Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Version 5.7.0
| Release date | Scope |
|---|---|
| Oct 31th, 2023 | MetaDefender Email Gateway Security 5.7.0 focuses on new features, such as a new My OPSWAT integration; Trusted senders list; QR code sanitization; Improved Anti-Phishing detection and more. |
Breaking Changes
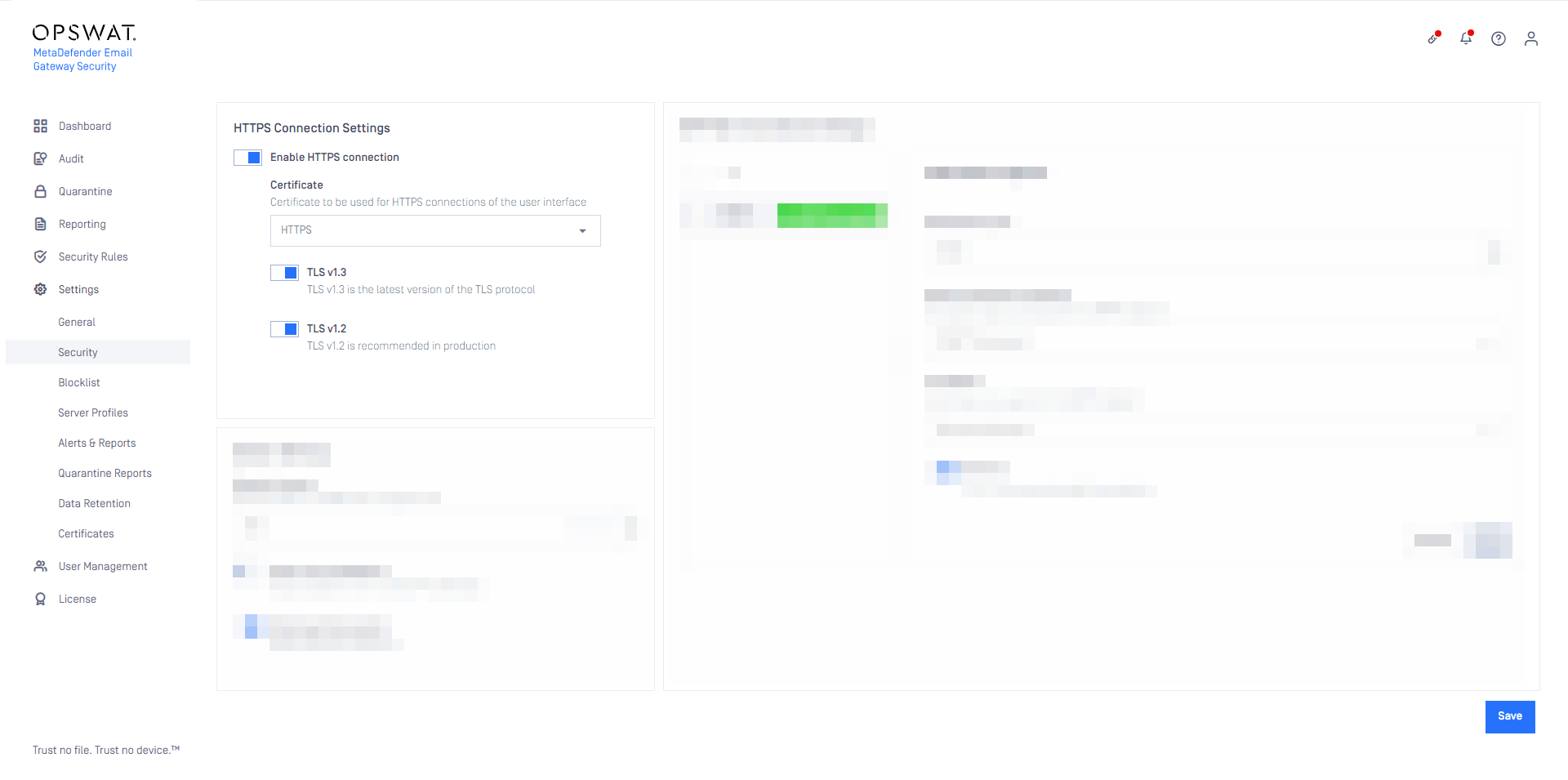
TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 are no longer supported
Transport Layer Security (TLS) versions 1.0 and 1.1 are protocols used to establish encrypted channels over computer networks. Due to changing regulatory standards and the discovery of security vulnerabilities in TLS 1.0 and 1.1, we advise customers to transition away from these versions and adopt TLS 1.2 or later in their environments.
Before upgrading to MetaDefender Email Gateway Security 5.7.0, ensure your deployment is already utilizing TLS 1.2 or a higher version.
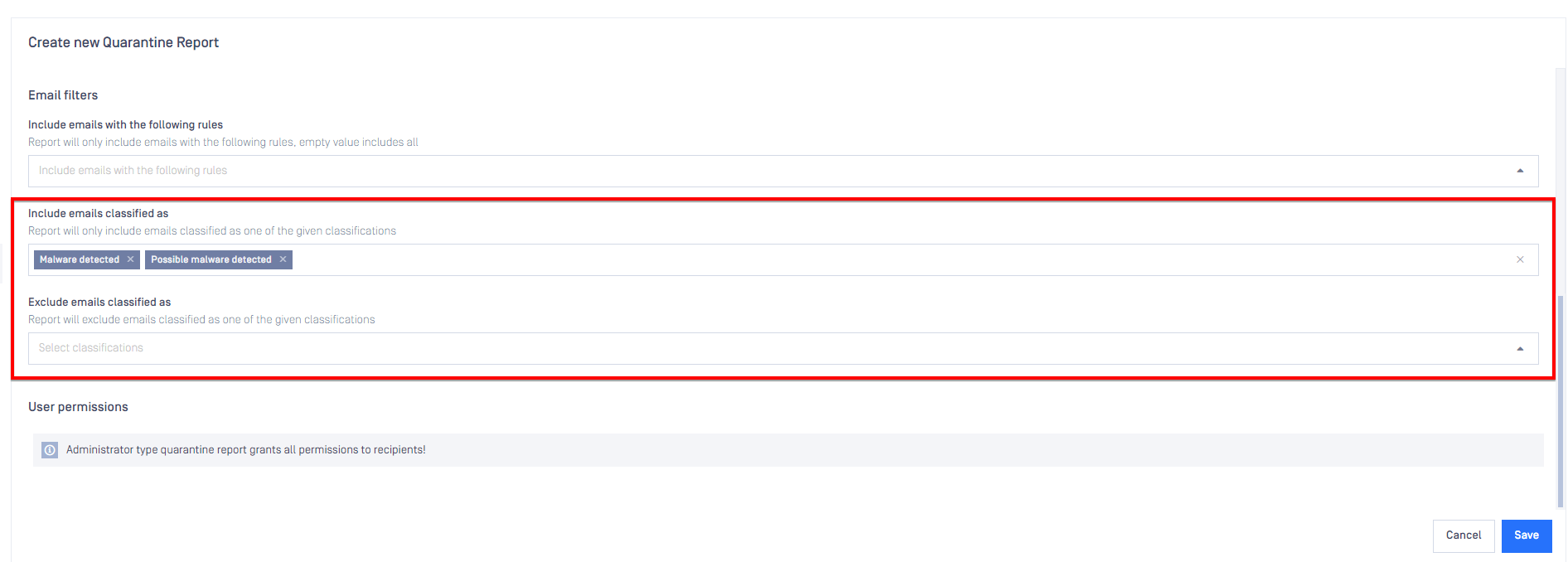
Quarantine reports
Email Gateway Security 5.7.0 contains breaking changes to the Quarantine Report classification filter selection. The filter now uses the logical OR operator when selecting emails to include in the report.
