Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Policy
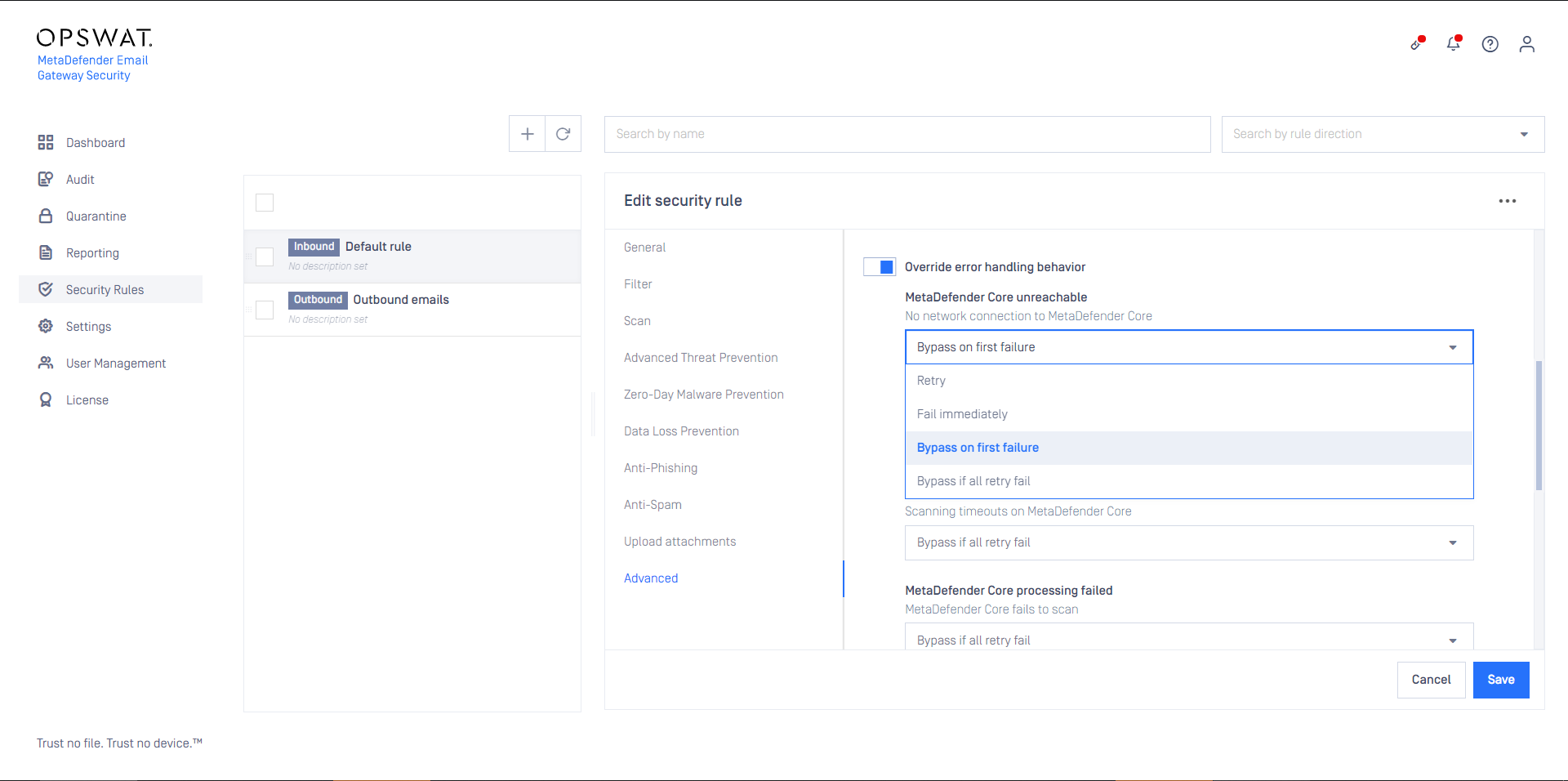
The policy how emails are handled in MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can be configured by the rules under the Security Rules page.
Direction
In traditional configurations MetaDefender Cloud Email Security is wedged between the organization's email gateway and mail server (see the image below). In case of inbound email directions the email is received from the email gateway and sent towards the mail server. In case of outbound directions the email is received from the mail server and sent towards the email gateway.
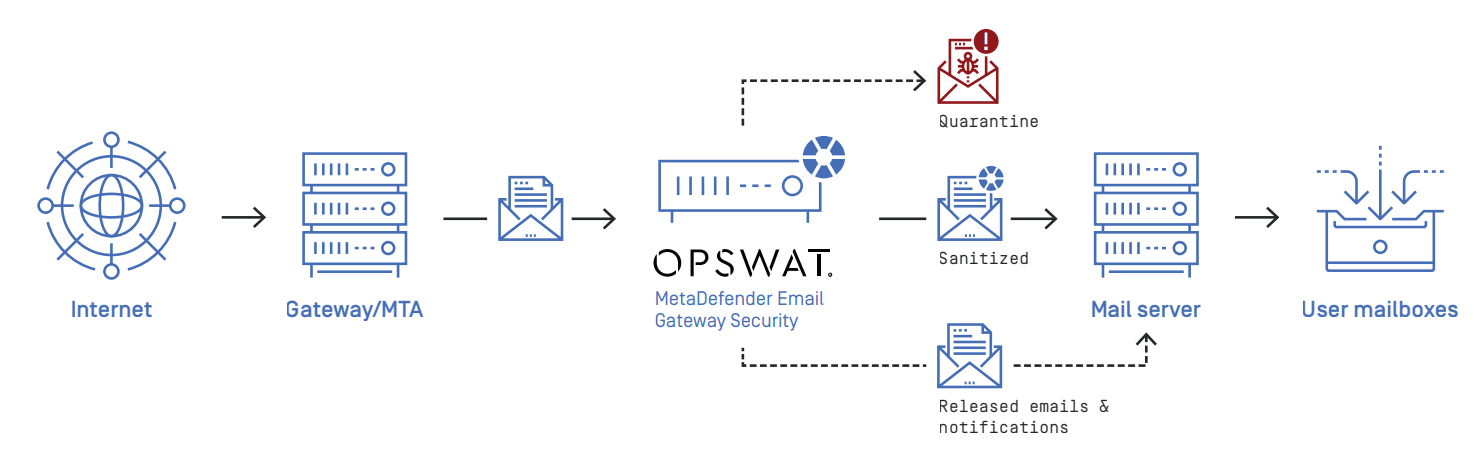

The direction of the email flow can be mapped to security rules in MetaDefender Cloud Email Security with defining:
- Where emails are coming from, and
- Where emails should be sent next after processing.
To configure direction for a certain security rule:
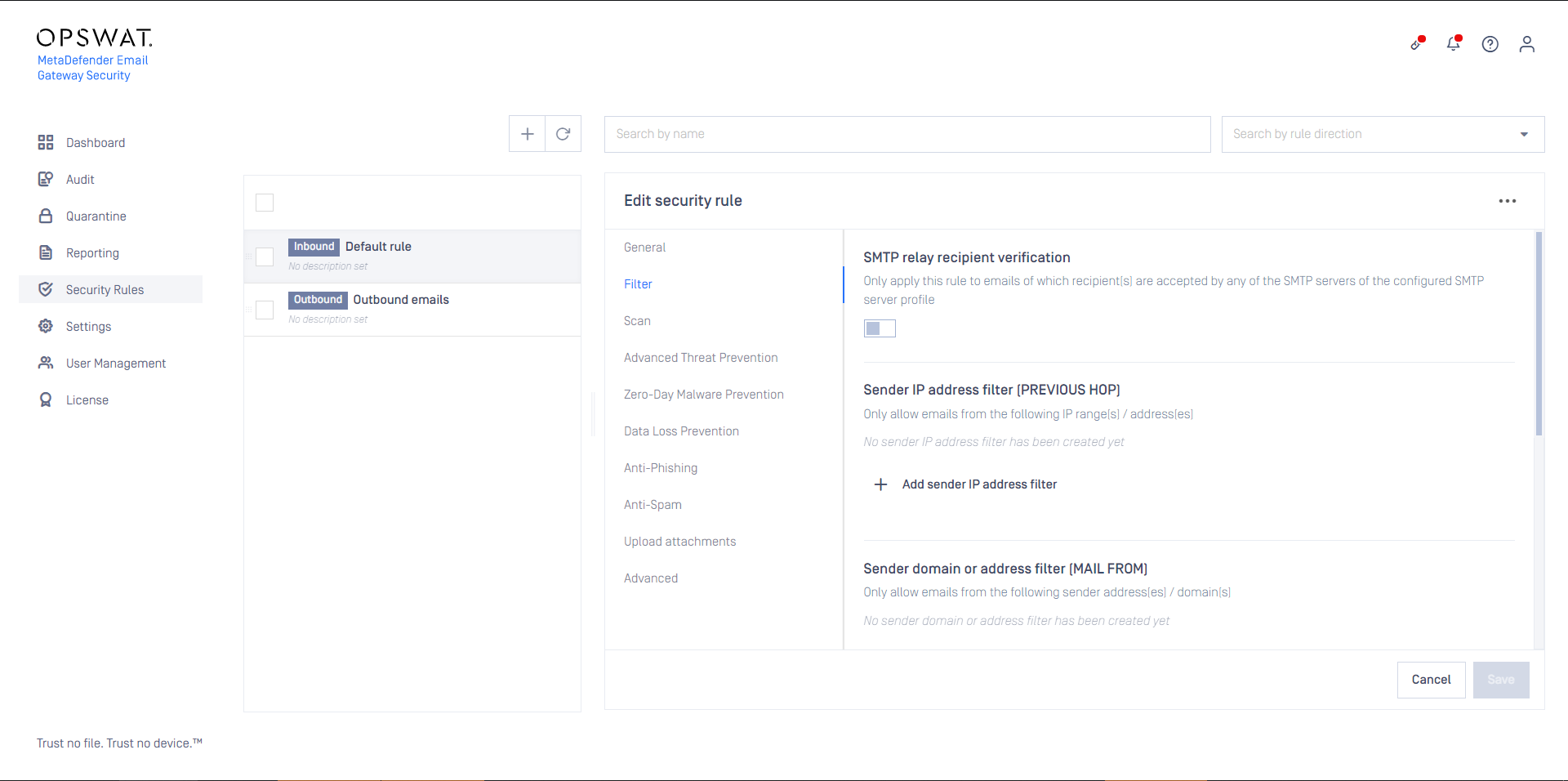
- Apply appropriate filter settings for the Security rules >rule/ FILTER / Sender IP address filter (PREVIOUS HOP) to define where emails matching this rule are coming from.
