Make sure that APIENDPOINT, APIKEY, and STORAGECLIENTID are configured as environment variables accessible to the cloud function.
Refer to the Event-based handling documentation for details on these variables.
AWS Lambda Function with S3 Trigger Setup Guide
Before proceeding with the setup, ensure the following requirements are met:
1. IAM User Permissions
- Your IAM user must have the necessary permissions to:
- Create Lambda functions
- Assign IAM roles
- Configure S3 triggers
- Access the target S3 buckets
2. Account-Level Verification
- Confirm there are no account-level naming restrictions that would prevent your chosen Lambda function name
- Verify your AWS account has sufficient permissions and service quotas to create new Lambda functions in the desired region
- Ensure you have access to the target AWS region where the Lambda function will be deployed
3. S3 Bucket Configuration
- Verify that S3 bucket policies are configured to allow access from the Lambda function's execution role
- Required S3 permissions may include:
s3:GetObject- to read objects from the buckets3:PutObject- to write objects to the bucket (if applicable)s3:DeleteObject- to delete objects from the bucket (if applicable)
4. IAM Execution Role
- Ensure you have a pre-configured IAM role with:
- Lambda execution permissions
- S3 access permissions for your target bucket(s)
- CloudWatch Logs permissions for function monitoring
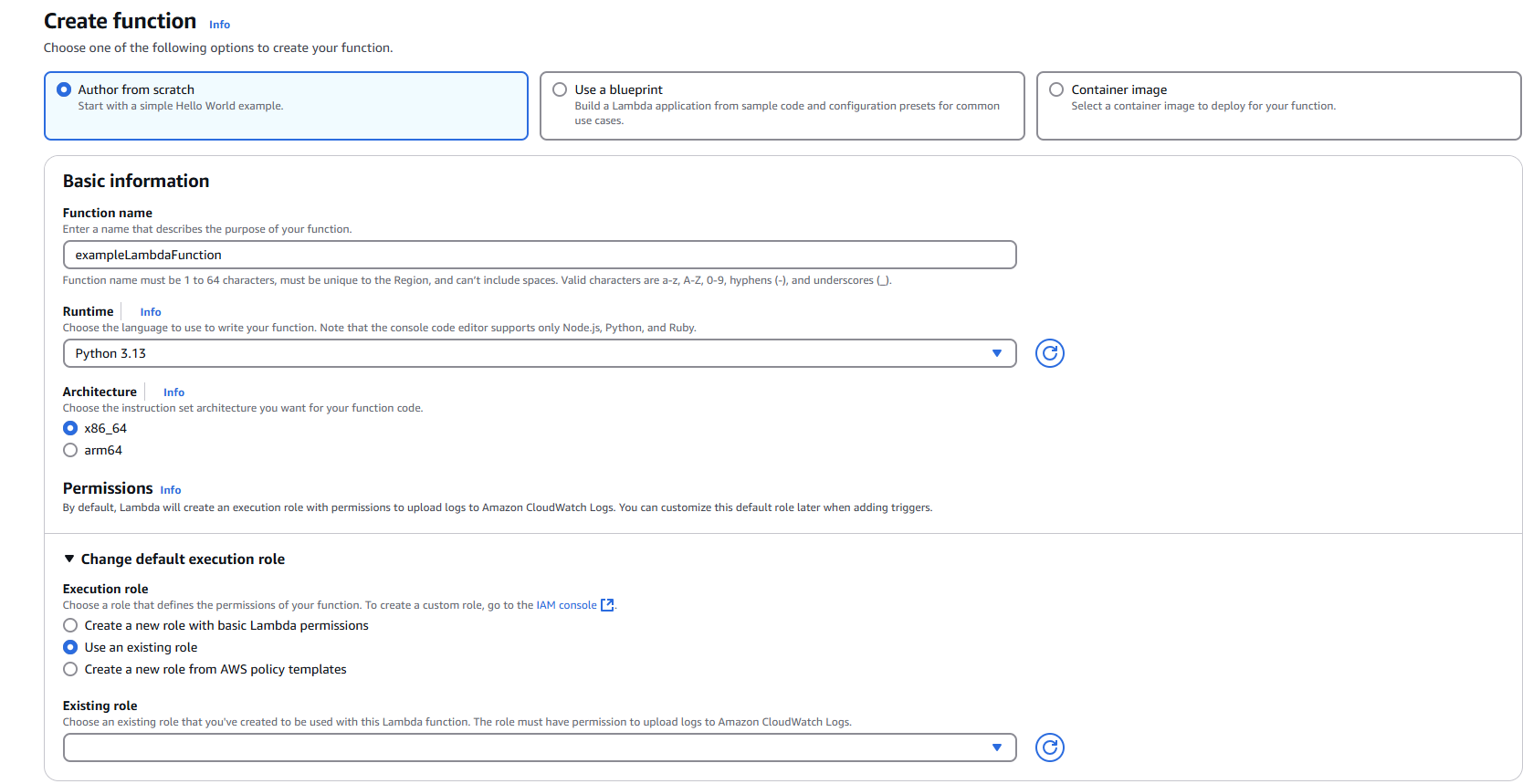
Step 1: Creating the Lambda Function
1.1 Navigate to Lambda Service
- Open the AWS Management Console
- Navigate to the Lambda service
1.2 Initialize Function Creation
- Click "Create function"
- Select "Author from scratch"
1.3 Configure Basic Settings
Function name: Enter a descriptive name for your Lambda function
- Example:
MetaDefenderStorageSecurityProcessor - Ensure the name complies with AWS naming conventions and any account-specific policies
