Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Event-Based Real-Time handling for AWS
AWS Lambda Function with S3 Trigger Setup Guide
Before proceeding with the setup, ensure the following requirements are met:
1. IAM User Permissions
- Your IAM user must have the necessary permissions to:
- Create Lambda functions
- Assign IAM roles
- Configure S3 triggers
- Access the target S3 buckets
2. Account-Level Verification
- Confirm there are no account-level naming restrictions that would prevent your chosen Lambda function name
- Verify your AWS account has sufficient permissions and service quotas to create new Lambda functions in the desired region
- Ensure you have access to the target AWS region where the Lambda function will be deployed
3. S3 Bucket Configuration
- Verify that S3 bucket policies are configured to allow access from the Lambda function's execution role
- Required S3 permissions may include:
s3:GetObject- to read objects from the buckets3:PutObject- to write objects to the bucket (if applicable)s3:DeleteObject- to delete objects from the bucket (if applicable)
4. IAM Execution Role
- Ensure you have a pre-configured IAM role with:
- Lambda execution permissions
- S3 access permissions for your target bucket(s)
- CloudWatch Logs permissions for function monitoring
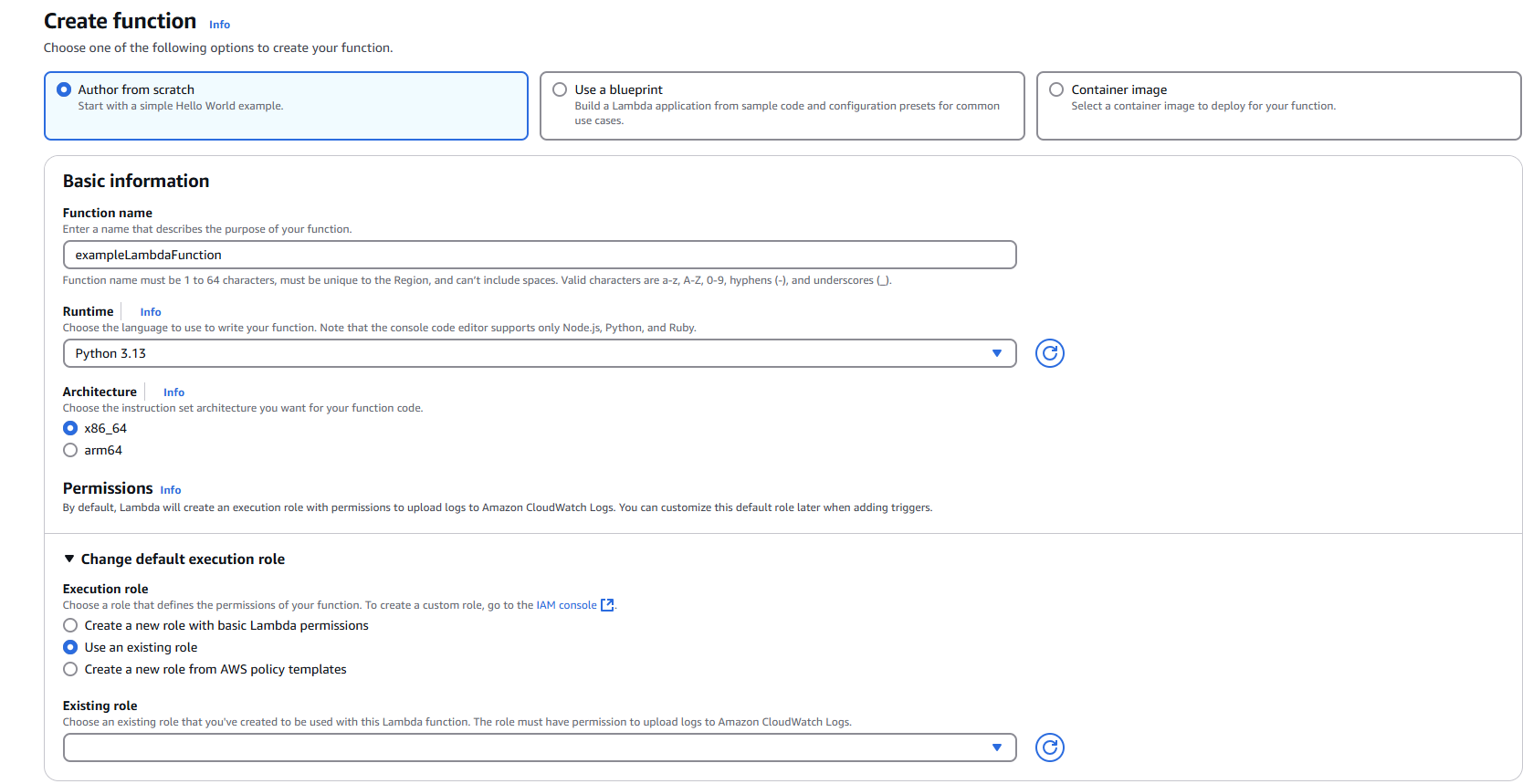
Step 1: Creating the Lambda Function
1.1 Navigate to Lambda Service
- Open the AWS Management Console
- Navigate to the Lambda service
1.2 Initialize Function Creation
- Click "Create function"
- Select "Author from scratch"
1.3 Configure Basic Settings
Function name: Enter a descriptive name for your Lambda function
- Example:
MetaDefenderStorageSecurityProcessor - Ensure the name complies with AWS naming conventions and any account-specific policies
- Example:
Runtime: Select Python (choose the latest compatible version)
1.4 Configure Permissions
- Under "Change default execution role", select "Use an existing role"
- From the "Existing role" dropdown, choose your pre-configured IAM role
- Verify role permissions:
- Navigate to the IAM console and review the selected role
- Confirm Permission policies include necessary access to S3, CloudWatch Logs, and other required services
- Verify Trust relationships allow the Lambda service (
lambda.amazonaws.com) to assume the role
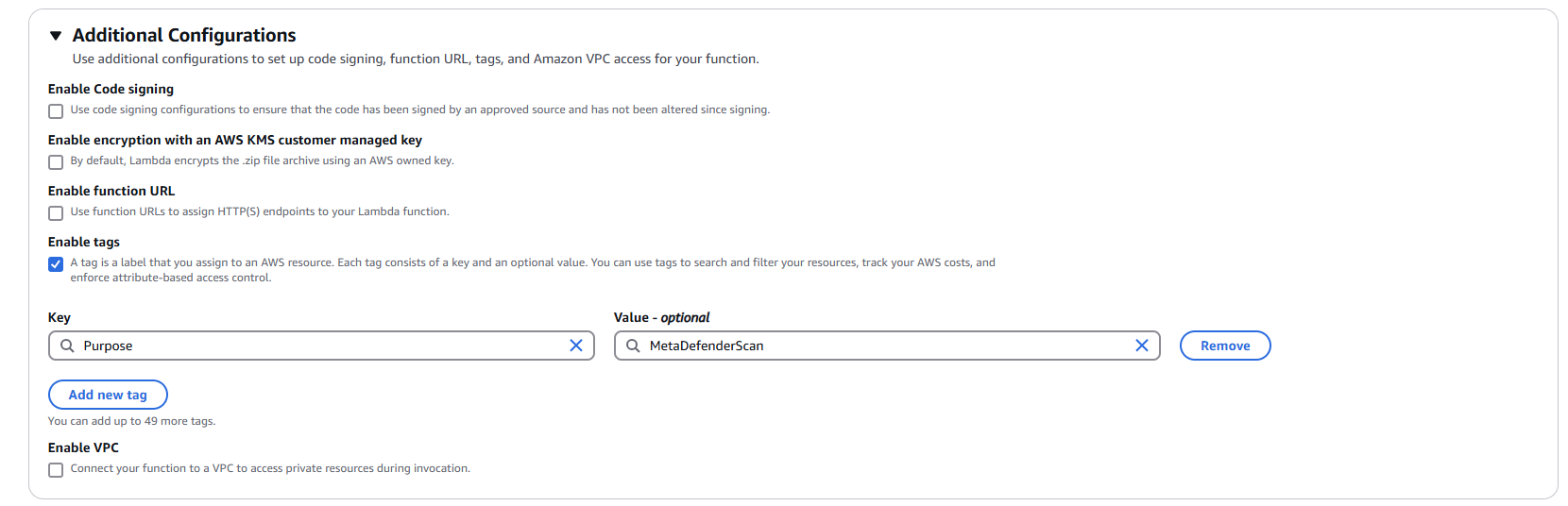
1.5 Configure Advanced Settings (Optional but Recommended)
- Expand "Advanced configuration"
- Enable "Tags"
- Add relevant tags for resource organization:
- Key:
Purpose| Value:MetaDefenderScan - Key:
Environment| Value:Production/Development - Key:
Owner| Value:[Your Team/Department]
- Key:
1.6 Create the Function
- Click "Create function"
- Wait for the function to be successfully created
Step 2: Adding S3 Trigger
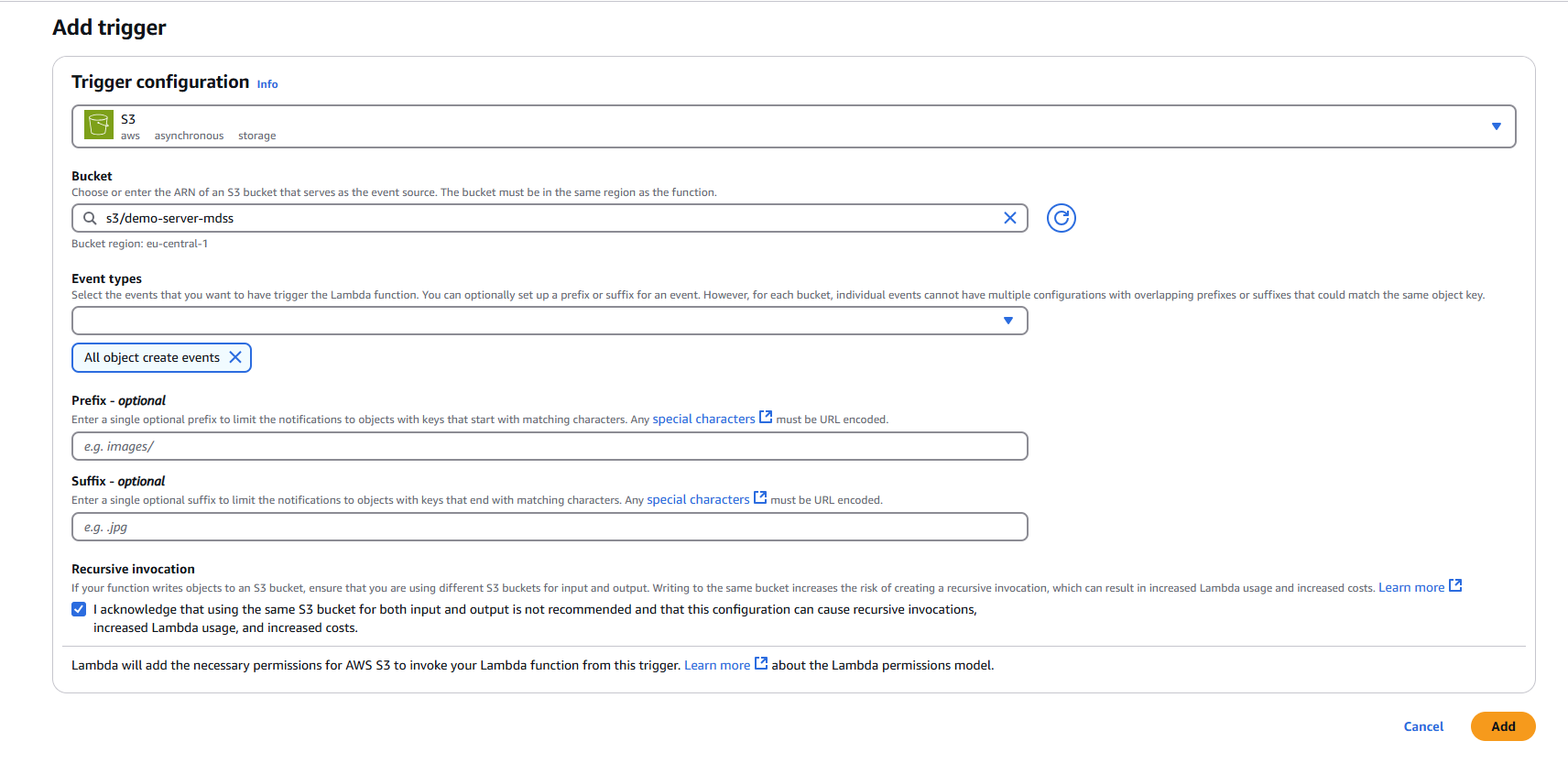
2.1 Add Trigger Configuration
- In your newly created Lambda function, click "Add trigger"
- Select "S3" as the trigger source
2.2 Configure S3 Trigger Settings
Bucket: Select your target S3 bucket from the dropdown menu
Event types: Choose the appropriate event type
- Default: "All object create events"
- Alternative options: Object create, delete, or restore events based on your requirements
Prefix (Optional): Specify a prefix to filter objects by path
- Example:
uploads/to only trigger on objects in the uploads folder
- Example:
Suffix (Optional): Specify a suffix to filter objects by file extension
- Example:
.pdfto only trigger on PDF files
- Example:
Recursive invocation: Check this option to acknowledge potential recursive invocations
2.3 Finalize Trigger Setup
- Review your trigger configuration
- Click "Add" to create the S3 trigger
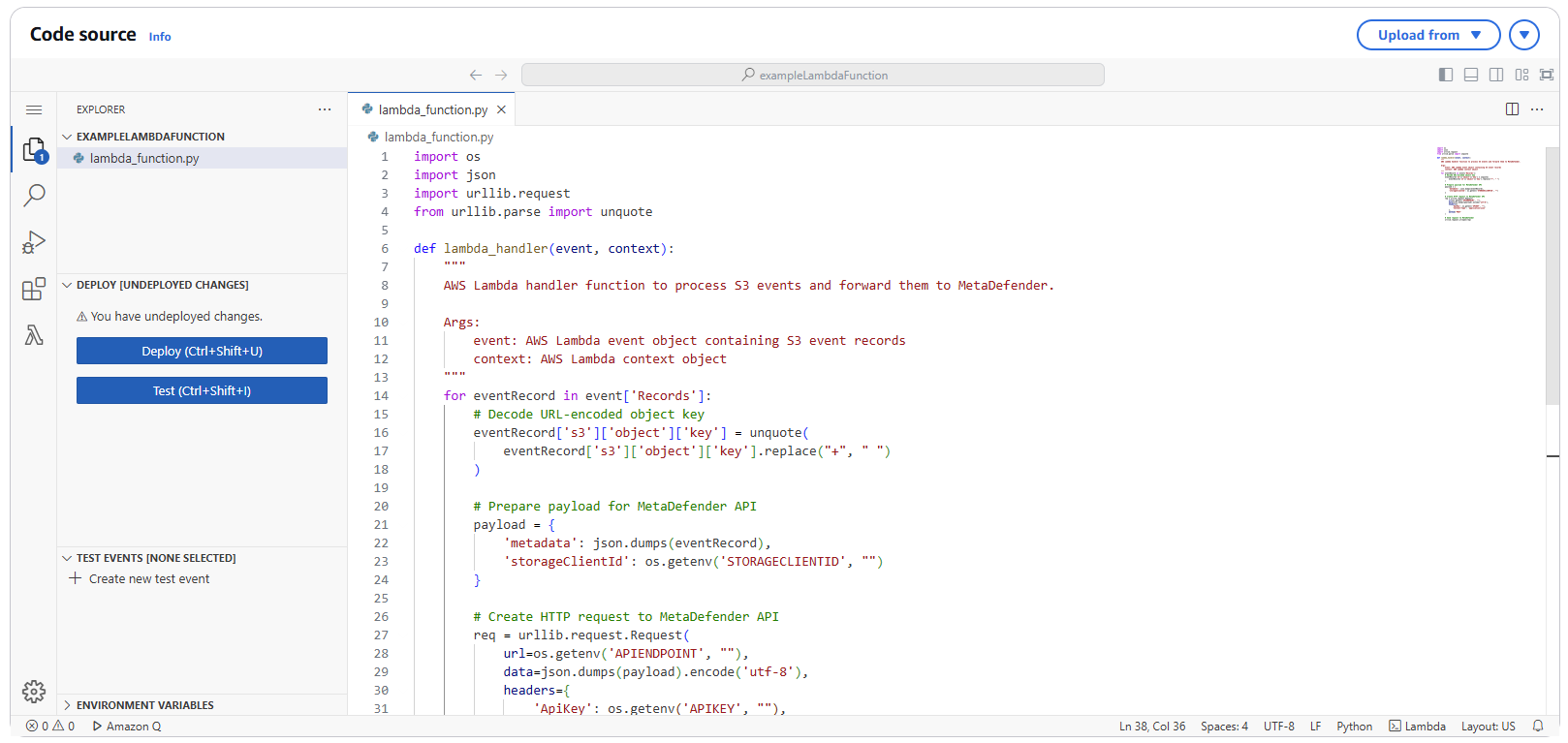
3.1 Navigate to Code Section
- In your Lambda function console, navigate to the "Code" tab