This option makes MetaDefender Cloud Email Security to ensure that it will be able to forward the accepted emails upon completed processing.
When this option is not enabled, and the recipient of the email is not accepted by any SMTP servers of the server profile, then the email will end up in a retry loop, and finally in permanent failure.
When this option is enabled with no further filtering, then for each email the first rule will match, that will be able to forward that email.
- Select the appropriate SMTP destination in Security rules >rule/ GENERAL / SMTP relay server profile to define where emails matching this rule should be sent next after processing.
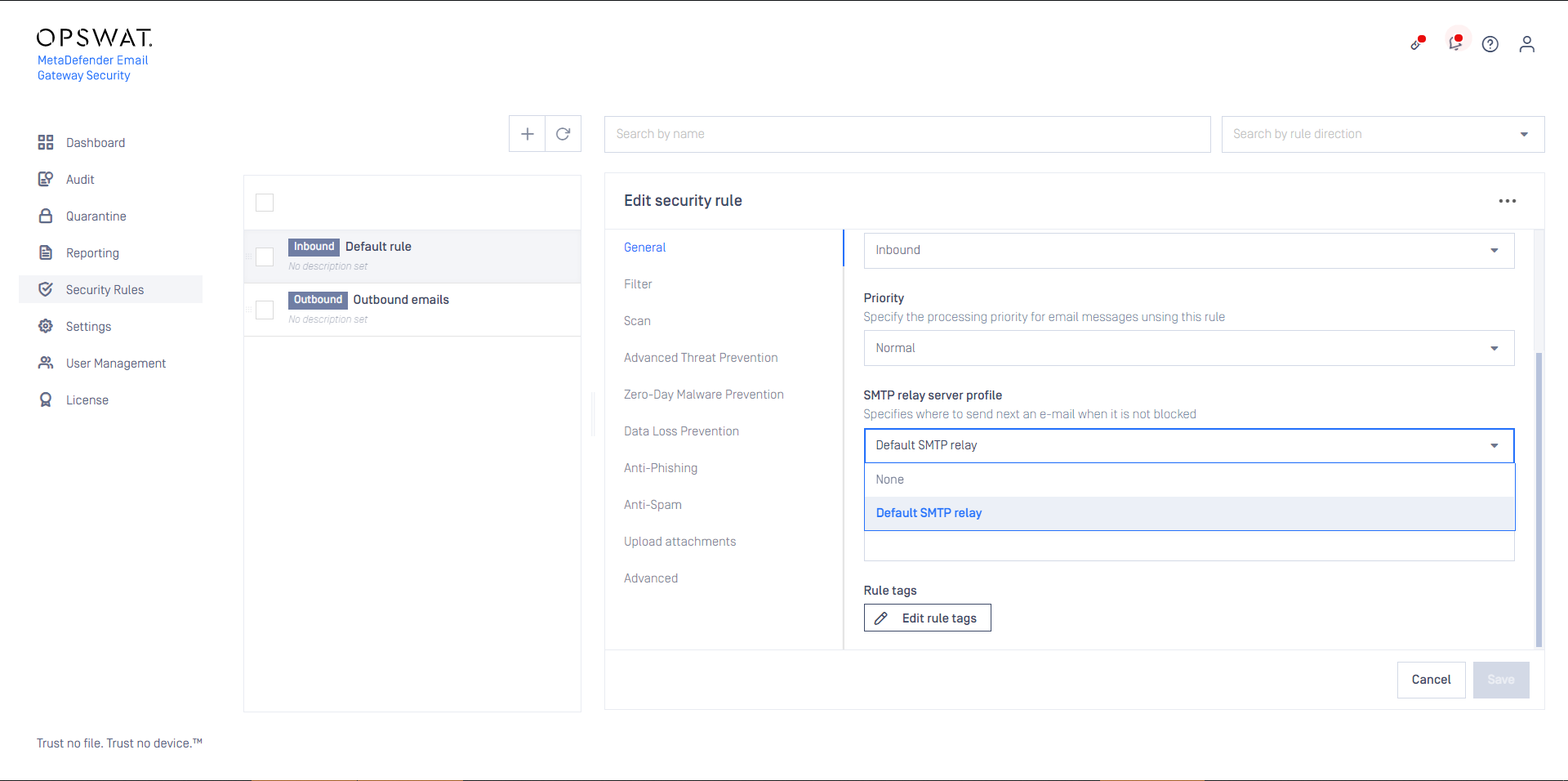
When the filter and the SMTP relay are set appropriately to match emails coming from or going to a certain direction, then the Security rules >rule/ GENERAL / Rule direction can be set accordingly to Inbound or Outbound depending on the direction of the email flow.
Rule order
Several security rules can be created that may target different messages from different sources going to different recipients. However, care must be taken how these rules are set up and ordered, as there is a first match and a no match policy (see the next two sections).
Specific rules should come first while generic rules should go at last.

First match policy
If there are more matching rules in the system, then the email message will be accepted/rejected and processed according to the security policy of the first matching rule in the list.
No match policy
If there is no matching rule in the system (or no rule at all), then the email message will be rejected.
Deleting all security rules from the system results all email messages being blocked.
Security rule configuration
Filtering
Recipient verification
When SMTP relay recipient verification is enabled for the rule, then MetaDefender Cloud Email Security will attempt to initiate sending an email to the recipient via the SMTP servers of the SMTP server profile configured for the rule (GENERAL / SMTP relay server profile).
The rule is applied to the email only, if the connection initiation succeeds.
For details see Configuration/Recipient verification.
Sender IP address conditions
Sender IP addresses are the addresses of infrastructure elements in the deployment, from which MetaDefender Cloud Email Security is allowed to receive emails according to this rule.
In case of a traditional setup, for example, sender is the email gateway for inbound messages and the mail server for outbound messages.
| Type | IP address or subnet | |
|---|---|---|
| Match type | EQUALS | |
| Examples | IP | 10.0.0.1 |
| Examples | IP range | 10.0.0.0/24 |
There is OR relation among entries in sender IP address conditions.
Sender domain or address conditions
Sender filter makes possible to apply security rule based on from what email address the email was sent. The value is taken from the SMTP communication’s MAIL FROM command that holds an email address.
When using this filter please be aware of the fact that spoofing the sender of the email is a very easy task. A more secure way to use this filter would be for OUTBOUND emails only along with filtering to the sender IP.
Field details
| Value type | email address |
|---|---|
| Field type | .NET Regex |
| Match type | regular expression match |
| Examples |
|
To avoid unexpected matching, special regular expression characters must be taken into consideration.
For example:
- The
.(dot) in a regular expression matches any character. This means that.+@opswat.comcan matchtest@opswat1com. If you want to match explicitly for a dot you should escape it like this:.+@opswat\.com - The
^(hat) and$(dollar) characters match the beginning and end of the string respectively. The regular expressiontest@opswat\.commay unexpectedly matchthis_is_test@opswat.combesidestest@opswat.com. To matchtest@opswat.comexplicitely, use the regular expression^test@opswat\.com$.
For more details see .NET Regular Expressions.
There is OR relation among the sender domain or email address conditions.
Recipient domain or address conditions
Recipient conditions can help to restrict emails matched by the rule to specific recipients. The value is taken from the SMTP communication’s RCPT TO command that holds an email address.
Benefits of recipient filtering
Recipient domain or email address conditions can also help to counter emails sent to invalid recipients; that do not even exist at an organization or among the partners, for example.
This kind of defense may protect against unnecessary overloads or even against malicious attacks.
Field details
The field details are identical to the field details of the sender domain or address conditions (for details see the Sender domain or address conditions section).
Security policy
The security policy of a certain rule is defined by the settings on the SCAN, ADVANCED THREAT PREVENTION, ZERO-DAY MALWARE PREVENTION, ANTI-PHISHING, UPLOAD ATTACHMENTS and ADVANCED tabs.