New & improved
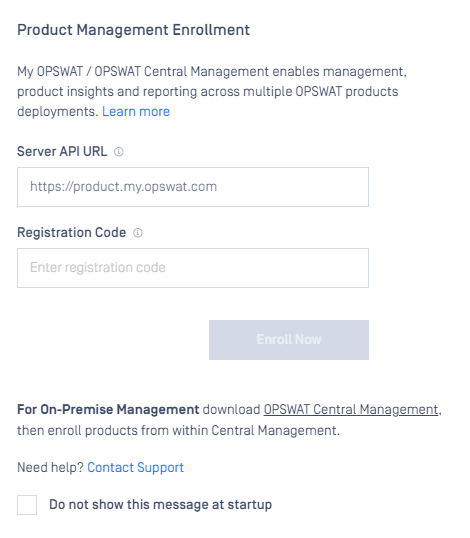
Integrate with My OPSWAT
It is now possible to enroll MetaDefender Email Gateway Security to the My OPSWAT portal. Enrolling the instance will allow you to monitor you licenses and the overall health of each enrolled instance. Upon logging in to the MetaDefender Email Gateway Security Administration console you will be prompted with an option to enroll the product. For more information, refer to the My OPSWAT documentation.
It is still possible to connect MetaDefender Email Gateway Security to your on-premise Central Management.
QR code sanitization
With the CDR engine version 6.7 QR code sanitization is available for emails.
The QR code processing can be configured in the CDR engine. Two modes of operation are supported:
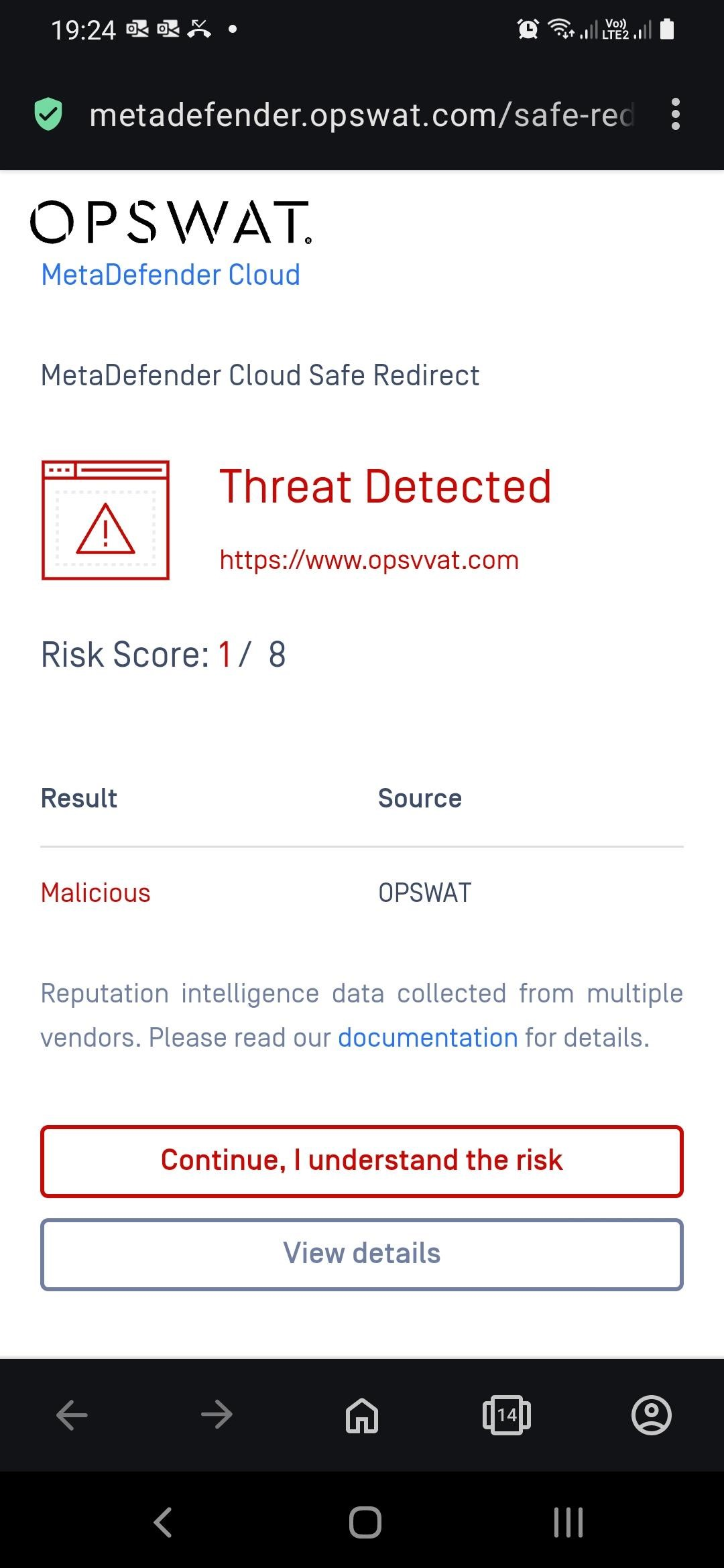
- Prefix the URL encoded by the QR code (e.g. redirect the URL through OPSWAT Safe URL Redirect for time-of-click analysis; for details see Dynamic anti-phishing).