- Replace the default code with the following implementation:
import osimport jsonimport urllib.requestfrom urllib.parse import unquotedef lambda_handler(event, context): for eventRecord in event['Records']: eventRecord['s3']['object']['key'] = unquote(eventRecord['s3']['object']['key'].replace("+", " ")) payload = { 'metadata': json.dumps(eventRecord), 'storageClientId': os.getenv('STORAGECLIENTID', "") } req = urllib.request.Request( url=os.getenv('APIENDPOINT', ""), data=json.dumps(payload).encode('utf-8'), headers={ 'ApiKey': os.getenv('APIKEY', ""), 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, method='POST' ) urllib.request.urlopen(req)3.2 Deploy the Code
- Click "Deploy" to save and deploy your function code
Request Format (with examples)
The request body differs based on storage type. Below are the specifications for each supported storage:
Amazon S3 and S3 Compatible
{ "storageClientId": '{Storage Client Id}', "metadata": "{'s3': { 'object': {'key': '{Object Path}' }}}"}Response Formats
Success
When a webhook is successfully processed, the system returns:
{ "correlationId": "67ea85a36f2f5732a82834d0"}| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| correlationId | A unique identifier that references the submitted file in our database. You can use this ID for tracking the file's processing status or for future API calls related to this file. |
Error
When an error occurs during processing, the system returns:
{ "responseKey": "REST_API_MSG_FAILED_STORAGE_RTP_NOT_ENABLED", "responseMessage": "Real-Time Process is not enabled."}| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| responseKey | Machine-readable error code that identifies the specific error condition. |
| responseMessage | Human-readable explanation of the error. |
Common error responses
| Response Message | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| The storage could not be found | The specified storage client ID does not exist in the system. | Verify the storageClientId is correct and the storage has been properly configured in the system. |
| Real-Time Process is not enabled. | Real-time processing has not been activated for this storage client. | Enable real-time processing for the storage client in your account settings. |
| Real-Time Process is enabled, but it is not set to Event Based. | The storage is configured for real-time processing, but is using polling rather than event-based processing. | Stop the current RTP scan and start another one using Event-Based |
Step 4: Configuring Environment Variables
