A minimum of three RabbitMQ nodes must be installed on separate hosts for High Availability solution to function properly.
An odd number of RabbitMQ nodes is required.
All RabbitMQ nodes must be of an identical version.
RabbitMQ cluster
- Install RabbitMQ nodes on servers.
- Ensure each node can resolve its own hostname and those of the others.
- Start Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Linux, and run the following command to get hostname.
# Windows> hostname# Debian/Ubuntu or Red Hat/Rocky$ hostname- In Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Linux of any RabbitMQ node, and run the following command to ping to the other using its hostname.
# Windows> ping <other_node_hostname># Debian/Ubuntu or Red Hat/Rocky$ ping <other_node_hostname>- On each RabbitMQ nodes, open the following ports.
| Default port | Process |
|---|---|
| 5672 | Used by MDDC Control Center, MDDC API Gateway and MetaDefender Core. |
| 4369 | Used by discovery daemon on each RabbitMQ nodes and rabbitmqctl tool. |
| 25672 | Used by each RabbitMQ nodes and rabbitmqctl tool to communicate to the other nodes. |
| 15672 | Used by rabbitmq-management plugin. |
- Verify that the Erlang cookies of all RabbitMQ nodes are identical.
RabbitMQ nodes and rabbitmqctl tool use a cookie to determine whether they are allowed to communicate with each other. For two nodes to be able to communicate they must have the same shared secret called the Erlang cookie. The cookie is a string of alphanumeric characters up to 255 characters in size.
- In Windows, access the specified locations to check the cookie contents.
| Type | Location |
|---|---|
| Server cookie | C:\Windows\system32\config\systemprofile.erlang.cookie |
