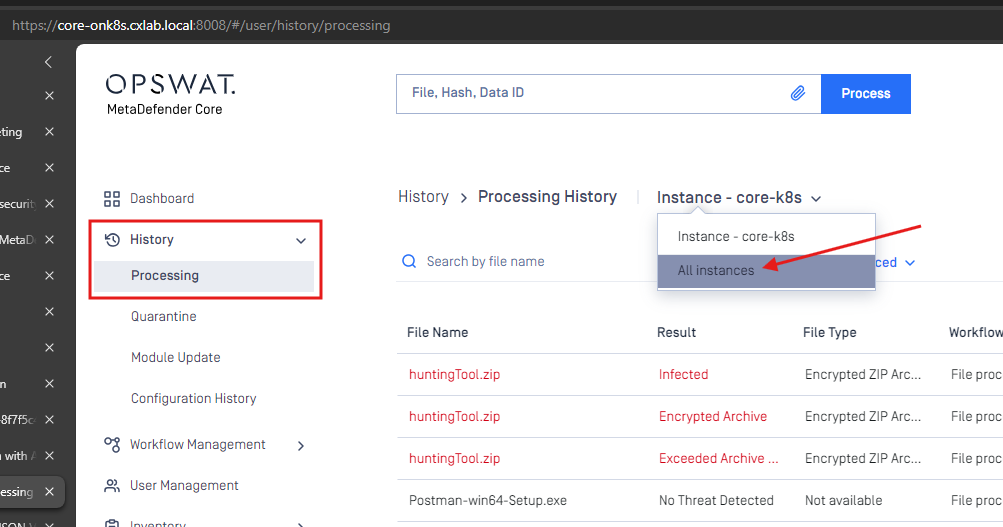
As long as the PostgreSQL database is persistent, the Processing History will be retained and can be accessed by choosing “All Instance” in the page:
Making DLP, Sanitization files Persistent
According to our Documentation (Docker image published on OPSWAT Docker Hub - MetaDefender Core), MetaDefender Core on containerized platforms supports an environment variable named STORAGE_PATH. This variable allows you to specify a full file system path for storing sanitized, DLP-processed, and quarantined files.
To ensure these files persist after a Pod restart, you must set the STORAGE_PATH environment variable and map a Persistent Volume to the specified path. This configuration enables the application to retain critical processing data across Pod lifecycles.
- In the
values.yamlfile, set the STORAGE_PATH environment value to a custom path
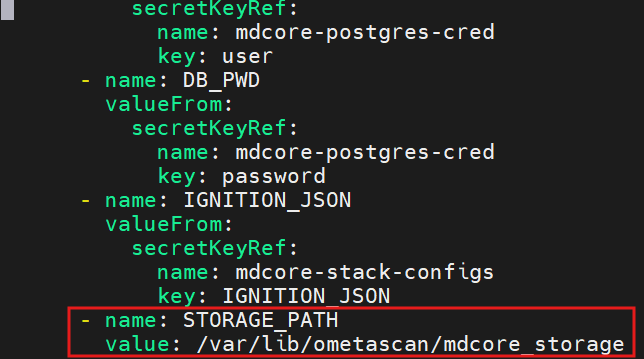
- Define a
storage_configsfor a persistentVolumeClaim
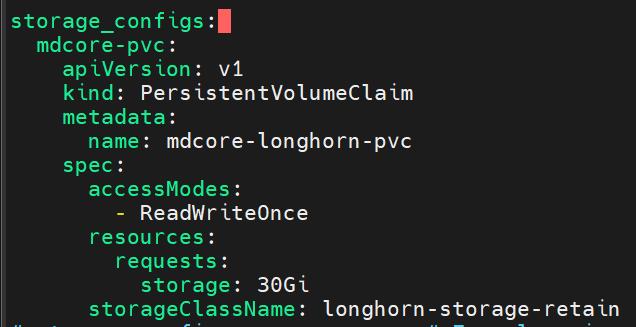
Note that the storageClassName should match an available Storage Class in your Kubernetes platform for proper persistent volume provisioning.
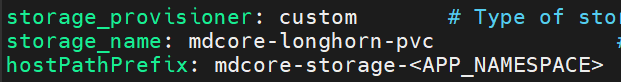
- Set
storage_provisioner,storage_nameandhostPathPrefix (optional)
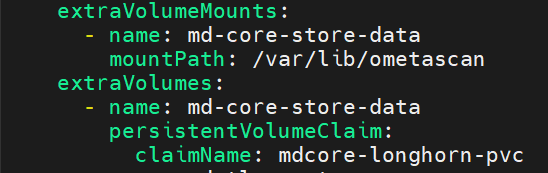
- Finally, mount the persistent Storage by using
extraVolumeMountsandextraVolumes
If Further Assistance is required, please proceed to log a support case or chatting with our support engineer.