- Example:
Runtime: Select Python (choose the latest compatible version)
1.4 Configure Permissions
- Under "Change default execution role", select "Use an existing role"
- From the "Existing role" dropdown, choose your pre-configured IAM role
- Verify role permissions:
- Navigate to the IAM console and review the selected role
- Confirm Permission policies include necessary access to S3, CloudWatch Logs, and other required services
- Verify Trust relationships allow the Lambda service (
lambda.amazonaws.com) to assume the role
1.5 Configure Advanced Settings (Optional but Recommended)
- Expand "Advanced configuration"
- Enable "Tags"
- Add relevant tags for resource organization:
- Key:
Purpose| Value:MetaDefenderScan - Key:
Environment| Value:Production/Development - Key:
Owner| Value:[Your Team/Department]
- Key:
1.6 Create the Function
- Click "Create function"
- Wait for the function to be successfully created
Step 2: Adding S3 Trigger
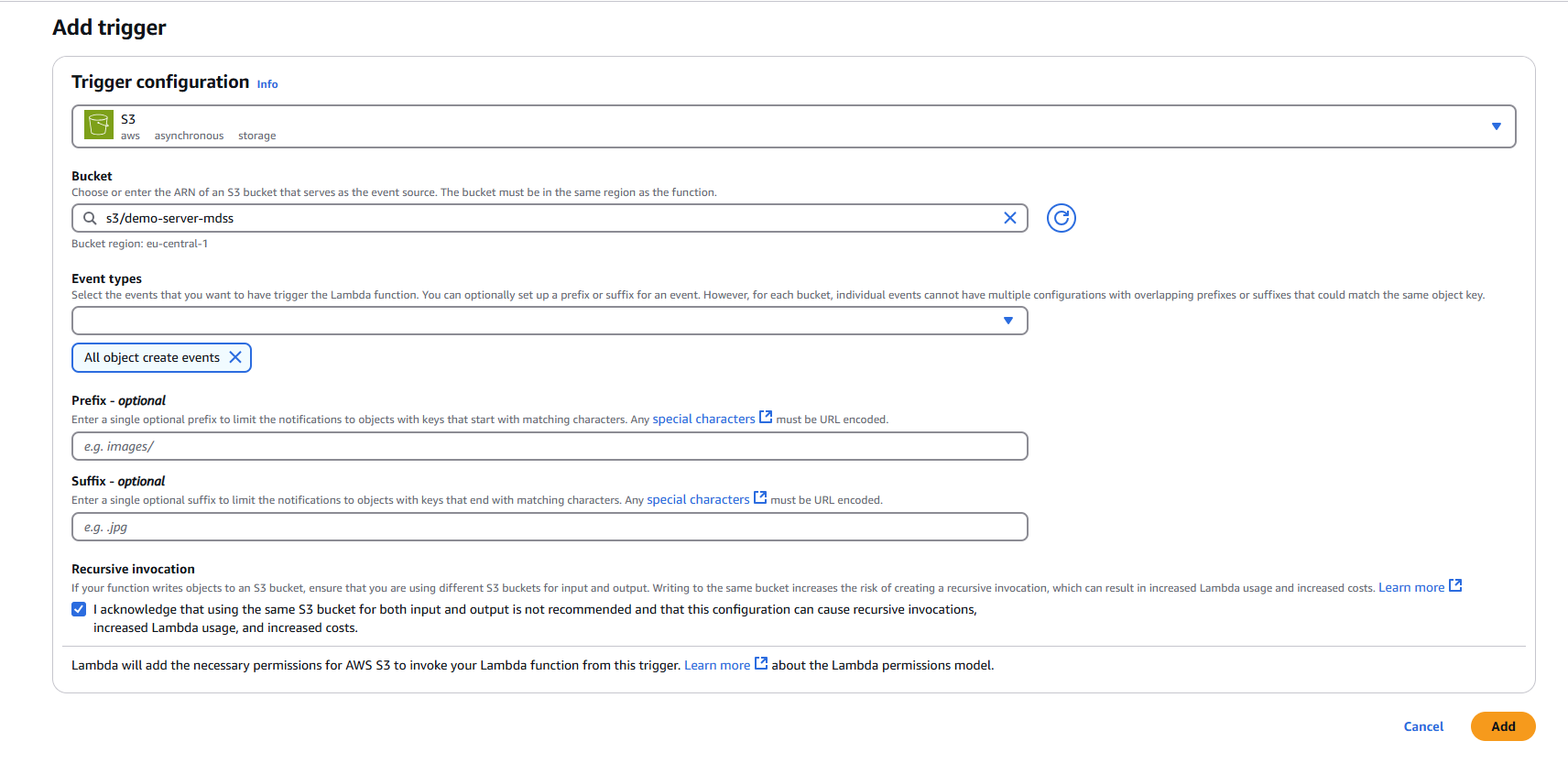
2.1 Add Trigger Configuration
- In your newly created Lambda function, click "Add trigger"
- Select "S3" as the trigger source
2.2 Configure S3 Trigger Settings
Bucket: Select your target S3 bucket from the dropdown menu
Event types: Choose the appropriate event type
- Default: "All object create events"
- Alternative options: Object create, delete, or restore events based on your requirements
Prefix (Optional): Specify a prefix to filter objects by path
- Example:
uploads/to only trigger on objects in the uploads folder
- Example:
Suffix (Optional): Specify a suffix to filter objects by file extension
- Example:
.pdfto only trigger on PDF files
- Example:
Recursive invocation: Check this option to acknowledge potential recursive invocations
2.3 Finalize Trigger Setup
- Review your trigger configuration