| Command line cookie | C:\Users%USERNAME%.erlang.cookie |
- In Linux, access the specified locations to check the cookie contents.
| Type | Location |
|---|---|
| Server cookie | /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie |
| Command line cookie | $HOME/.erlang.cookie |
- Select one node to be the leader of RabbitMQ cluster.
- In Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Linux of the server hosting the leader, run the following command to obtain its node name.
# Windows> rabbitmqctl status# Debian/Ubuntu or Red Hat/Rocky$ rabbitmqctl status- In Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Linux of each member node server, run the following command to join the node to the same cluster as the leader.
# Windows> rabbitmqctl stop_app> rabbitmqctl reset> rabbitmqctl join_cluster <leader_node_name>> rabbitmqctl start_app# Debian/Ubuntu or Red Hat/Rocky$ rabbitmqctl stop_app$ rabbitmqctl reset$ rabbitmqctl join_cluster <leader_node_name>$ rabbitmqctl start_app- In Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Linux of all nodes, ensure they are in the same cluster.
# Windows> rabbitmqctl cluster_status# Debian/Ubuntu or Red Hat/Rocky$ rabbitmqctl cluster_statusSetup Instructions
- Sign to MDDC Control Center console with your Administrator account.
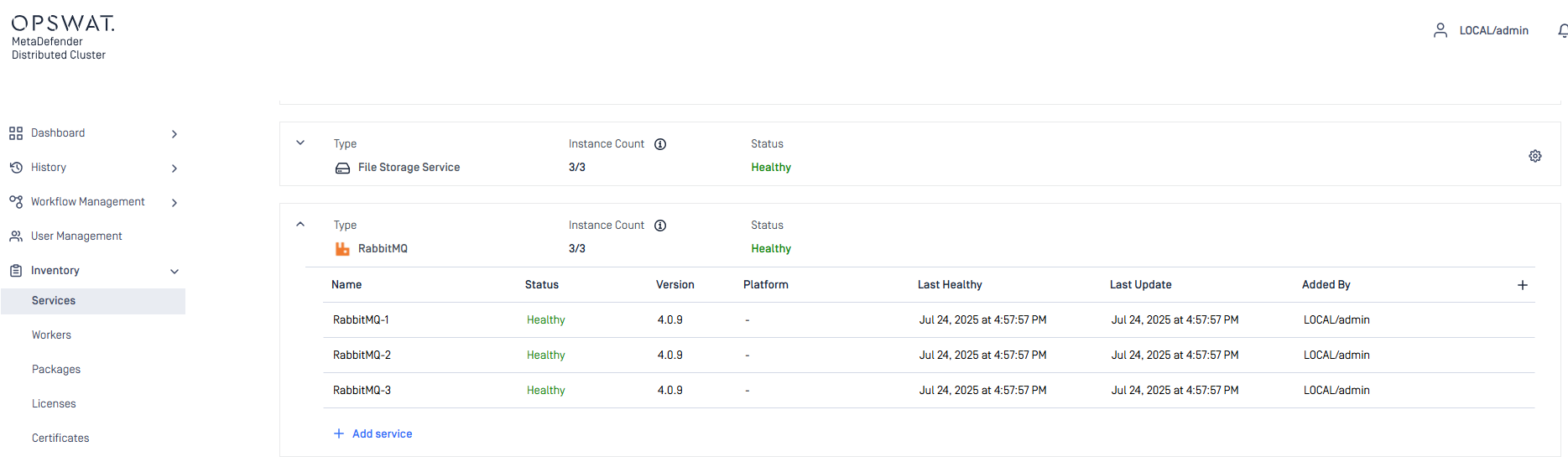
- Navigate to
Inventory>Services. - Expand the
RabbitMQgroup. - Click
Add service. - Enter the values for
Name,Host,Port,UsernameandPasswordfields of individual RabbitMQ nodes set up in Build RabbitMQ cluster.
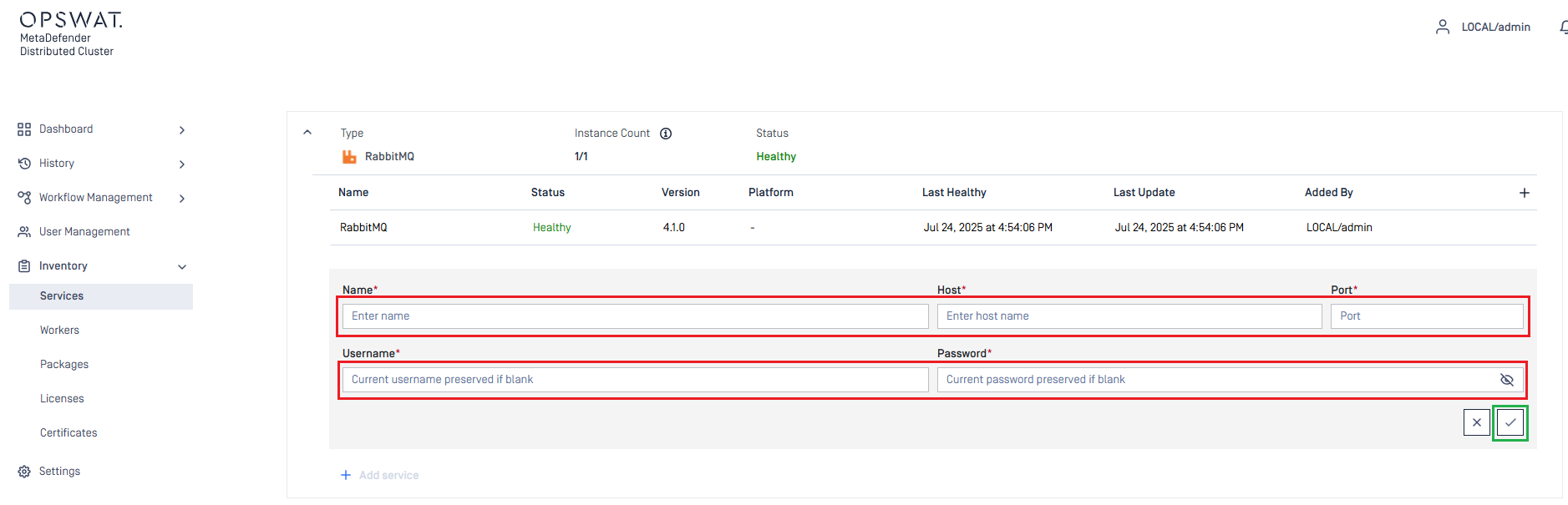
- Click the Check icon in the bottom right to complete.
- Ensure all RabbitMQ nodes are reachable by the MDDC Control Center.