Scan
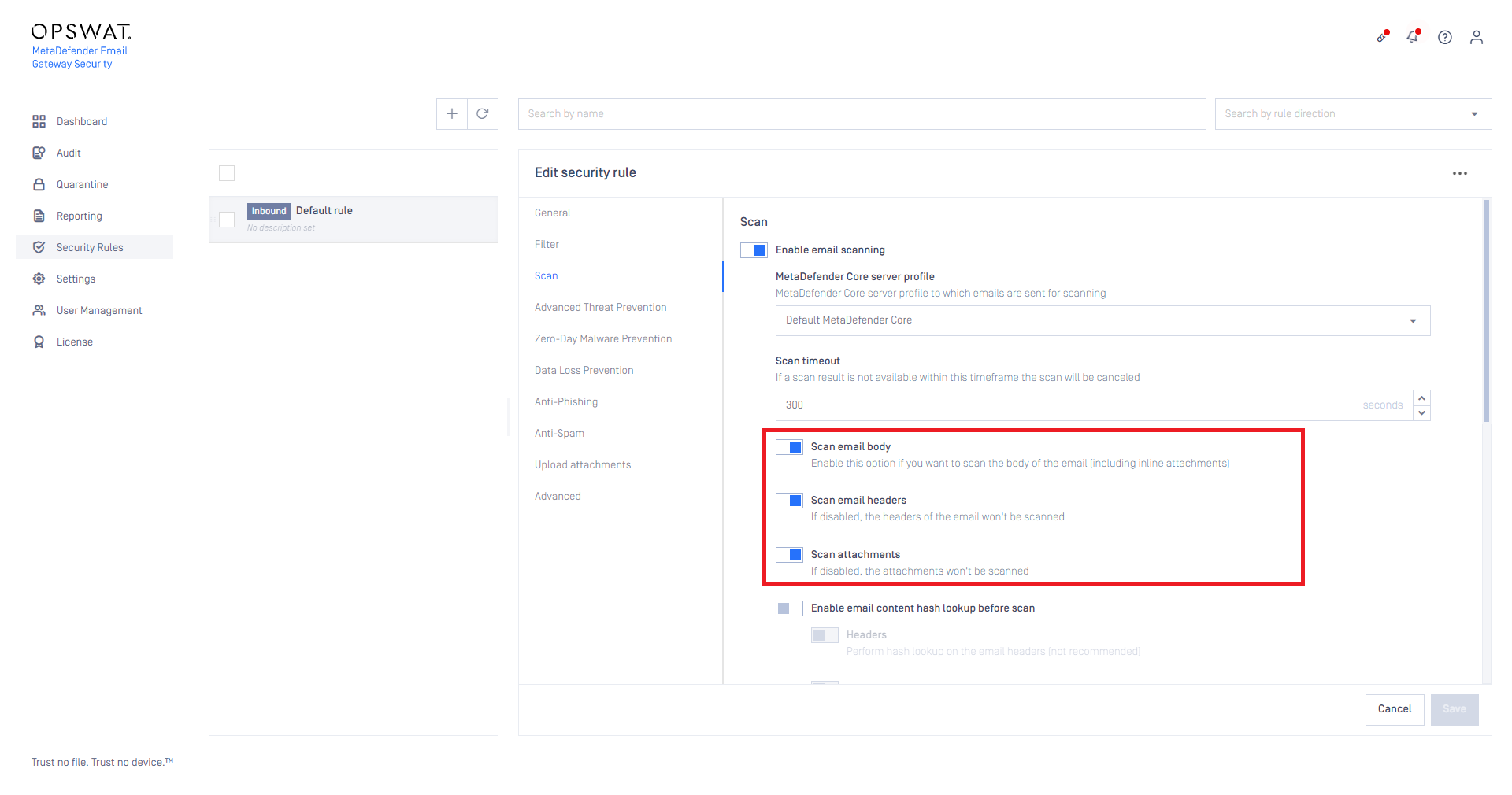
On the Scan tab of a certain rule it can be defined if emails matching this rule must be scanned at all, or not.
Scan email headers, body and attachments
MetaDefender Cloud Email Security is capable to process email headers, body and attachments, thus find malicious or sensitive content not only in attachments, but even in the body or headers.
Scan email body will scan the body (both the HTML and the plain text body) including all the inline, embedded attachments (inline attachments are the non-text elements embedded into the HTML email body, e.g. inline images).
Scan attachments can toggle scanning the regular (non-inline) attachments.
An email with an embedded (inline) image attachment:
An email with a regular attachment (in Thunderbird):
Hash lookup
To shorten email processing time MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can be configured to perform hash lookups to the MetaDefender Core backend.
If the email header, body or attachment is found by the hash, then it won't be sent to MetaDefender Core backend for scanning or processing. This way the scanning and processing time can be saved.
The MetaDefender Core backend will return the cached scan results and the cached processed version of the header, body or attachment.
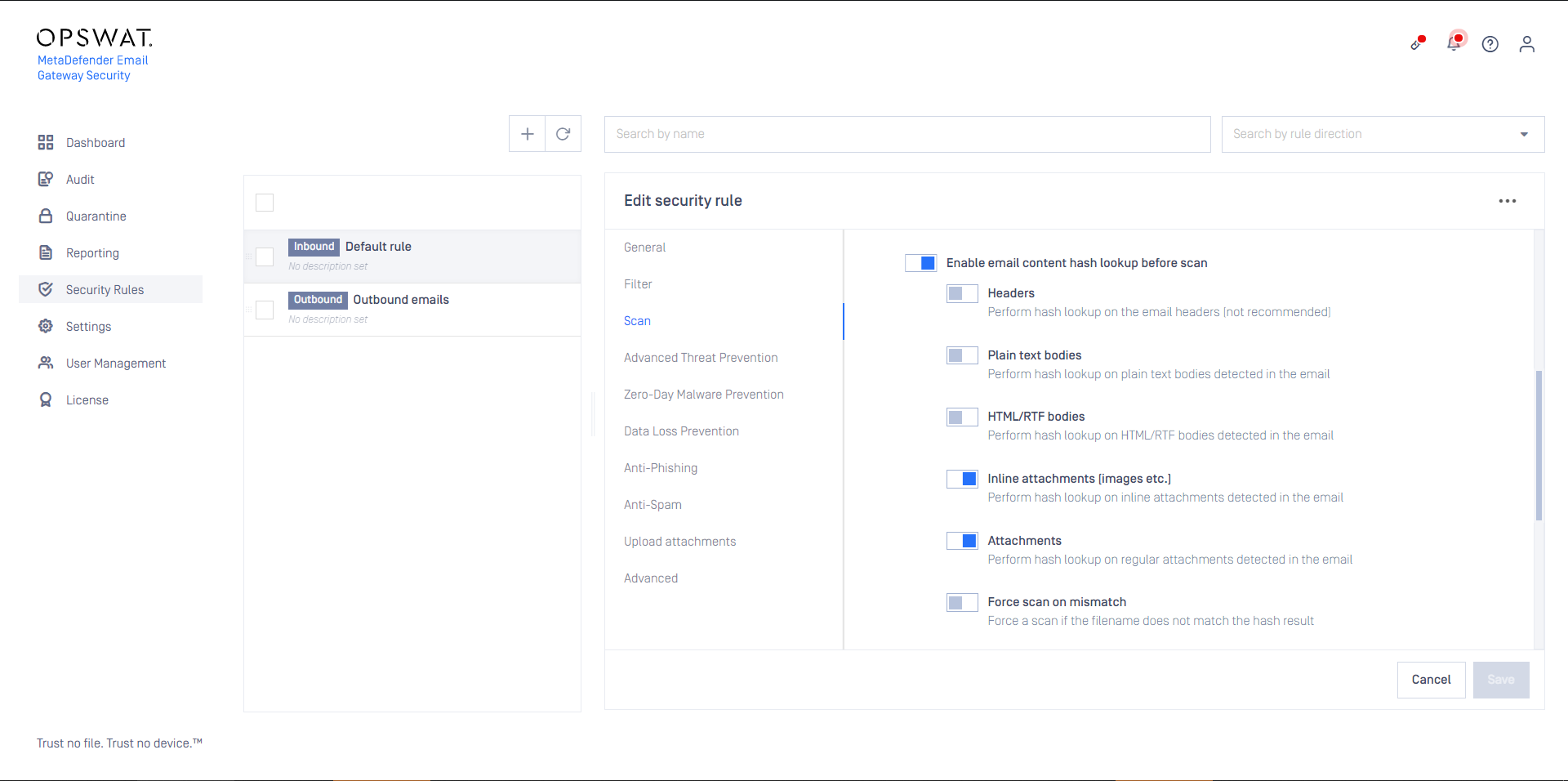
Email headers are always different, but bodies and attachments can be the same among separate emails (for example in case of a newsletter that is sent to hundreds of recipients within an organization). MetaDefender Cloud Email Security comes with reasonable defaults to do hash lookup on attachments (both inline and non-inline attachments).
Hash lookups give a benefit only when parts of the email were previously scanned and exist in the cache.
If the email part does not exist in the cache, then the time of the hash lookup adds to the time of the processing and as so for such a case the total processing time will be longer than without the hash lookup.
Enabling Force scan on mismatch the hash lookup will be omitted when the actual file name and the cached file name do not match. In this case the header, body or attachment will be forcibly scanned, even if the result already exists in the cache based on the hash of the file.
Advanced Threat Prevention
Using multiscanning, MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can utilize even 20 anti-malware engines to prevent advanced, unknown threats.
On this tab it can be configured what MetaDefender Cloud Email Security should do if its Advanced Threat Prevention feature found malware in one or more components of the email.
If Quarantine original email is enabled, then the original copy of the email is put into the Operating/Quarantine regardless of how Handling of the email is set.