- List the URL encoded by the QR code among the CDR-ed URLs in the appropriate disclaimer (for details see Hyperlink reference listing).
Example
Original email with QR code:
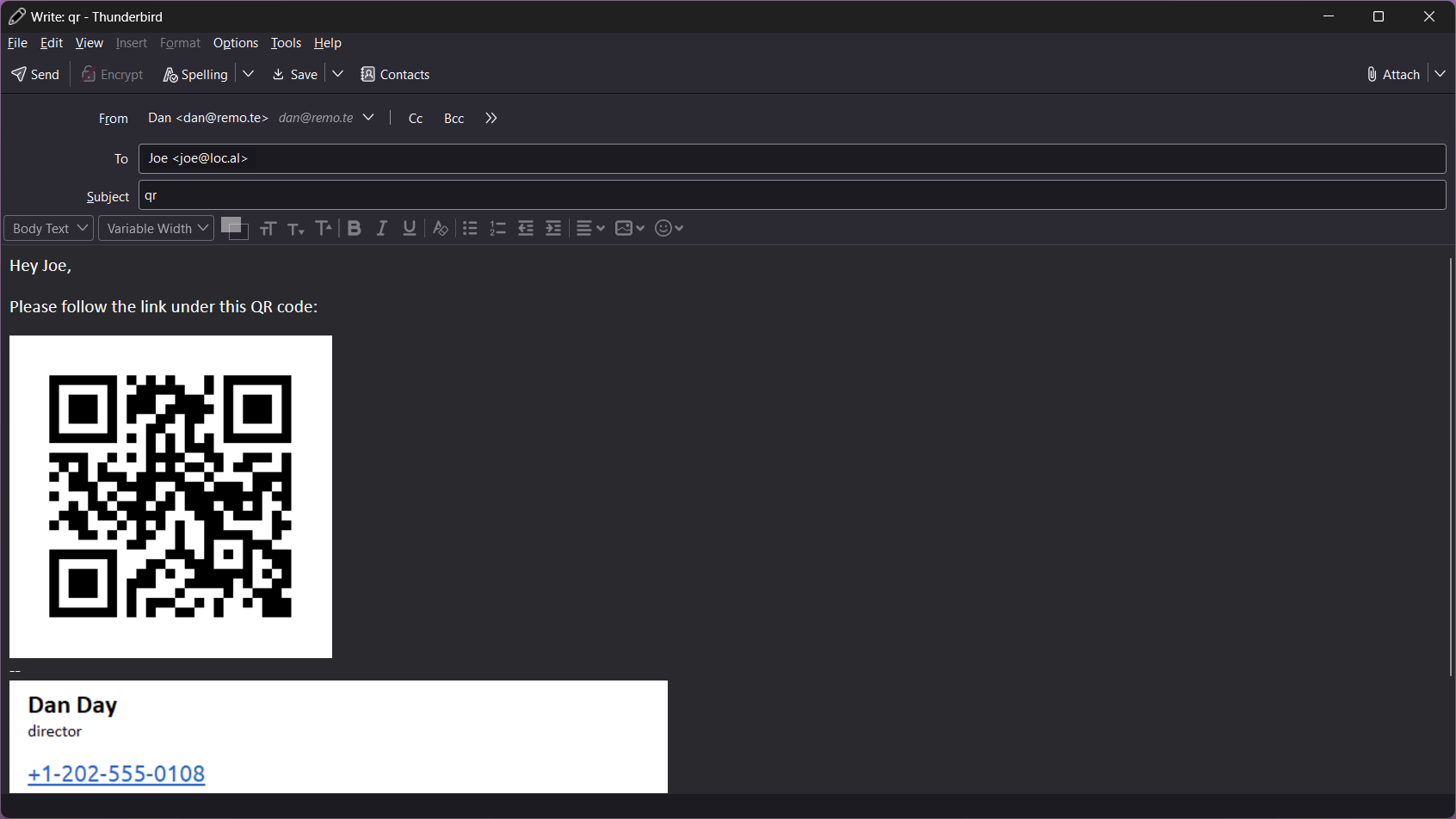
Sanitized email with the processed QR code (note the changes in the QR code itself compared to the original):
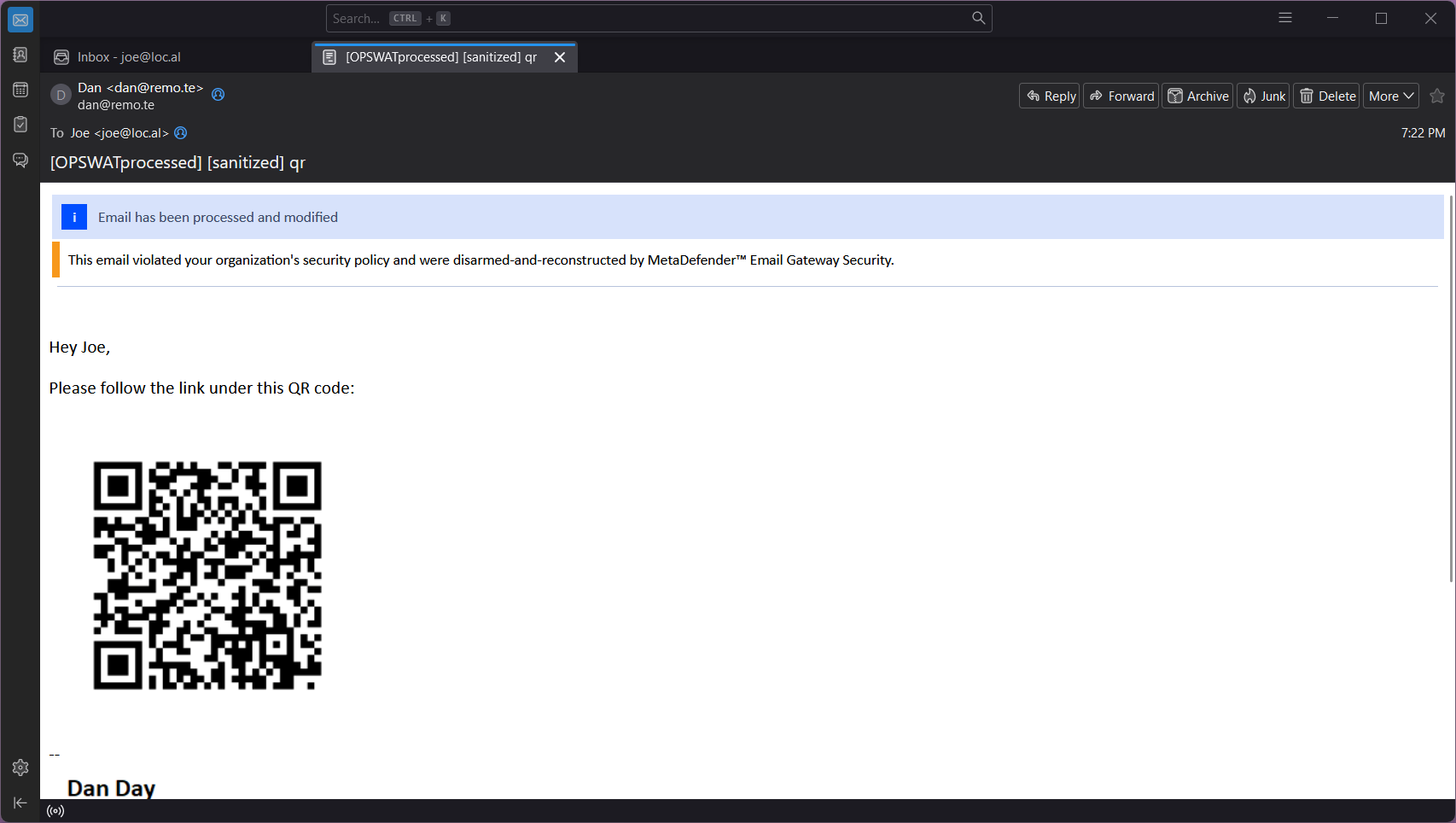
Reading the QR code activates Safe URL Redirect (that is what was configured in this case in the CDR engine):
Improved Anti-Phishing (SPF & DKIM, Dynamic Anti-Phishing)
Email Gateway Security now check Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) alignments or violations of emails.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an method which ensures the sending mail server is authorized to originate mail from the email sender's domain. For details see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sender_Policy_Framework.
DKIM allows the receiver to check that an email that claimed to have come from a specific domain was indeed authorized by the owner of that domain. It achieves this by affixing a