- Click "Add" to create the S3 trigger
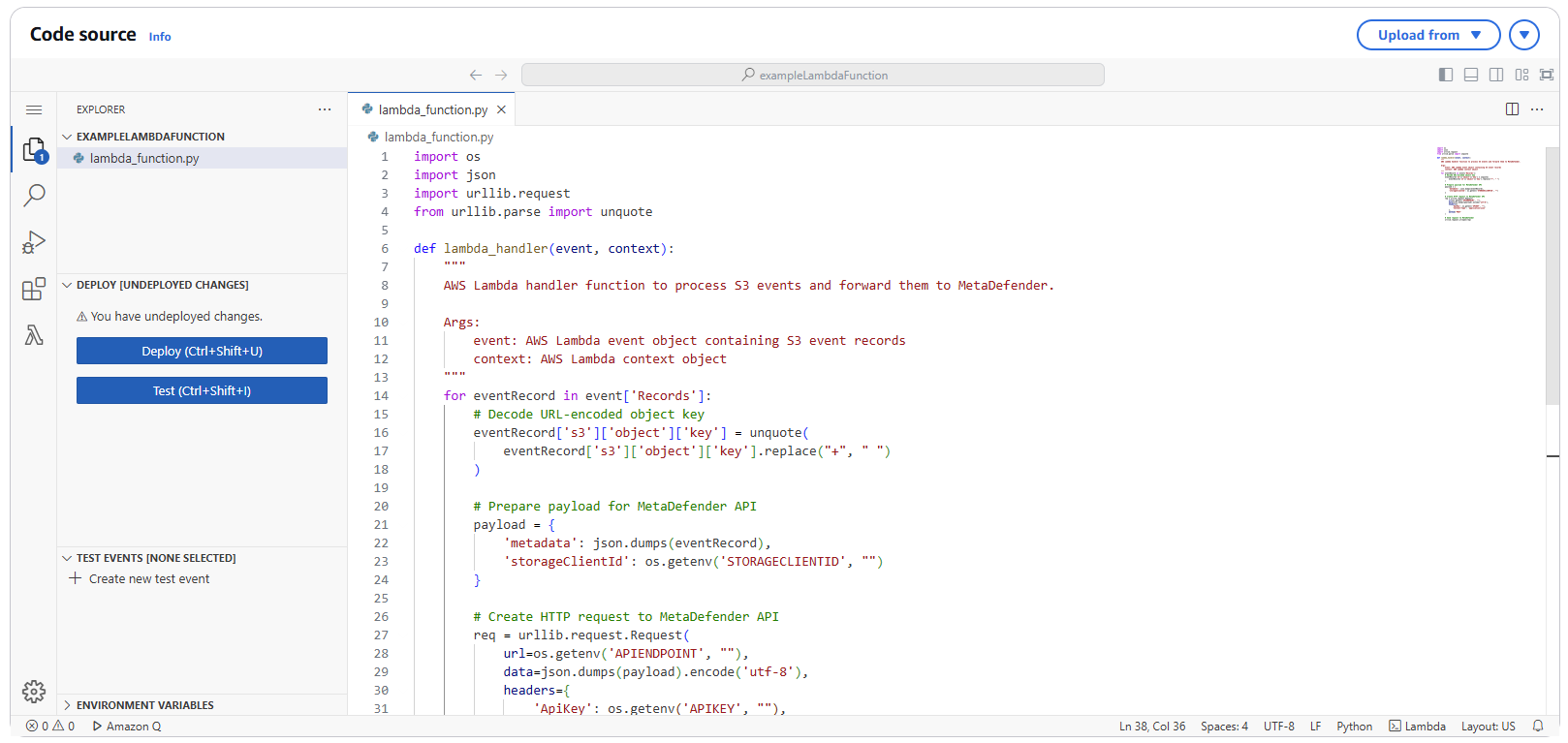
3.1 Navigate to Code Section
- In your Lambda function console, navigate to the "Code" tab
- Replace the default code with the following implementation:
import osimport jsonimport urllib.requestfrom urllib.parse import unquotedef lambda_handler(event, context): for eventRecord in event['Records']: eventRecord['s3']['object']['key'] = unquote(eventRecord['s3']['object']['key'].replace("+", " ")) payload = { 'metadata': json.dumps(eventRecord), 'storageClientId': os.getenv('STORAGECLIENTID', "") } req = urllib.request.Request( url=os.getenv('APIENDPOINT', ""), data=json.dumps(payload).encode('utf-8'), headers={ 'ApiKey': os.getenv('APIKEY', ""), 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, method='POST' ) urllib.request.urlopen(req)3.2 Deploy the Code
- Click "Deploy" to save and deploy your function code
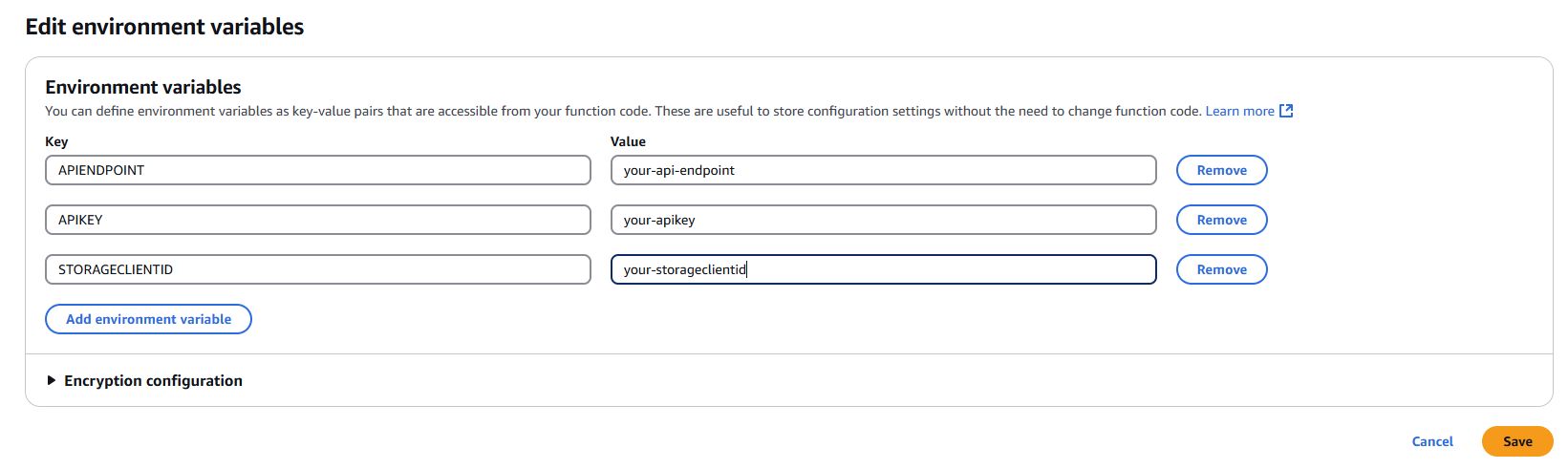
Step 4: Configuring Environment Variables
4.1 Navigate to Configuration
- In your Lambda function console, click on the "Configuration" tab
- Select "Environment variables" from the left sidebar
4.2 Add Required Environment Variables
Click "Edit" and add the following environment variables:
APIENDPOINT
- Key:
APIENDPOINT - Value: Your MDSS URL +
/api/webhook/realtime - Example:
https://mdss-example.com/api/webhook/realtime
- Key:
APIKEY
- Key:
APIKEY - Value: Your MDSS user API key
- Note: Ensure this key has appropriate permissions for webhook operations
- Key:
STORAGECLIENTID
- Key:
STORAGECLIENTID - Value: Your storage client ID from MDSS
- To obtain: Navigate to your desired storage configuration and copy the
storageClientId
- Key:
4.3 Save Configuration
- Click "Save" to apply the environment variable changes
Step 5: Testing and Validation
5.1 Test the Function
- Upload a test file to your configured S3 bucket