Handling of the email may be:
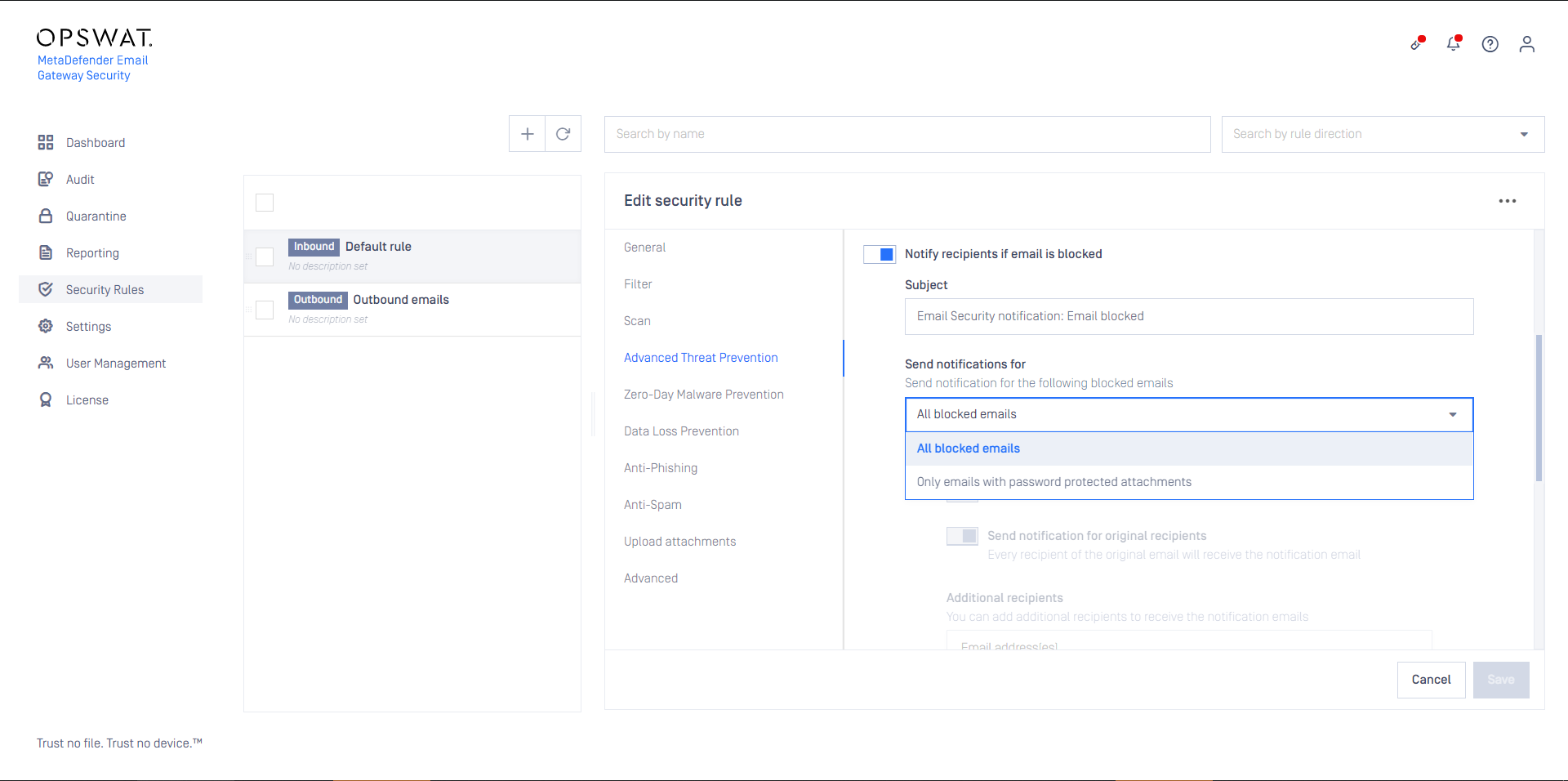
- Block email: the email is blocked. If Notify recipients if email is blocked is enabled, then a notification will be sent to the recipients.
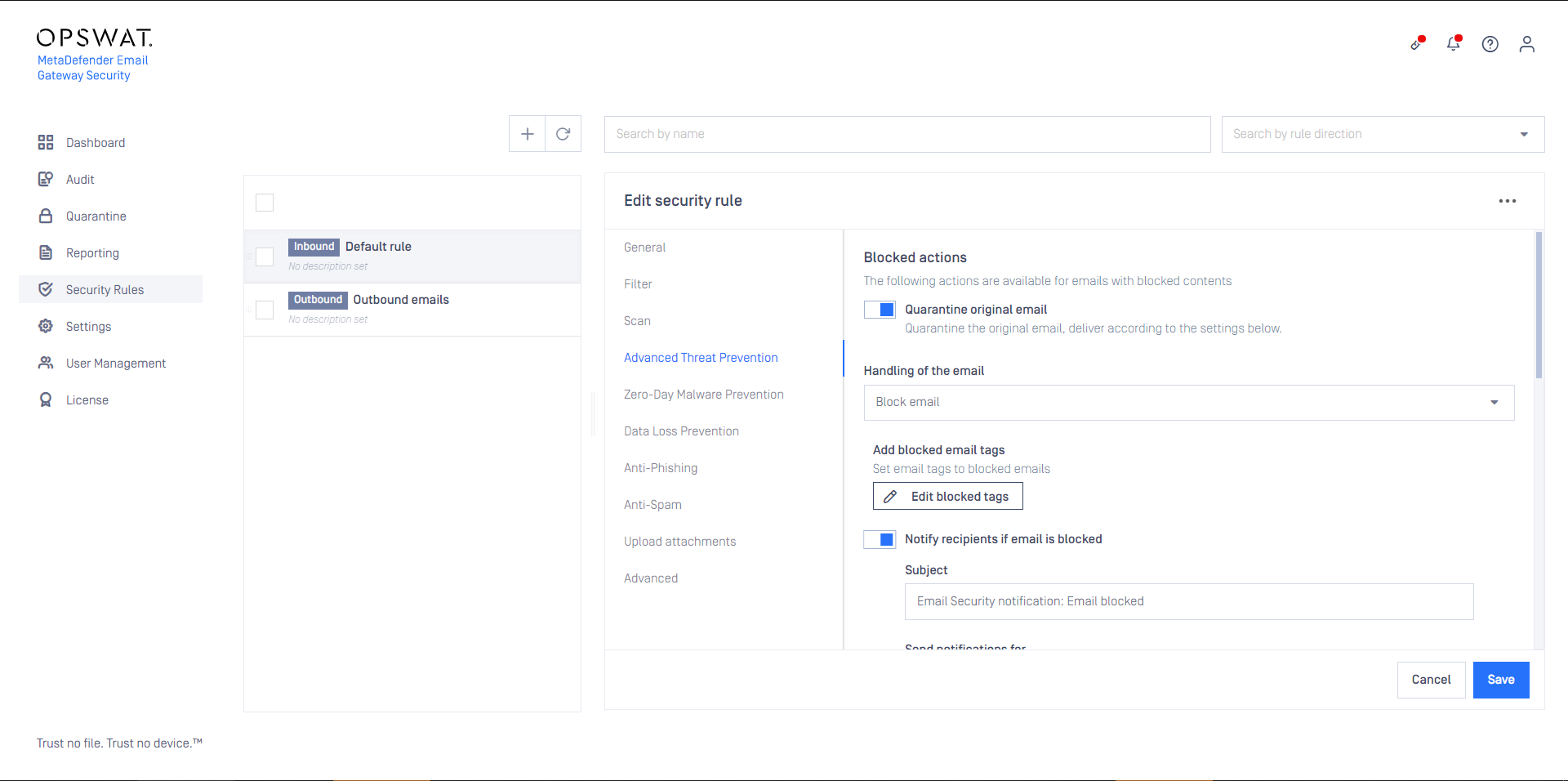
- Delete blocked contents: the blocked contents (e.g. infected attachments) are removed from the email. The remaining is delivered.
- Deliver blocked contents: the email is delivered containing the potentially malicious (infected) contents.