digital signature, linked to a domain name, to each outgoing email message. For details see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DomainKeys_Identified_Mail.
New classifications has been introduced that allows observing SPF verification & DKIM validation results from the Email History & Quarantine views. For details about classifications see Email classifications.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF)
The following new classifications are available:
- SPF Pass
- SPF Neutral
- SPF Soft fail (Triggers Known Phishing)
- SPF Fail (Triggers Known Phishing)
- SPF No record
- SPF Error
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
The following new classifications are available:
- DKIM Valid
- DKIM Invalid (Triggers Known Phishing)
- DKIM No signature
- DKIM Error
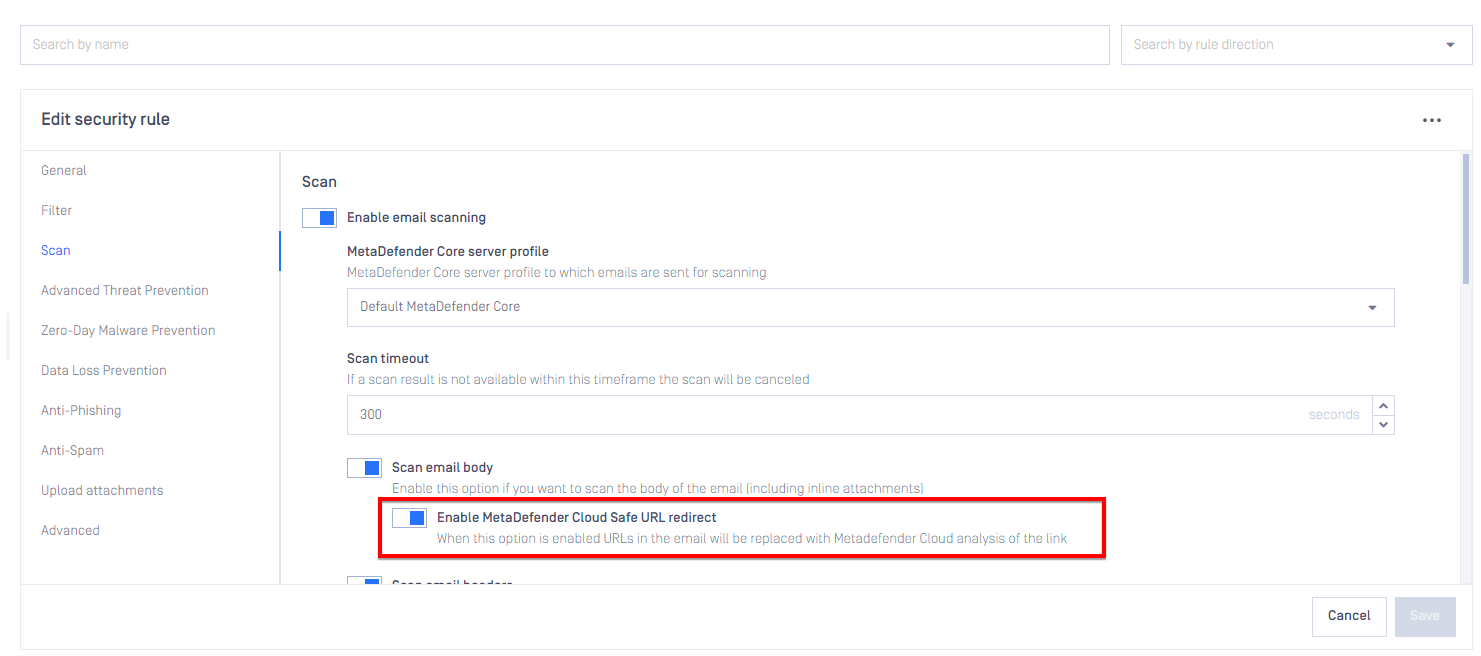
Dynamic Anti-Phishing (MetaDefender Cloud Safe URL redirect)
The Dynamic Anti-Phishing feature has been moved to the Scan tab and renamed MetaDefender Cloud Safe URL redirect. The feature no longer requires an Email Gateway Security Anti-Spam license.
