Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Kubernetes Deployment
An existing cluster is the primary requirement for installing the MDSS Helm chart. Provisioning a Kubernetes cluster from scratch is complex task but in general, for production use cases, users choose managed Kubernetes. The differences between them are:
- Managed Kubernetes Services: These services abstract away much of the complexity of managing a Kubernetes cluster, but they may be more expensive.
- Self-Managed Kubernetes: Gives you more control over your cluster's configuration and may be cheaper, but requires more setup and maintenance.
Convenience Script
The simplest way of deploying MDSS (and other MetaDefender products) is to use the metadefenderk8s.sh convenience script from our public GitHub here: metadefender-k8s/metadefenderk8s.sh
This script guides the user through all the required steps to provision a Kubernetes cluster and install MDSS on it.
Prerequisites
In case of provisioning with the MetaDefender scipt the resources recommended from OPSWAT
- Knowledge of choosen CSP: OPSWAT assume familiarity with AWS or Azure in case you provision the infrastructure with the MetaDefender Script
- Account of the choosen CSP to create all the resources needed
Scripting languages supported: Linux - shell
Pre-requisites:
Example
Running ./metadefenderk8s.sh --help will give a few examples on how to run the script.
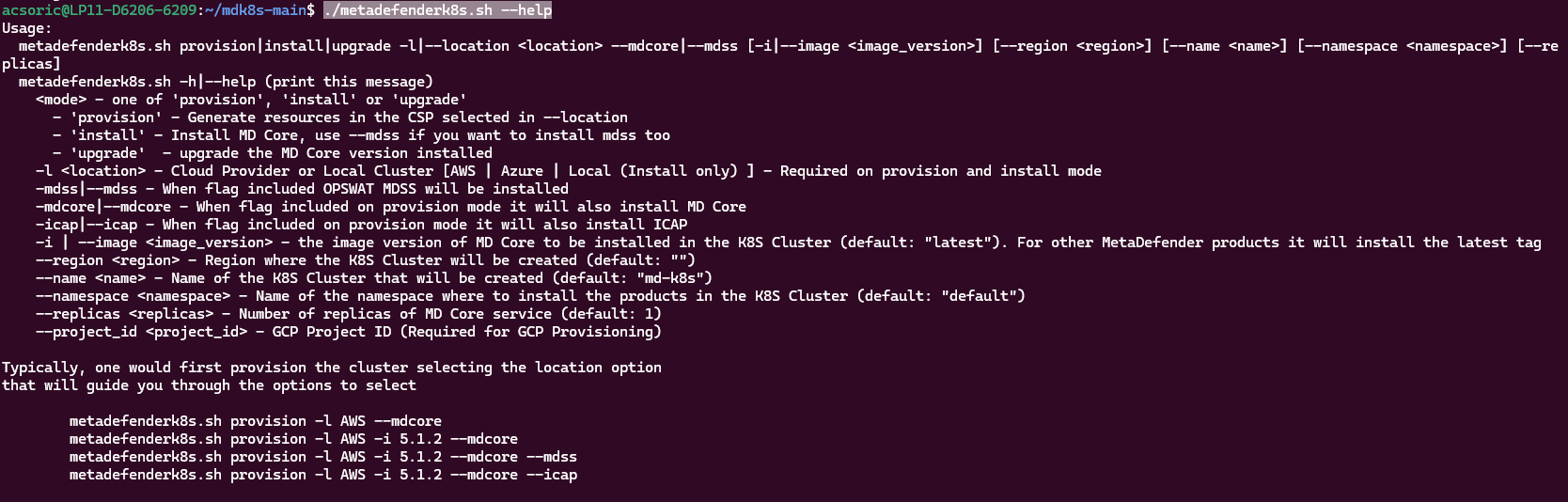
For example, installing both MD Core and MDSS in AWS will look something like this:
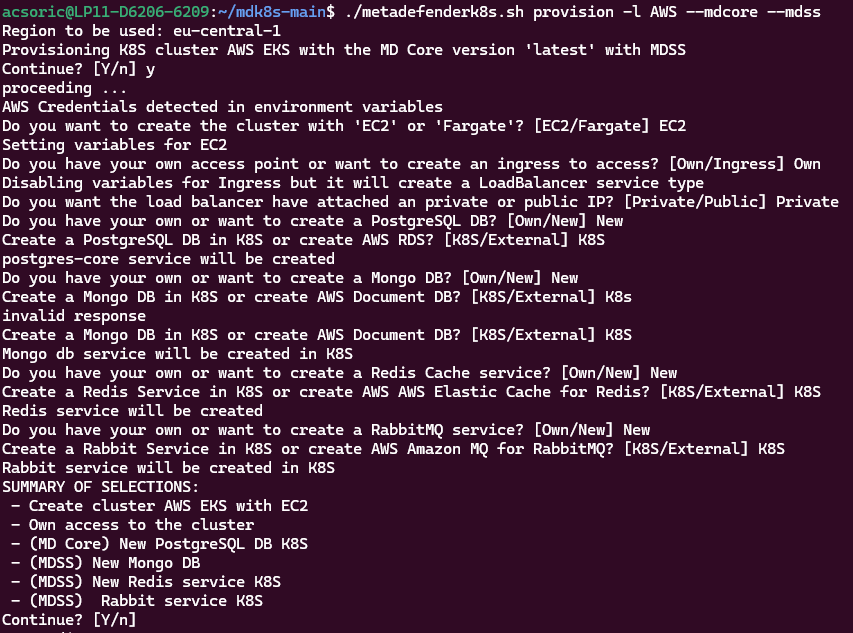
This method will only deploy a generic cluster with MDSS installed that suitable for non-production use cases but it can be expanded and configured to handle production workloads.
Provisioning a Kubernetes Cluster
Provisioning a cluster usually require the following high-level steps:
Choose a cloud provider or a local environment for hosting your Kubernetes cluster. Options include:
- Cloud Service Providers: AWS (Amazon EKS), Google Cloud (GKE), Microsoft Azure (AKS), etc.
- Local Self-Managed Environments (non-production only): Minikube, Docker Desktop with Kubernetes, Kind (Kubernetes in Docker), k3s, etc.
Set up an account with your chosen cloud provider if necessary.
Follow the provider's documentation or use their management console to create a Kubernetes cluster.
Configure networking, security, and other settings as needed.
(Optional but recommended) Setup an external database like AWS DocumentDB, Azure CosmosDB, MongoDB Atlas etc.
(Optional but recommended) Setup an external Redis cache like Amazon ElastiCache.
(Optional but recommended) Setup an external RabbitMQ like Amazon MQ.
Install and configure the Kubernetes command-line tool (
kubectl) and thehelmcli on your local machine to interact with the cluster and install Helm charts.
Installing Storage Security on Kubernetes (k8s)
MDSS for Kubernetes comes packaged as a Helm chart and it’s available on GitHub here: metadefender-k8s
Detailed installation steps can be found in our public documentation: Kubernetes deployment
Additionally, it’s recommended to have MD Core installed on the same cluster for best performance and flexibility. Similarly to Storage Security, MD Core can be installed using it’s own helm chart: https://docs.opswat.com/mdcore/cloud-deployment/md-core-installation#helm-chart