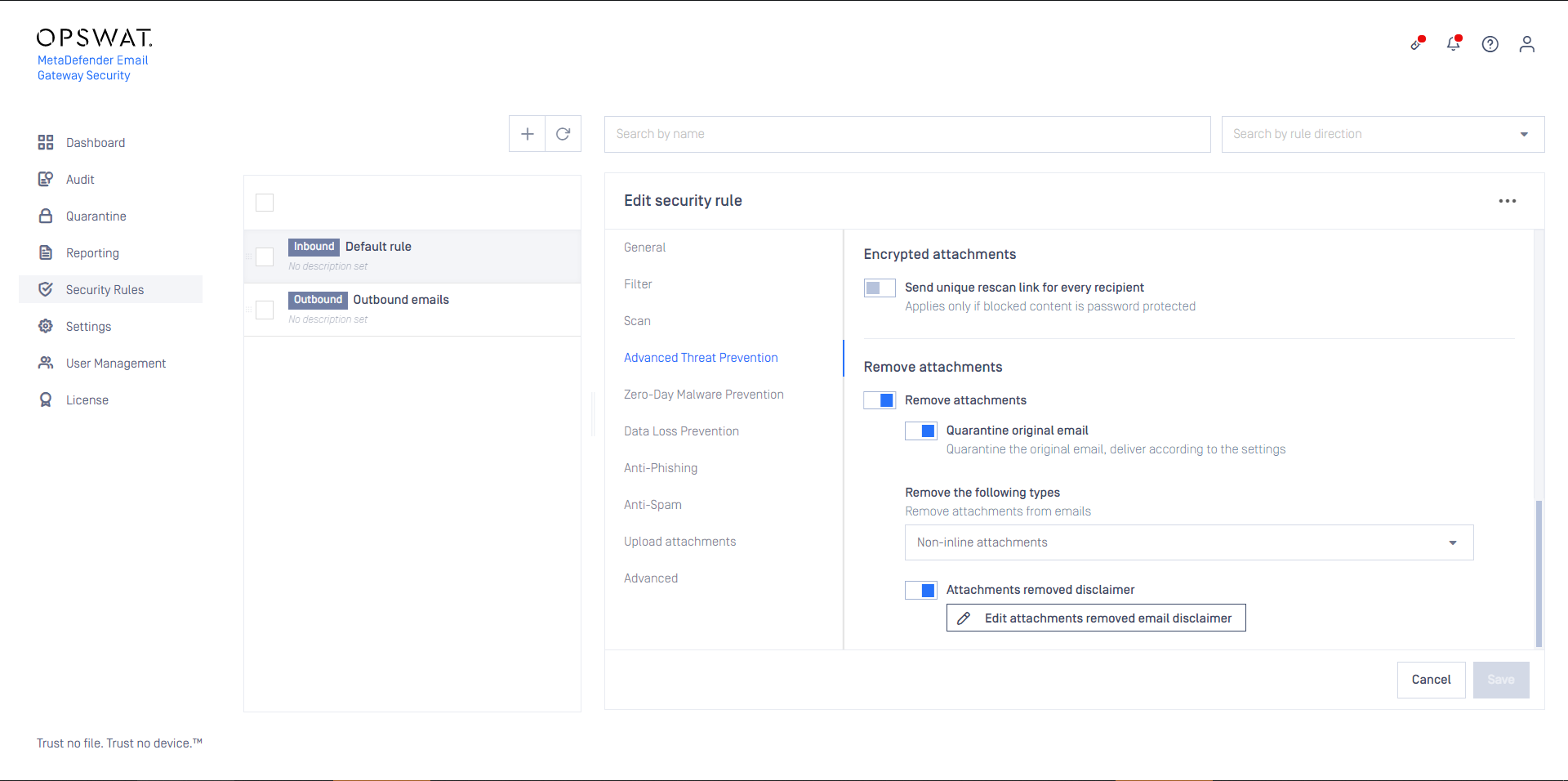
For Delete blocked contents or Deliver blocked contents options MetaDefender Cloud Email Security provides customization to remove attachments.
Selecting Deliver blocked contents will deliver potentially malicious contents to recipients.
If MetaDefender Cloud Email Security is set to Notify recipients if email is blocked then notifications may be limited to the case of emails with password protected attachments. To do so set Send notifications for to Only emails with password protected attachments.
Zero-Day Malware Prevention
Using content disarm and reconstruction, MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can prevent zero-day malware in over 100 common file types.
On this tab it can be configured what MetaDefender Cloud Email Security should do if its Zero-Day Malware Prevention feature applied disarm and reconstruction to one or more components of the email.
If Quarantine original email is enabled, then the original copy of the email is put into the Operating/Quarantine.
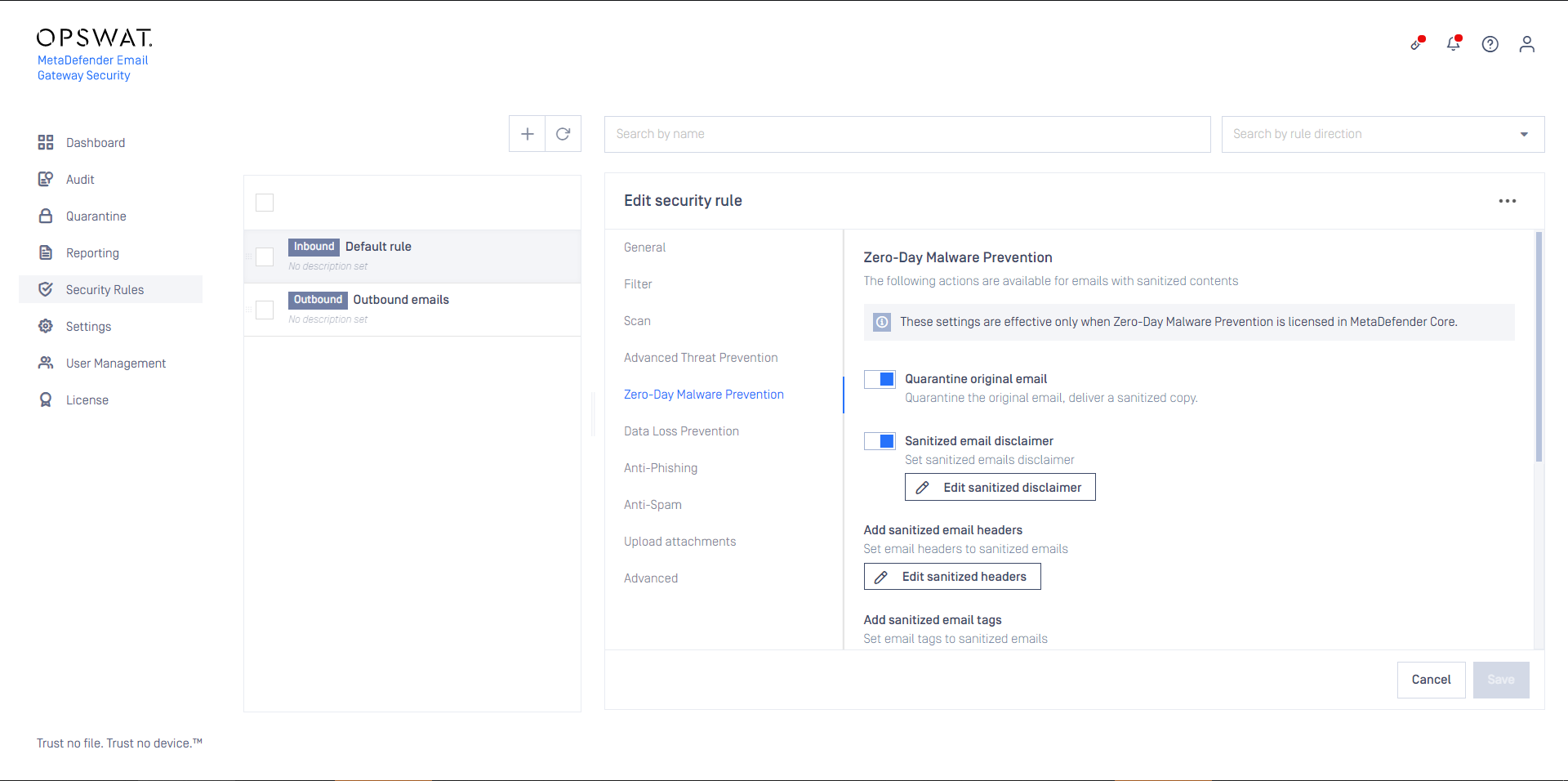
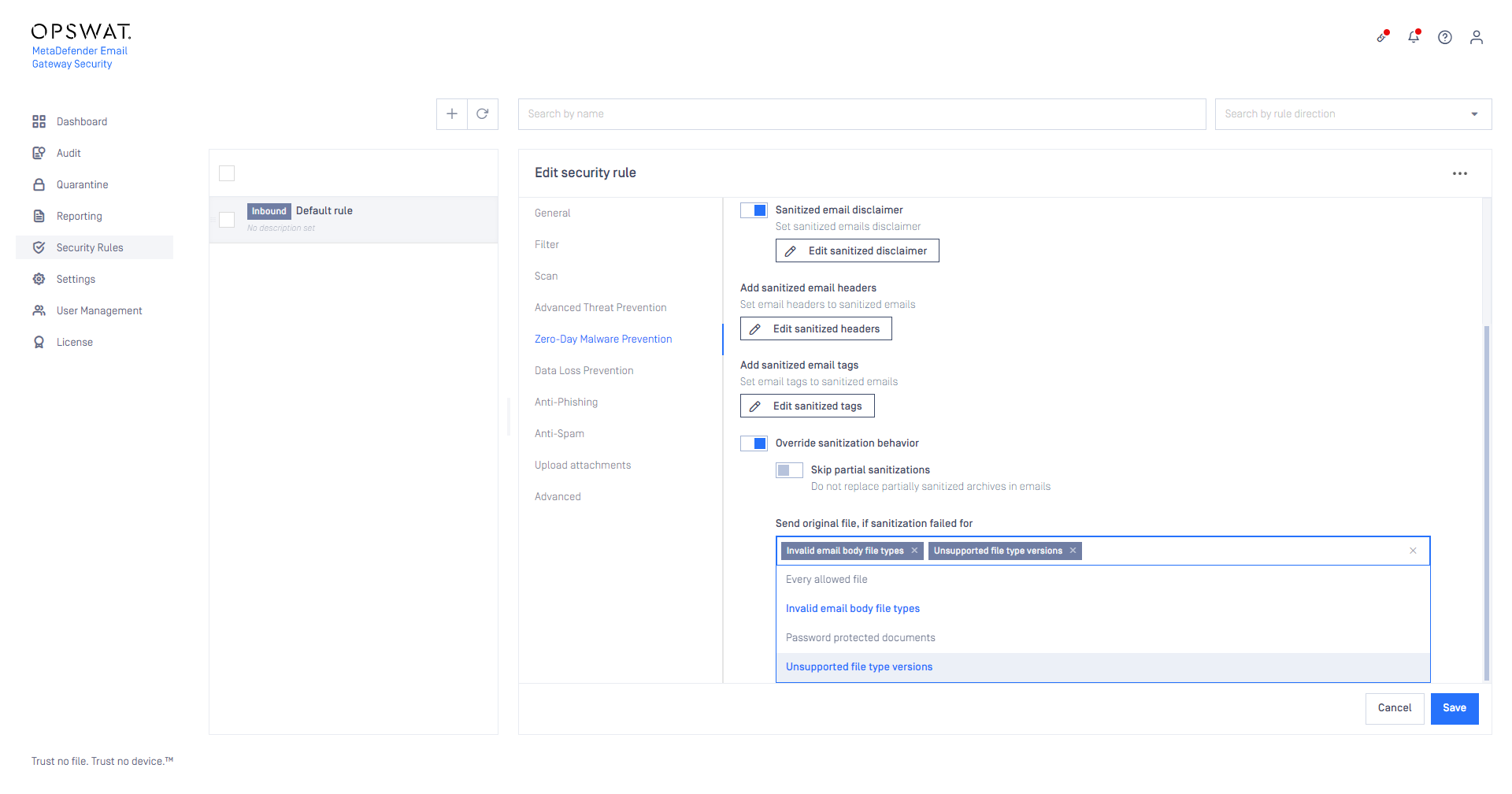
Overriding sanitization behavior
Sanitization can fail for two reasons in MetaDefender Cloud Email Security:
- The Deep CDR engine fails to sanitize the file (the file type version is not supported or the engine has other trouble)
- The email body is converted by the Deep CDR engine to a file type that is not supported as email body (e.g. the plain text body is converted to pdf).