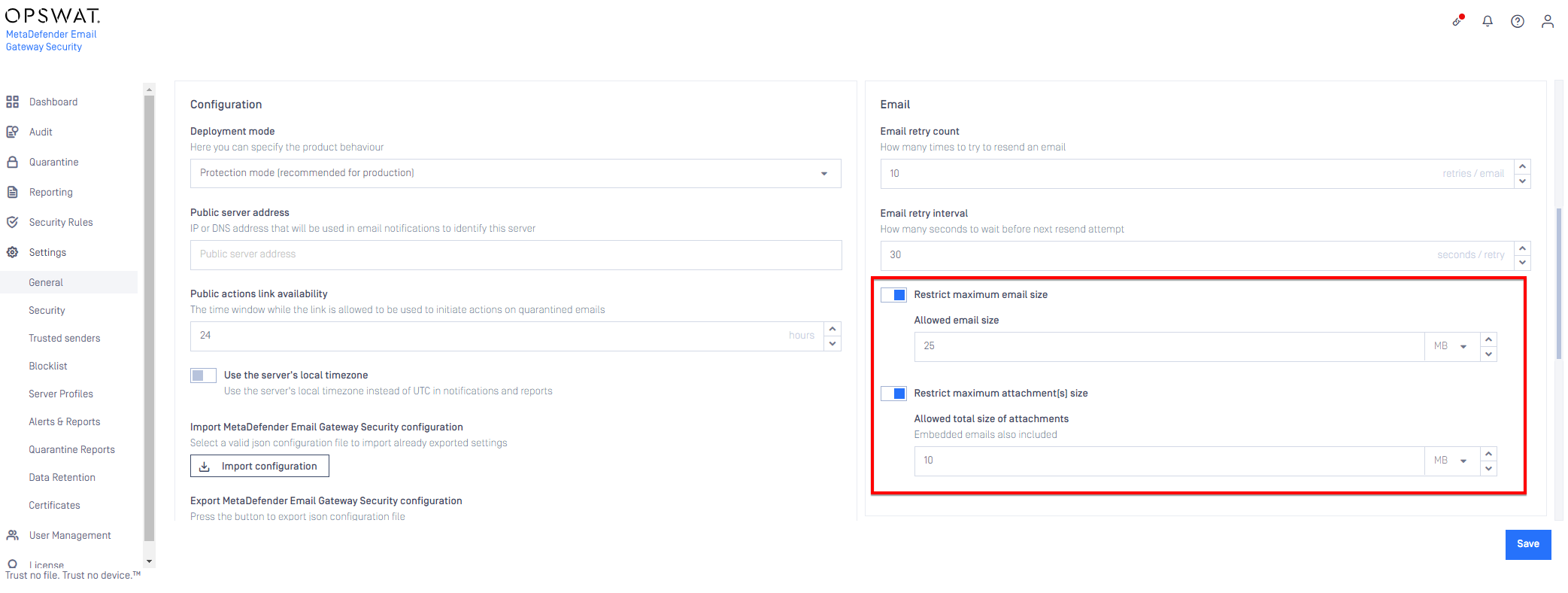
Email/attachment size restrictions
It is now possible to restrict the maximum size of emails (or individual attachments) accepted by Email Gateway Security. Enable and configure limits in Settings > General. For details see Settings.
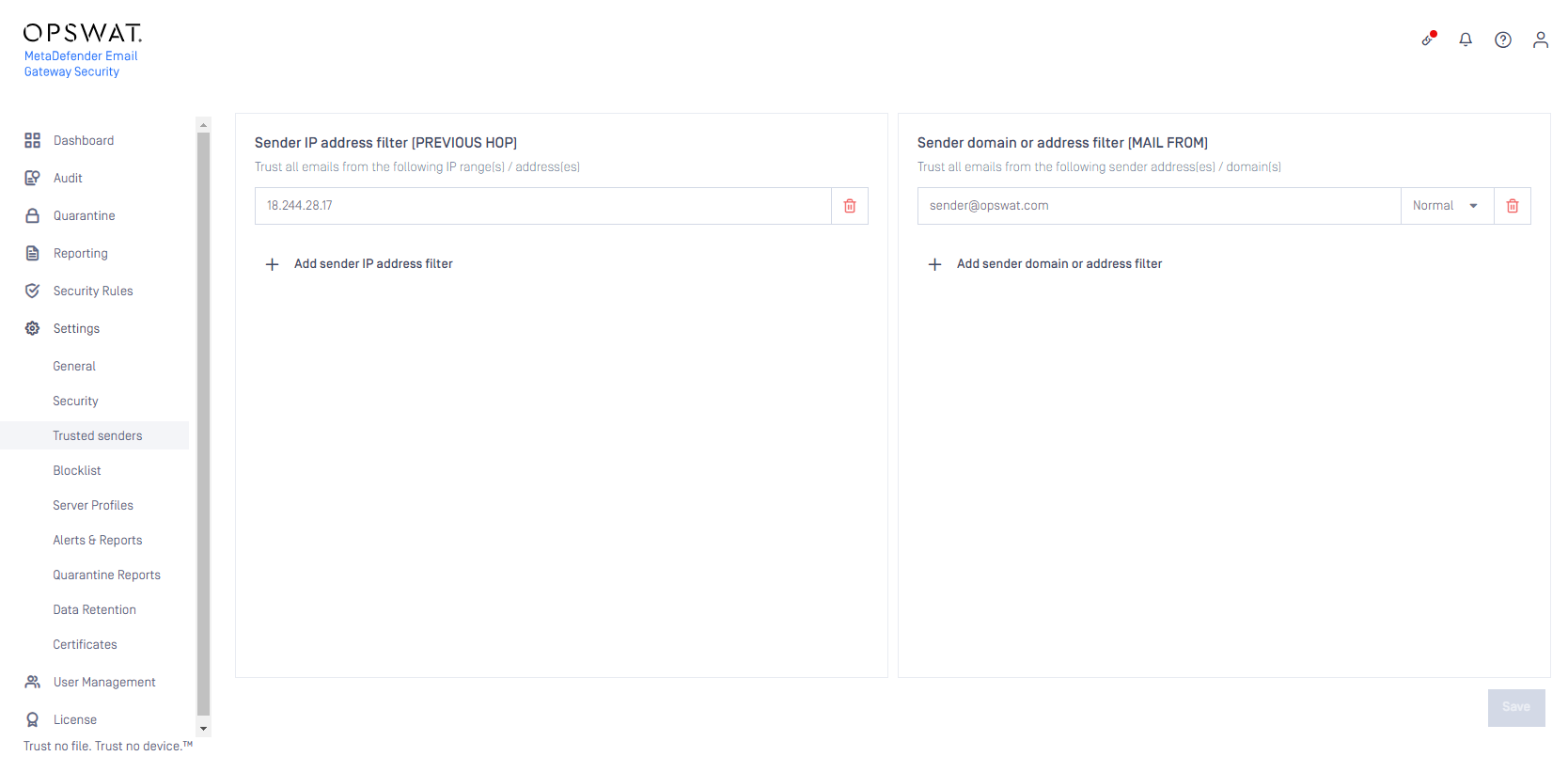
Trusted senders
A global trusted senders list has been added to Email Gateway Security. Both IP/IP ranges & Sender email addresses (including regular expression support) can be added to the list. Any email marked as having a trusted sender will omit the Anti-Spam & Anti-Phishing checks while processing the email (Multi-scanning & sanitization will still be for for trusted senders, provided that the applicable rule has those options enabled)
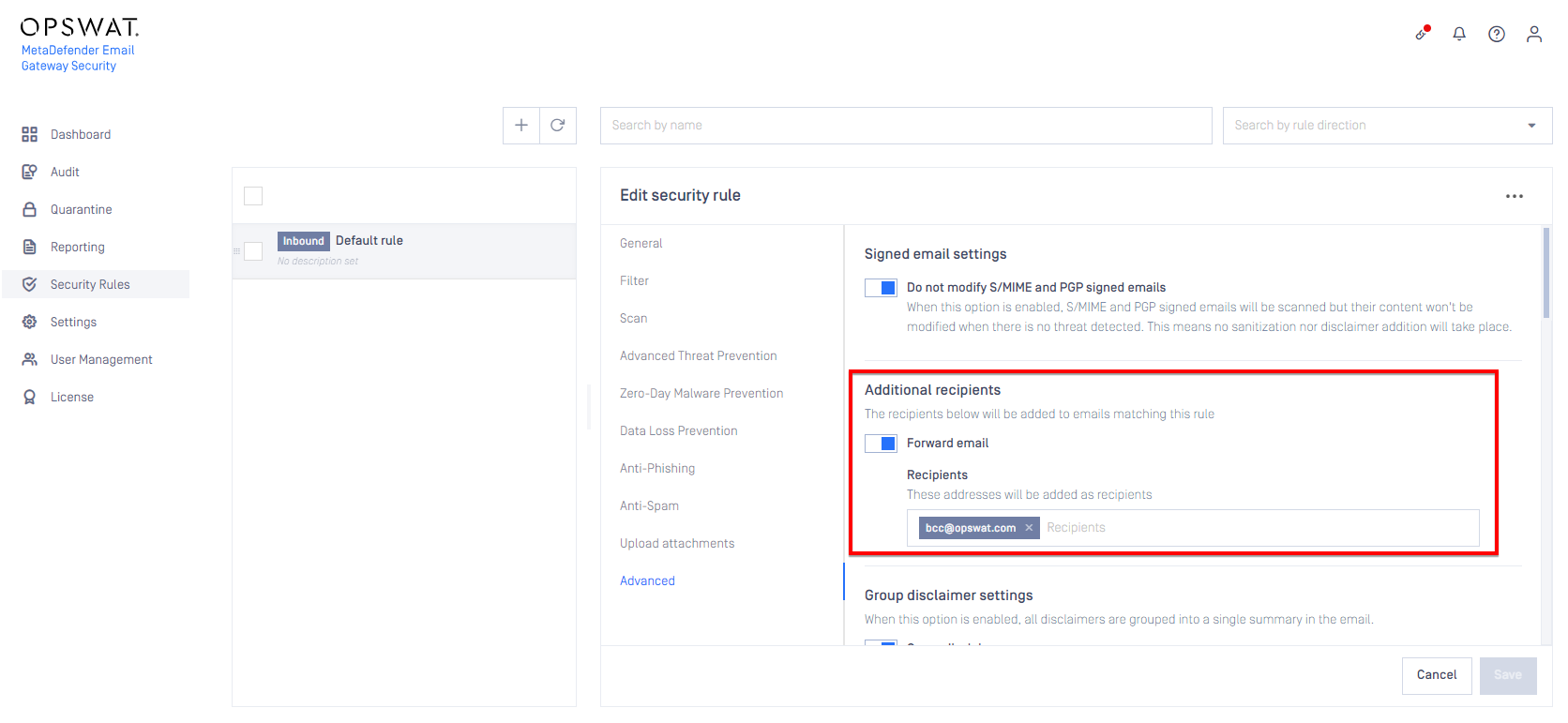
Auto forwarding of emails (Additional recipients)
Any email processed by a rule can now also be forwarded (BCC) to additional recipients. This allows for use cases, such as automatic archiving of emails etc.
Other
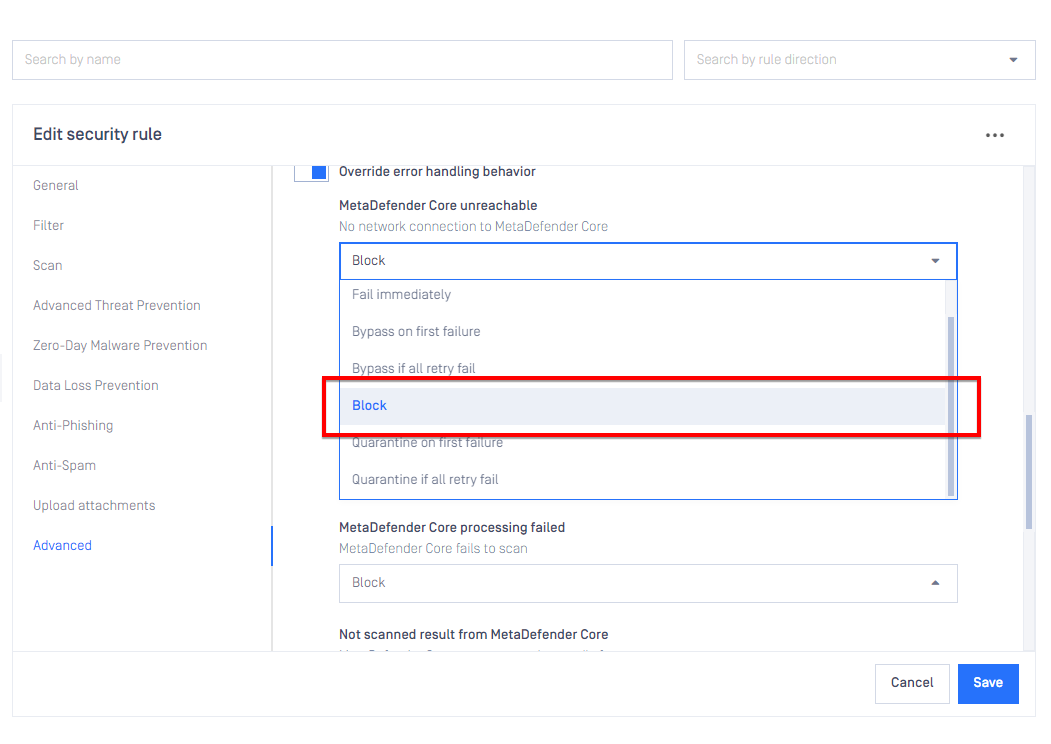
Block option for failure overrides
It is now possible to treat a scan failure etc. as a blocked email result and optionally send a blocked notification about the failure to the recipient or any other destination configured in the security rule.
