Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
AVEVA PiToPi Configuration for MetaDefender Security Gateway
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide configuration guidelines for using PiToPi with MetaDefender Security Gateway. There are numerous configurations that may work, but this is the one we used for testing.
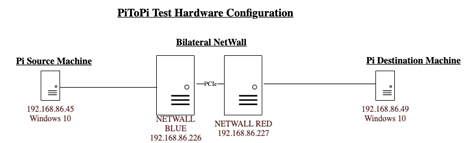
Hardware Configuration
Our test consisted of a Pi Source Machine whose values were passed through MetaDefender Security Gateway to a Pi Destination Machine using PiToPi configured as a ‘Push’ on the Pi Source machine. The tag configurations for each machine are shown below.
Configuring MetaDefender Security Gateway
MetaDefender Bilateral Security Gateway is easily configured to enable port 5450 (the default PI port) between the Pi Source Machine and the Pi Destination machine.
To do so, first, click on Streams to create a stream for the Pi system
Please, remember that you need to create the stream in both sides, BLUE and RED, with the same channel number in both sides. You need a security dongle connected to be able to do so.
Once created you can go back to Streams and check the new PitoPi Stream.
The Source IP is the Pi Source Machine (192.168.86.45). Note there is a 2nd machine defined (192.168.86.36) which is our laptop. The laptop has Excel on it, and we configured the Destination Pi Machine tags using the Excel extensions on the laptop.
The Destination IP is the Pi Destination Machine (192.168.86.49).
Configuring the PI tags
Tags on Pi Source Machine
Tags on Pi Destination Machine
Adding Destination Pi Server Address to the Source Pi Server
The Destination Pi Server IP address is seen as the MetaDefender Security Gateway Blue IP address (192.168.86.226) to the Source Pi Server. Add this Address to the Source Pi Server using Pi System Management Tools and the File | Add Server option.
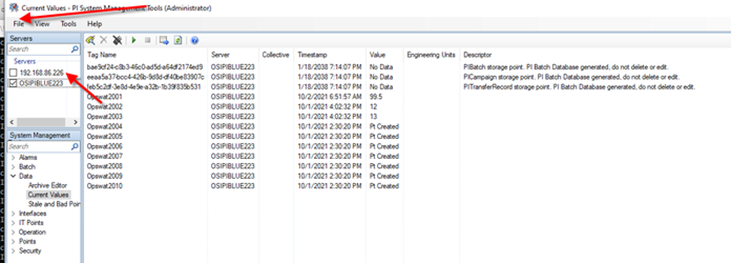
Add Destination Pi Server
Once you’ve done this, you can use PI SMT on the Source PI Server and select the Destination PI Server using MetaDefender Security Gateway, as shown below. Note that you cannot select the Source PI Server from the Destination PI Server. MetaDefender Security Gateway will not allow a connection in that direction.
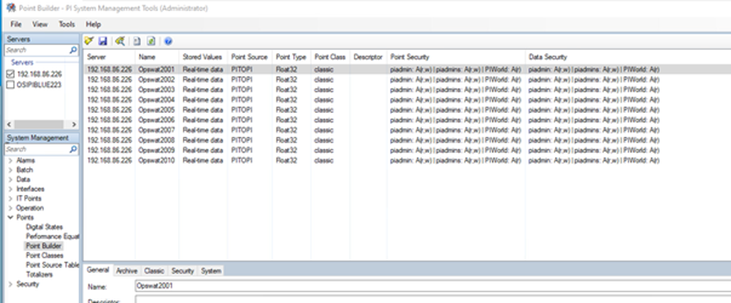
Tags on Destination Pi Server from Source Pi Server
Creating Trust On Destination Pi Server
Note that the Pi Destination Machine sees MetaDefender Security Gateway Red as the Pi Source machine. So, the IP address used in creating the trust on the Pi Destination Machine is the IP address of MetaDefender Security Gateway Red. Note that we used piadmins as the PI Identity.
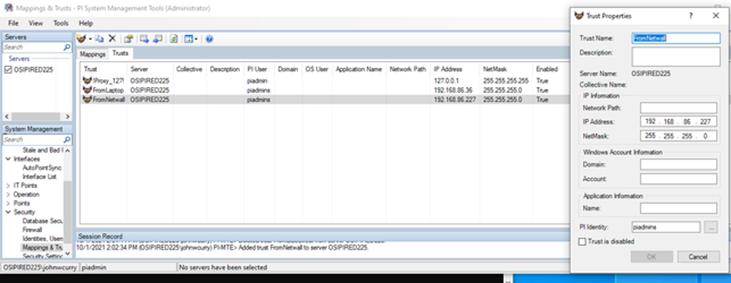
Trust on Pi Destination Machine
Configuring PiToPi on the Pi Source Machine
We installed a new copy of PiToPi on the Pi Source Machine, and then used the Pi ICU (Interface Configuration Utility) to create an instance.
An important step when using the ICU for the first time is the following:
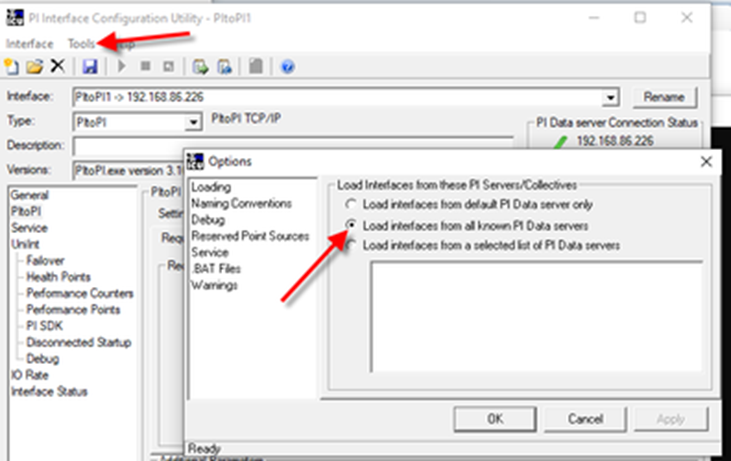
ICU Initial Configuration
Make sure to select “Load Interfaces from all know PI Data Servers.”