Only the following email body file type conversions are allowed in MetaDefender Cloud Email Security:
- txt
txt - html
html - html
txt
Any other email body file type conversion set in the Deep CDR engine will cause a sanitization failure.
By default MetaDefender Cloud Email Security removes all the bodies and attachments for which the sanitization failed from the email to be delivered.
The default behavior can be customized enabling the Override sanitization behavior option and selecting the cases for which MetaDefender Cloud Email Security should deliver the original copy of the body or attachments in case of a sanitization failure.
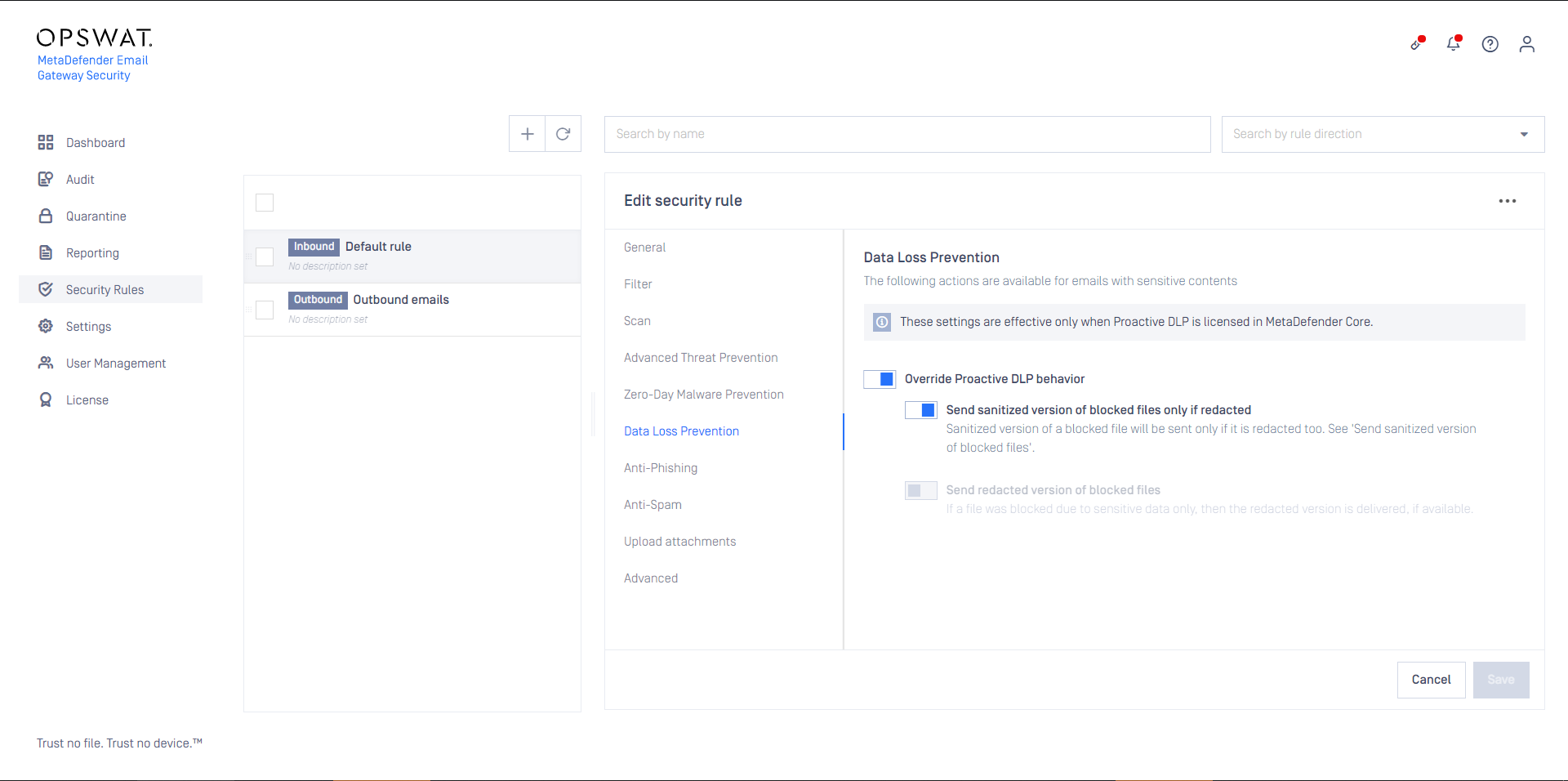
Data loss prevention
When Proactive Data Loss Prevention is licensed, certain behavior of the technology can be modified on this tab.
Enabling Send sanitized version of blocked files only if redacted can influence the setting under Zero-Day Malware Prevention / Override sanitization behavior / Send sanitized version of blocked files. A sanitized version is sent only, if it could have been successfully redacted, too.
As of today, Proactive DLP can detect sensitive data in PowerPoint presentations (.ppt), but can not redact.
If both Send sanitized version of blocked files and Send sanitized version of blocked files only if redacted then the sanitized version won’t be sent for .ppt files as they can not be redacted.
Enabling Send redacted version of blocked files will deliver redacted email contents - when redaction is available for the file type - if they were blocked due to sensitive data only.
Malware infected contents won’t be delivered even when this option is enabled.
Anti-phishing and anti-spam
MetaDefender Cloud Email Security provides cutting edge anti-spam and anti-phishing protection. Spam and phishing are handled by the same component so the settings are quite similar. For specific settings see the two subsections at the end of this section.
Probability level
The anti-spam and anti-phishing component use the Probability level setting to tell the component what it should treat as Possible spam or Possible phishing (for details see Operating/Email classifications) and what is known Spam or Phishing (for details see Operating/Email classifications).
MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can assign the following probability levels to spam and phishing emails:
- 0: not a spam or phishing,
- 1-8: possible spam or phishing (the higher the number, the higher the probability),
- 9: known spam or phishing.
The levels 0 and 10 are not configurable.