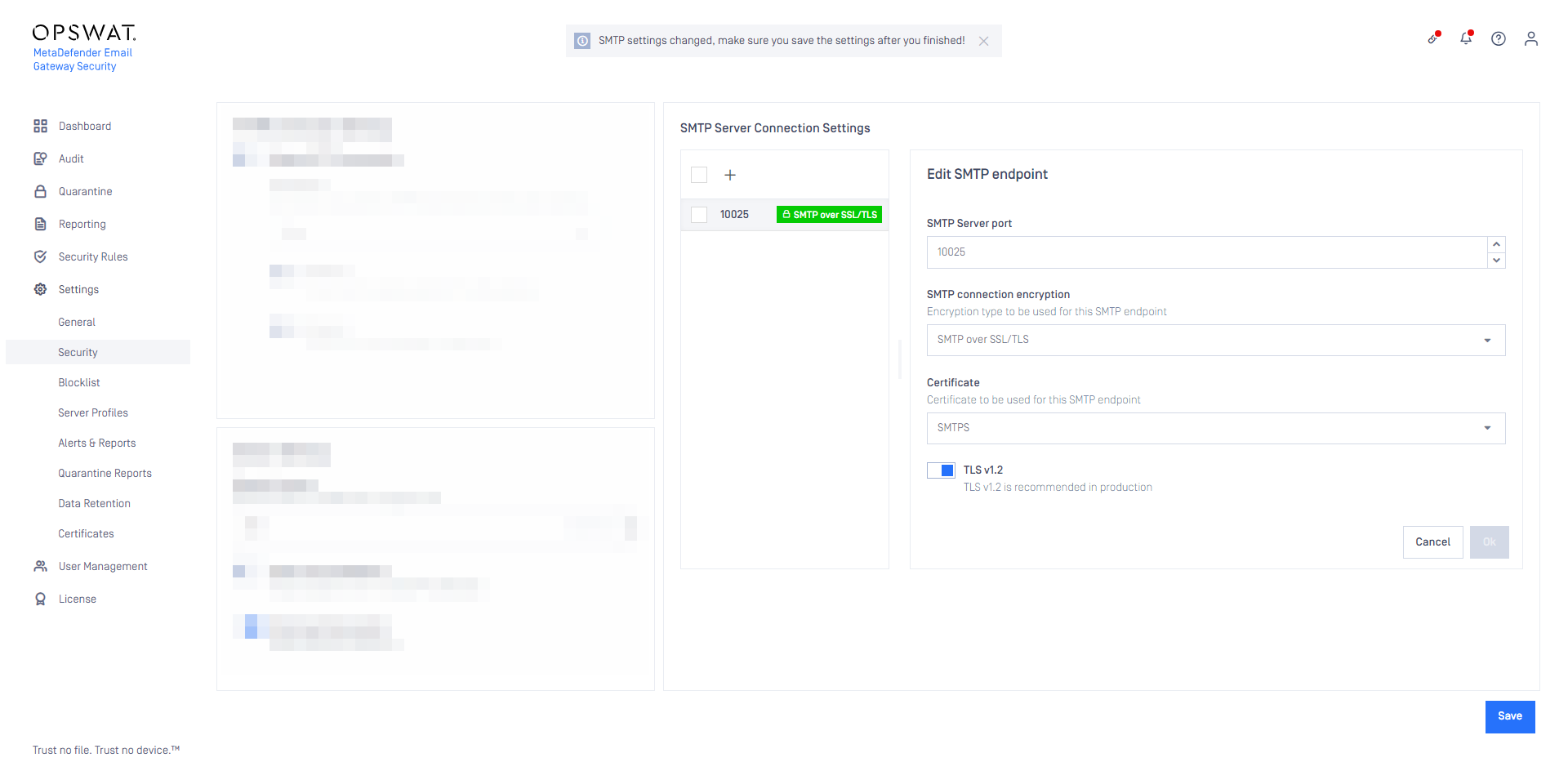
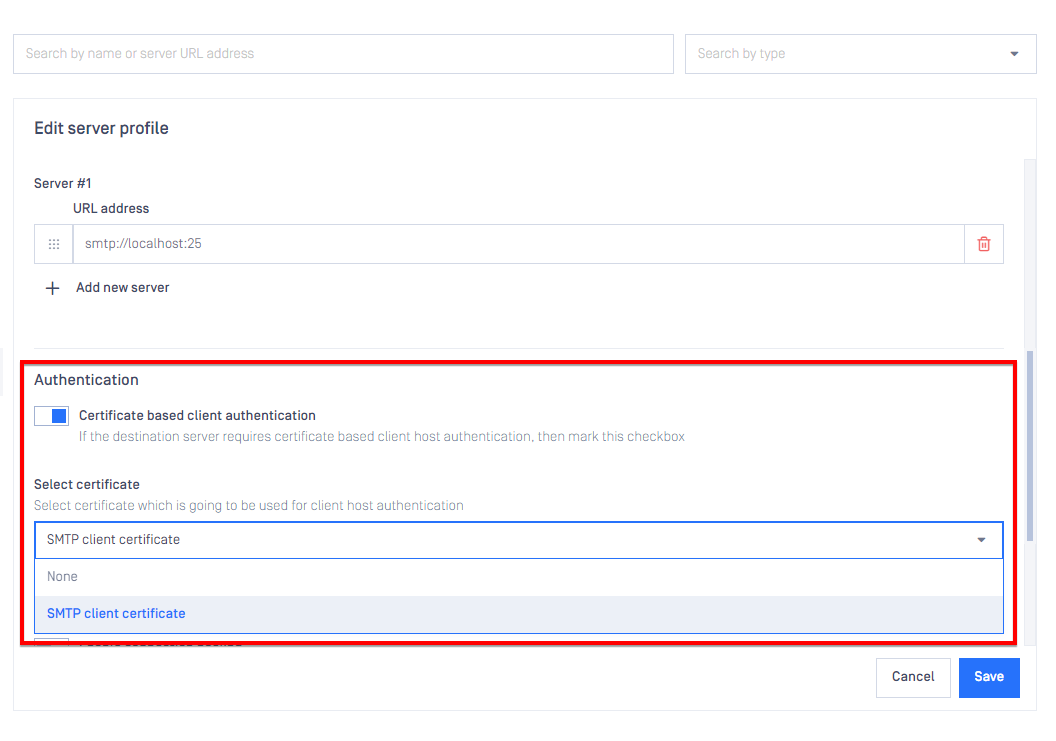
Custom client certificate (SMTP server profiles)
It is now possible to configure a custom client certificate for SMTP server profiles. Any TLS certificate imported via Settings > Certificates can be used as a client certificate.