- Monitor the Lambda function's execution in the "Monitor" tab
- Check CloudWatch Logs for any execution errors or successful processing
5.2 Verify Integration
- Confirm that file events are being sent to your MDSS instance
- Verify that scans are initiated as expected
- Review MDSS logs for successful webhook reception
Azure Blob function app setup
- Deploy the Azure function app using the Terraform script: https://github.com/OPSWAT/metadefender-k8s/tree/main/terraform/azure-function-docker
- Configure
STORAGECLIENTID,APIKEY, andAPIENDPOINTvariables in the.tvarsfile:
resource_group_name = "" #The name of the resource group in which the function app will be created."service_plan_name = "" #The name of the app service planstorage_account_name = "" #The name of the storage account to be createddocker_registry_server_url = ""docker_registry_server_username = "" #optionaldocker_registry_server_password = "" #optionaldocker_image_name = ""docker_image_tag = ""AzureWebJobsBlobTrigger = "" #The storage account connection string that triggers the functionCONTAINERNAME = "" #The blob container that needs to be scannedfn_name_prefix = "" #function namelocation = "" #azure regionSTORAGECLIENTID = ""APIKEY = ""APIENDPOINT = ""Azure Blob Event Grid RTP configuration
Refer to the example for detailed configuration: https://github.com/OPSWAT/metadefender-k8s/tree/main/terraform/CloudFunctions/Azure/webhook-notification
Event Notifications for Page and Append blob are NOT supported.
Events for these blob types are triggered upon the first block commit, potentially before the upload is complete.
Google Cloud Function Setup
- Configure the Cloud Run with the
google.cloud.storage.object.v1.finalizedtriggerto process newly added objects. - Python Function Example:
import functions_frameworkimport jsonimport requestsimport os# Triggered by a change in a storage bucket.cloud_eventdef hello_gcs(cloud_event): requests.post(os.getenv('APIENDPOINT', ""), headers={'ApiKey':os.getenv('APIKEY', "")}, json = {'metadata': json.dumps(cloud_event.data), 'storageClientId': os.getenv('STORAGECLIENTID', "") })- Requirements.txt example:
functions-framework==3.*requestsAlibaba Cloud Function Setup
- Follow the official Alibaba Cloud documentation to create a compute function with an OSS trigger: https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/function-compute/latest/configure-an-oss-trigger
- Specify the bucket to monitor and subscribe to the
oss:ObjectCreated:*event. - Python Function Example:
import oss2, json, osimport requestsdef handler(event, context): for eventRecord in json.loads(event)['events']: requests.post(os.getenv('APIENDPOINT', ""), headers={'ApiKey':os.getenv('APIKEY', "")}, json = {'metadata': json.dumps(eventRecord), 'storageClientId': os.getenv('STORAGECLIENTID', "") })Wasabi Function Setup
- Follow the official Wasabi documentation to create an event notification: https://docs.wasabi.com/v1/docs/event-notifications-bucket
- Establish a connection with a service capable of sending requests to MetaDefender Storage Security (MDSS).
- The Wasabi documentation example uses AWS SNS, which can be integrated with AWS Lambda (see Amazon S3 Lambda Function Setup: How do I configure Event Notifications on my Wasabi bucket using AWS SNS?
S3 Compatible function setup
- Event-based real-time processing configuration varies for different S3-compatible services.
- Most S3-compatible services offer event notification similar to Wasabi.
- The service must send a request to the MDSS endpoint:
http(s)://{baseurl}/api/webhook/realtimewith the appropriate request body:
{ "storageClientId": [Storage Client Id], "metadata": "{'s3': { 'object': {'key': [Object Path] }}}"}