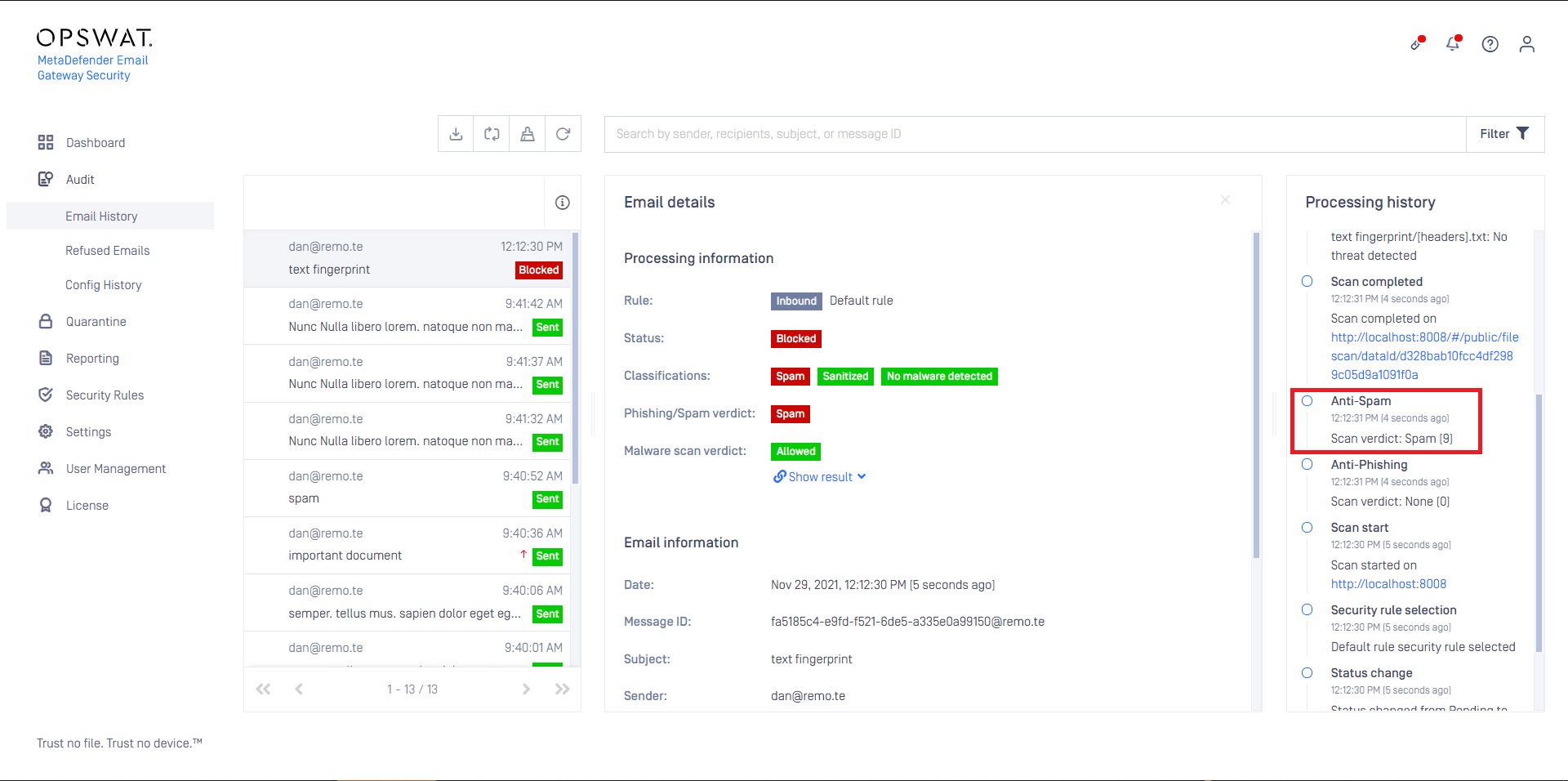
In the example below MetaDefender Cloud Email Security assigned the spam probability level 9 to the email.
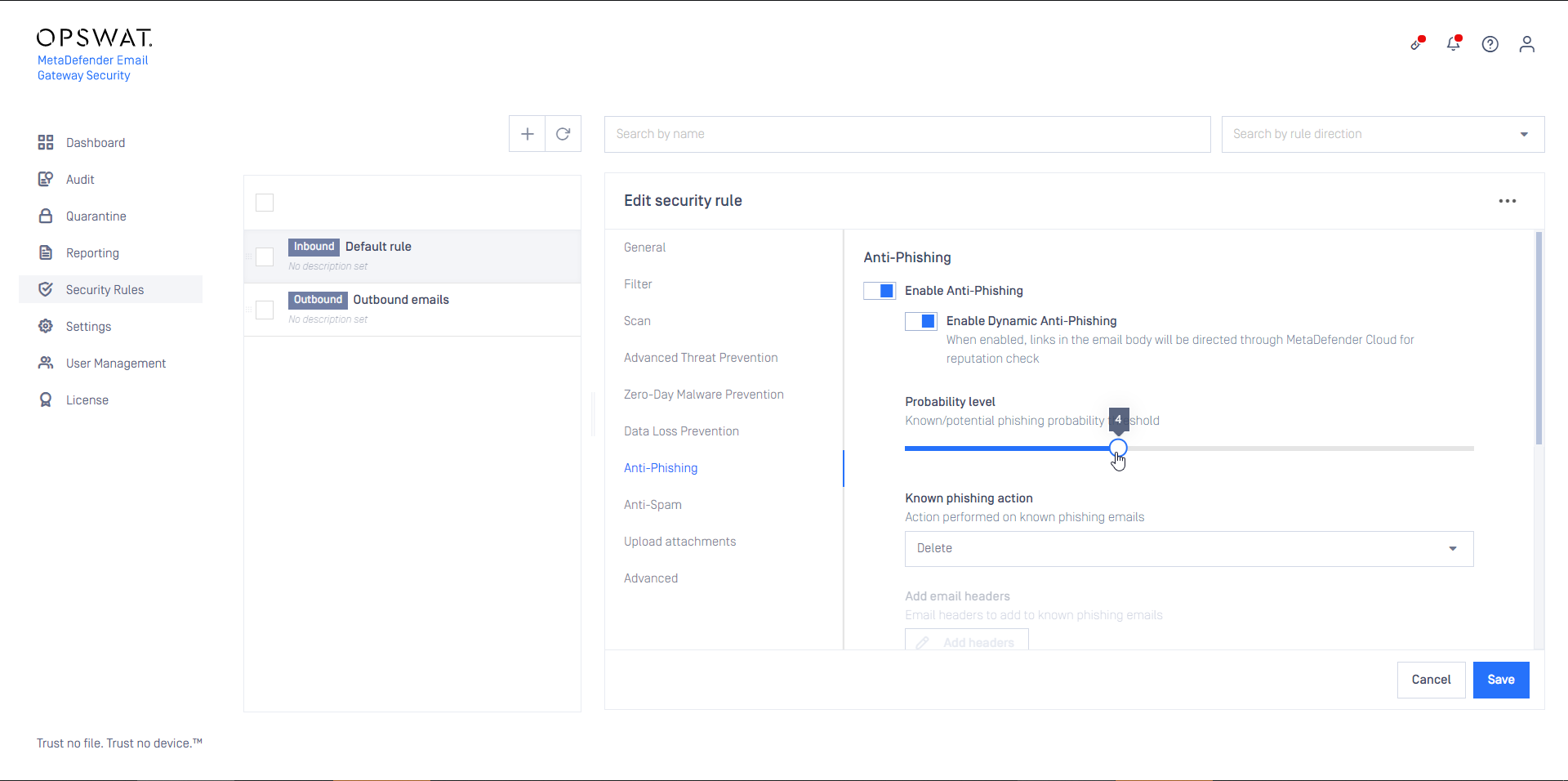
In the example below the Probability level is set to 4.
It means, that
- all email that’s probability level is higher or equal than 4, will be treated as known Phishing, while
- all email that’s probability level is lower than 4 will be treated as Possible phishing
- (all email that’s probability level is 0 will be treated as not phishing)
If the Probability level is set to 9, then only emails with probability level 9 will be treated as known Spam or Phishing. Emails with levels 1-8 will be treated as Possible spam or Possible phishing.
Actions for known or potential phishing and spam
Based on the probability level, MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can be configured to handle known and potential spam or phishing in different ways.
The following actions are available:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Reject | Perform an IP reputation check and if turns out to be a (potential) spam or phishing sender, then reject the email on the SMTP level. The email will show up in Audit > Refused Emails. |
| Delete | Receive the email, perform an IP reputation and/or content check, and if turns out to be a (potential) spam or phishing, then delete it. The email will show up in Audit > Email History with some additional details as if it was rejected and with the appropriate classifications added (for details see Operating/Email History and Operating/Email classifications). |
| Quarantine | Receive the email, perform an IP reputation and/or content check, and if turns out to be a (potential) spam or phishing, then quarantine it (just like infected emails). The email will show up in Quarantine with the appropriate classifications added (for details see Operating/Quarantine and Operating/Email classifications). |
| Deliver | Receive the email, perform an IP reputation and/or content check, but even if it turns out to be a (potential) spam or phishing, deliver it (just like clean emails). The email will show up in Audit > Email History with the appropriate classifications added (for details see Operating/Email History and Operating/Email classifications). |
| Add headers | If the known or potential action is set to Deliver, then headers can be added to the email for each case. These headers can indicate for example to the receiving side that a (potential) phishing has just been received. |
Anti-spam specific settings
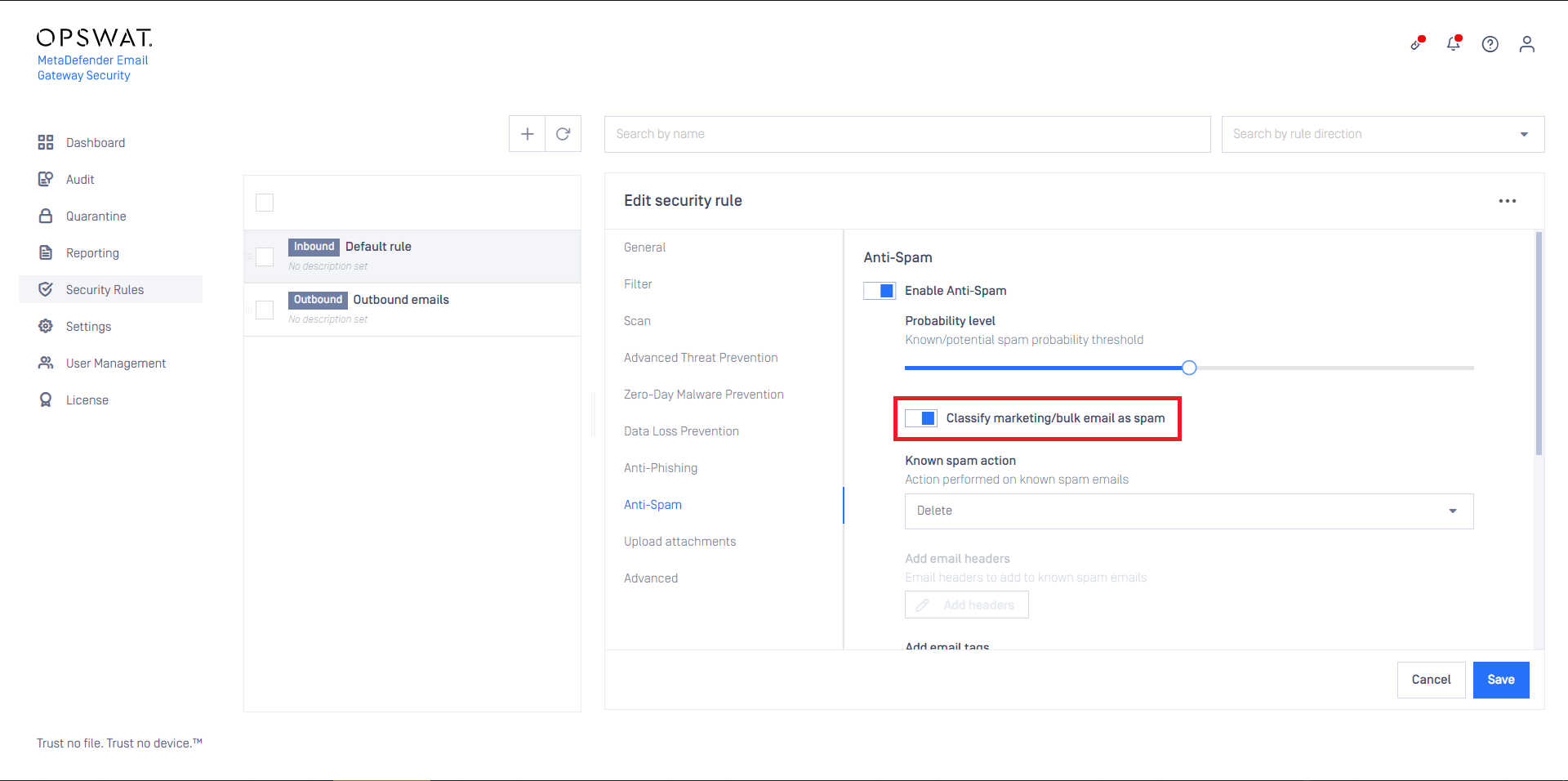
MetaDefender Cloud Email Security’s ant-spam component can detect some kind of graymail, too. Enabling Classify marketing/bulk email as spam will instruct MetaDefender Cloud Email Security to treat email detected as marketing and bulk as spam and handle it according to the anti-spam settings.