New classifications (DLP original, Yara match)
New following new classifications has been added to Email Gateway Security
- DLP original (Assigned to Quarantined, redacted emails)
- YARA match (Assigned to any email blocked by a YARA rule configured in MetaDefender Core)
Bug fixes
Paper clip visible after sanitizing inline attachments
In certain edge cases the attachment paperclip would display for sanitized inline attachments (images). This is limited to TNEF encoded emails.
Unable to configure Azure Open ID as SSO provider
Email Gateway Security can now be configured to use Microsoft Entra/Azure AD OpenID as an SSO provider.
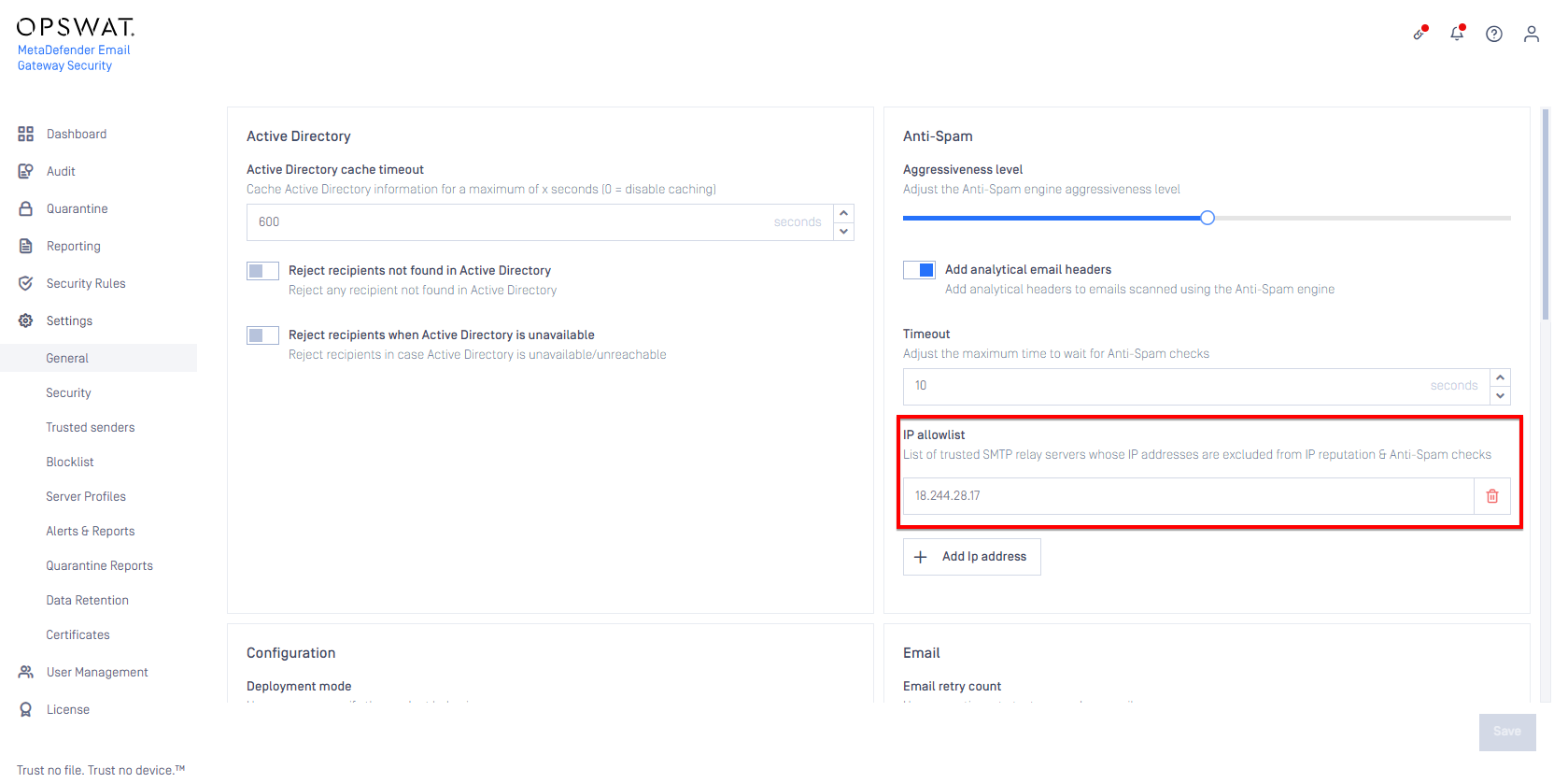
Unable to add IP address to Anti-Spam allow list
An incorrect validation could prevent IP addresses to be added to the Anti-Spam IP allow list.
Sanitization failure (No line break in HTML)
A sanitization failure was sometimes reported when an HTML body does not contain any line breaks.
Sanitization failure (special characters in attachment filename)
A sanitization failure was sometimes reported when an attachment filename contained illegal path characters (for example: |, < or >).