4.1 Navigate to Configuration
- In your Lambda function console, click on the "Configuration" tab
- Select "Environment variables" from the left sidebar
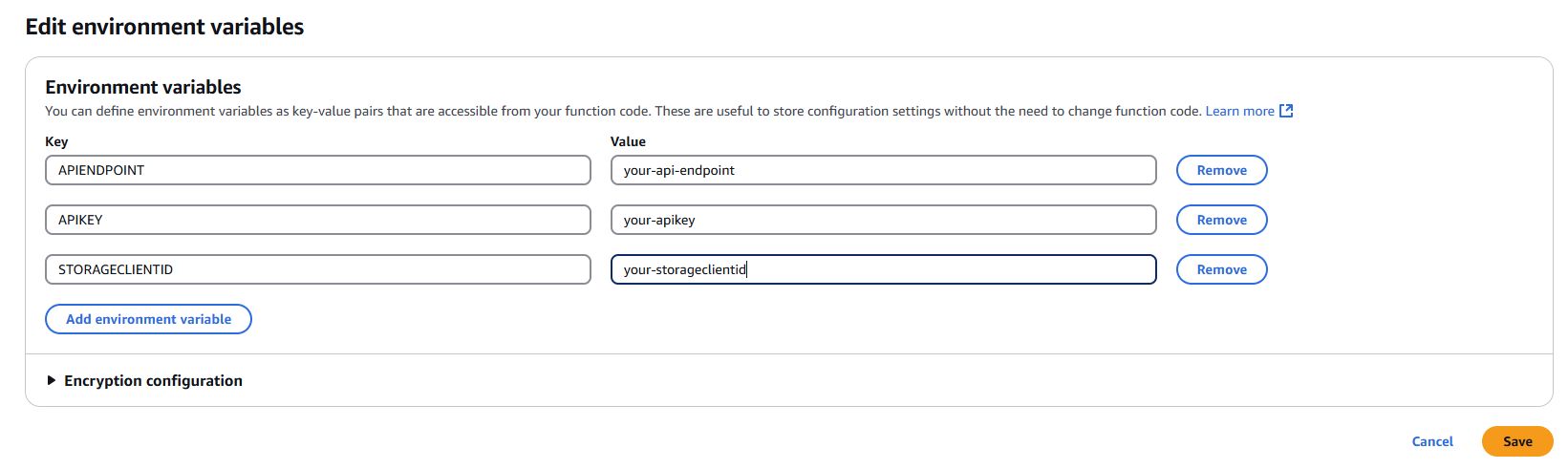
4.2 Add Required Environment Variables
Click "Edit" and add the following environment variables:
APIENDPOINT
- Key:
APIENDPOINT - Value: Your MDSS URL +
/api/webhook/realtime - Example:
https://mdss-example.com/api/webhook/realtime
- Key:
APIKEY
- Key:
APIKEY - Value: Your MDSS user API key
- Note: Ensure this key has appropriate permissions for webhook operations
- Key:
STORAGECLIENTID
- Key:
STORAGECLIENTID - Value: Your storage client ID from MDSS
- To obtain: Navigate to your desired storage configuration and copy the
storageClientId
- Key:
4.3 Save Configuration
- Click "Save" to apply the environment variable changes
Step 5: Testing and Validation
5.1 Test the Function
- Upload a test file to your configured S3 bucket
- Monitor the Lambda function's execution in the "Monitor" tab
- Check CloudWatch Logs for any execution errors or successful processing
5.2 Verify Integration
- Confirm that file events are being sent to your MDSS instance
- Verify that scans are initiated as expected
- Review MDSS logs for successful webhook reception