Anti-phishing specific settings
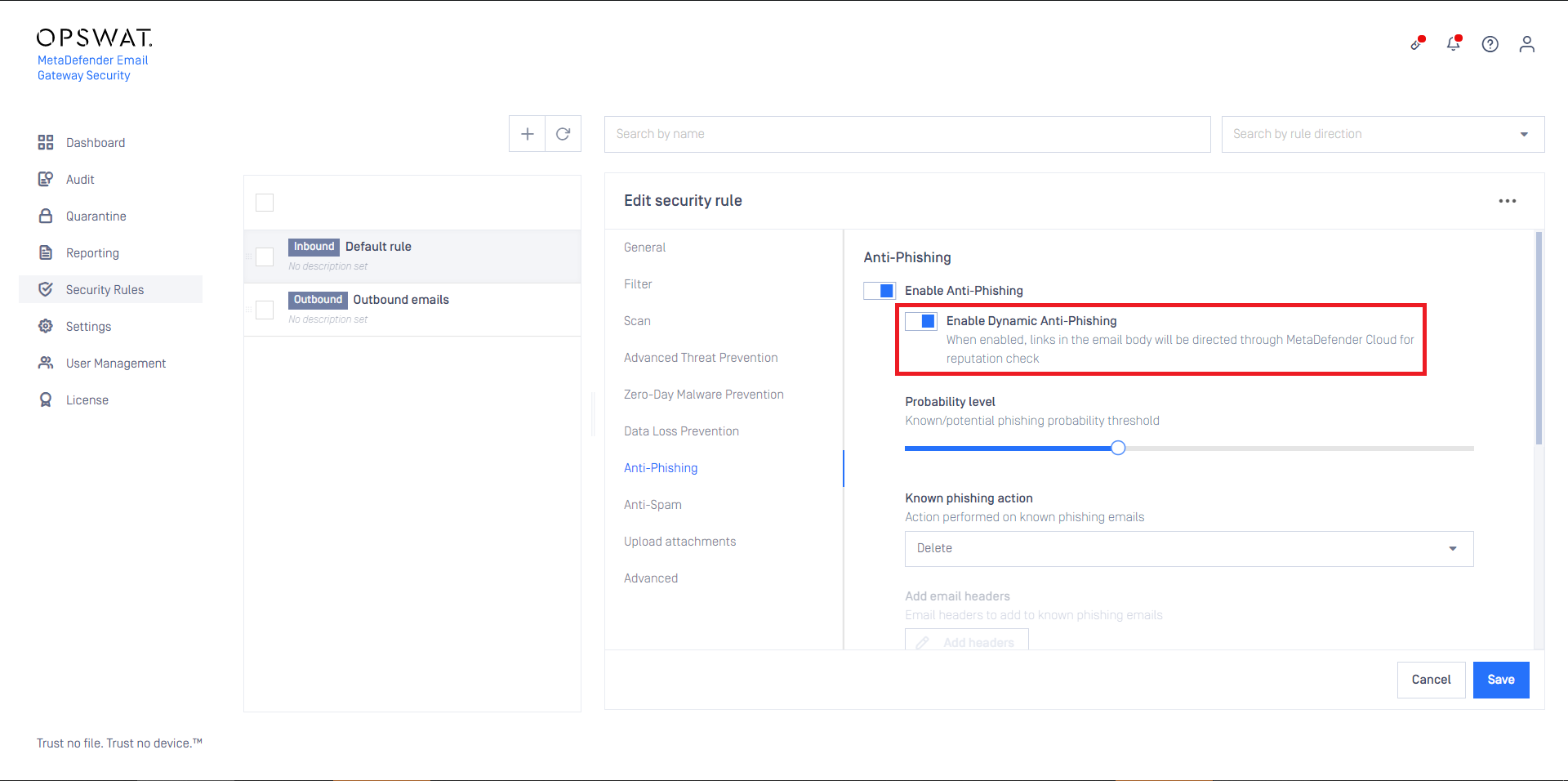
If Enable Dynamic Anti-phishing is turned on, all links in the email body will be redirected through MetaDefender.comSafe URL redirect service for URL reputation check.
For this functionality to work properly, MetaDefender Cloud’s Reputation API must be licensed.
For demonstration purposes, however, a limited number of Reputation API calls are available for free of charge.
Authenticated Received Chain (ARC)
In most of the cases Cloud Email Security acts as an intermediate email processing server between the original sender and the intended recipient. As Cloud Email Security is not the original sender the DKIM check will fail on the recipients side. Cloud Email Security usually modifies emails (adds custom headers, and with Deep CDR and Proactive DLP it often modifies the email bodies and attachments) and as a result the DKIM verification will fail at the recipient.
Authenticated Received Chain is an email authentication system designed to allow an intermediate mail server to sign an email's original SPF and DKIM authentication results. This allows a receiving service to validate an email when the email's SPF and DKIM records are rendered invalid by an intermediate server's processing.
With ARC, an intermediate processing server can digitally sign the SPF/DKIM results of the preceding server and its own modifications to the email with DKIM-like signatures.
To enable ARC, go to Security Rules > rule / Anti-Phising and enable the Sign with DKIM (ARC) option.
As a prerequisite DKIM certificates need to be configured under Settings > Security > Certificates.
For details see Transport Layer Security.
The following options need to be set:
- Certificate: Certificate in Settings > Certificates to be used to create the ARC signatures.
- Signer Domain: The domain for which to create the DKIM-like ARC signatures. The next email processing server will look up the public keys in the DNS records of this domain to verify Email Gateway Security's ARC signatures.
- DNS Selector: Specifies the DNS location of the public key. Receiving servers use this selector to find the public key.
Advanced
The advanced settings define certain exceptions for the rule from the default behavior.
MetaDefender Cloud Email Security can be configured to retry to process emails. If an option is set to Retry or Bypass if all retry fail then the retry mechanism under Settings > General / Email is applied.
For details see Configuration/Settings.
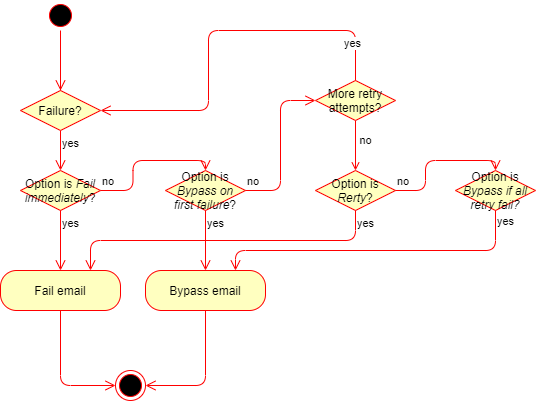
If Bypass on first failure or Bypass if all retry fail is configured for certain settings, and the email gets bypassed finally, then the original, potentially harmful email is delivered.
The recipient may be notified about the fact of bypassing. To do so set the Bypass email disclaimer. For details see Configuration/Disclaimers.