The first step was to create the Interface from a BAT file using the “open folder” Icon on the UCU toolbar and pointing to the PiToPi installation folder:
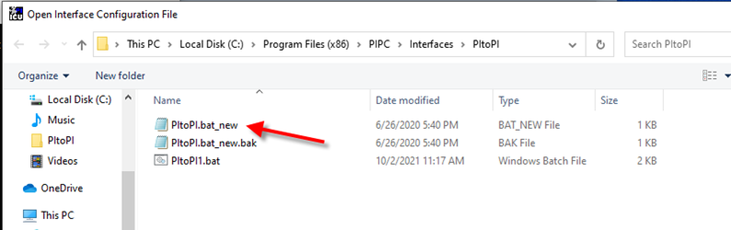
Selecting the PiToPi bat file
After configuration, the interface is shown below. Note that we chose to stay with just the .bat file (PItoPI1.bat) which is placed in the PiToPi installation folder.
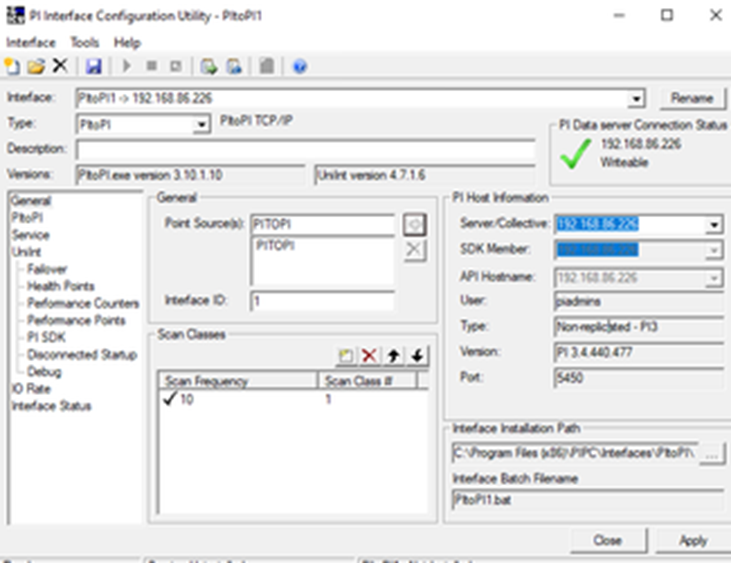
PiToPi configuraction on the Source Pi Machine
Note that the Hostname contains the address (192.168.86.226) of MetaDefender Security Gateway Blue. The port number was left at the default (5450).
The only additional change we made was to indicate the address of the Source Pi Server, as shown below.
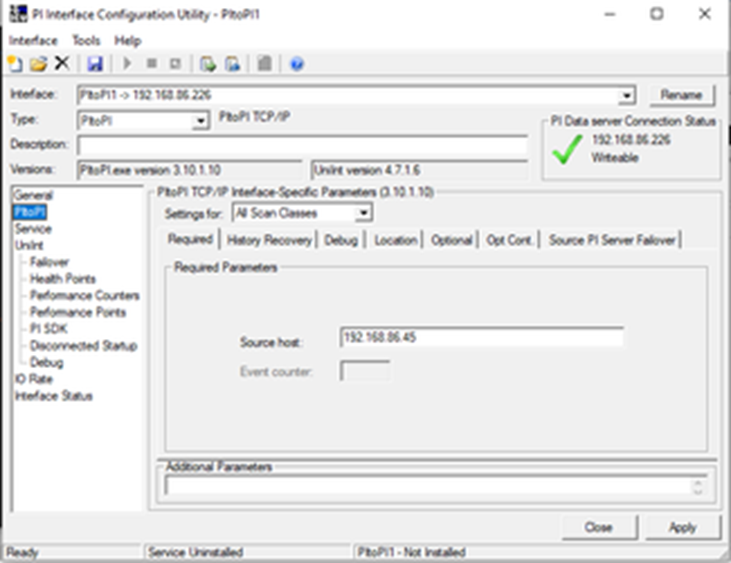
Adding the address of the Source Pi Server
We then started the PItoPI1.bat with administrative privileges. We made changes to current values on the Source Pi Machine using ipconfig. We then verified those values were present on the Destination Pi Machine.
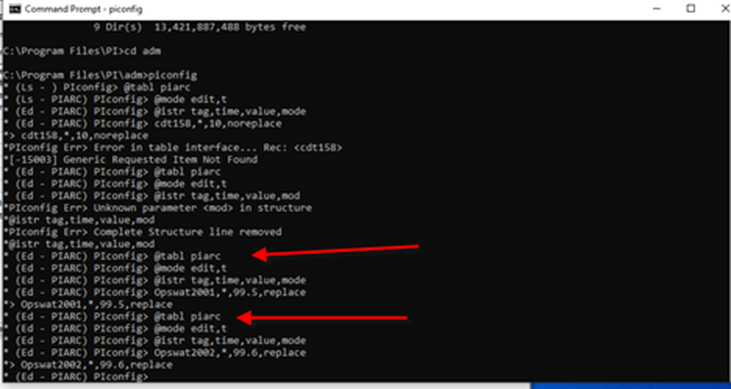
Using PiConfig to change values on the Pi Source machine

