Knowledge Base
3.3.x
Search this version
Knowledge Base
Knowledge Base
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Understanding and Configuring Double VLAN (802.1q Tunneling)
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
What is Double VLAN (802.1q Tunneling)?
Double VLAN, also known as 802.1q tunneling or Q-in-Q tunneling, is a network feature that encapsulates one VLAN tag inside another. It allows service providers or administrators to group multiple customer VLANs under a single service-provider VLAN (outer VLAN).
- Outer VLAN: Used by the service provider to manage traffic.
- Inner VLAN: Preserves customer-specific VLAN configurations.
This method ensures secure and isolated communication for each customer over a shared infrastructure.
User Cases
Service Provider Networks:
- Aggregate traffic from multiple customers while keeping their VLANs isolated.
Industrial OT Networks:
- Extend VLANs across subnets without modifying the internal VLAN structure.
How It Works
Encapsulation:
- Customer VLAN traffic (inner VLAN) is tagged with an additional service VLAN (outer VLAN) as it enters the provider’s network.
De-encapsulation:
- At the destination, the service VLAN tag is removed, restoring the customer VLAN.
Network Topology
Devices Involved: A PLC (acting as a server), Industrial Firewall, and clients on Network B.
Setup:
- Network A: 192.168.10.0/24 VLAN 100 (PLC resides here).
- Network B: 10.10.10.0/24 VLAN 200.100 (HMI or external device).
- The firewall has interfaces in both networks and translates traffic between them.

Configuration Steps
Create VLANs
- Configure the outer VLAN for the service provider.
- Allow inner VLANs for customer-specific traffic
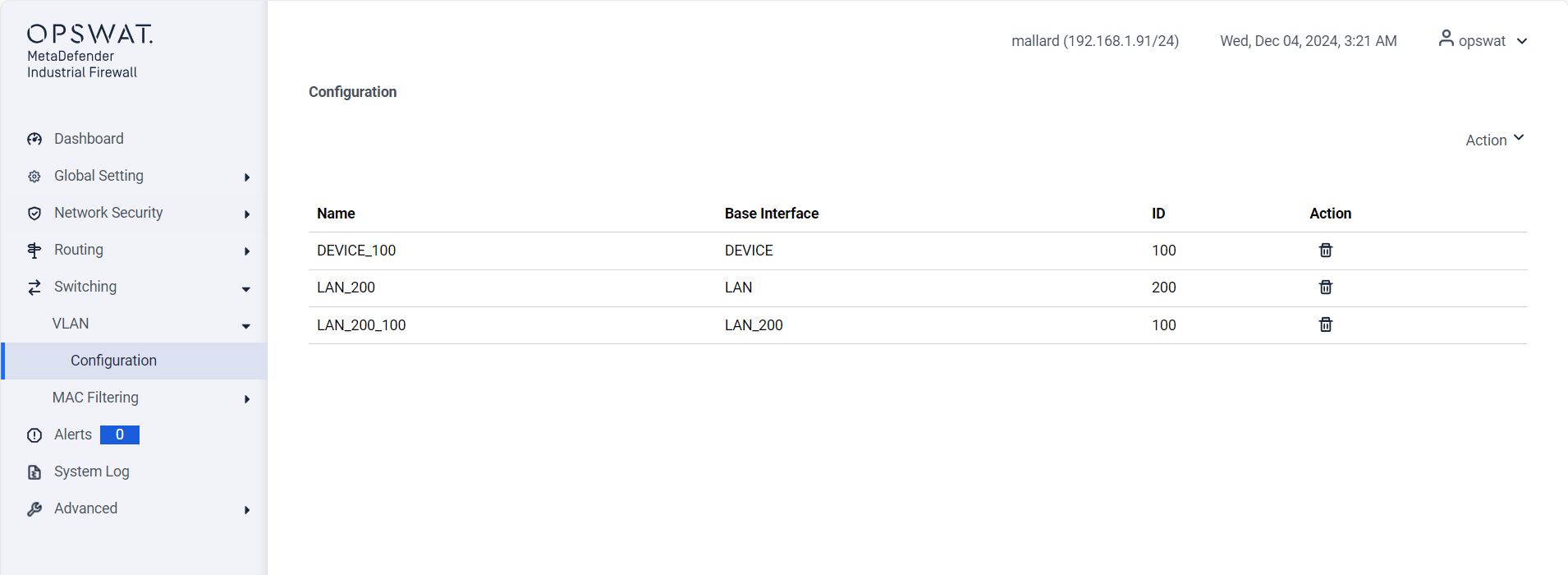
IP Configuration
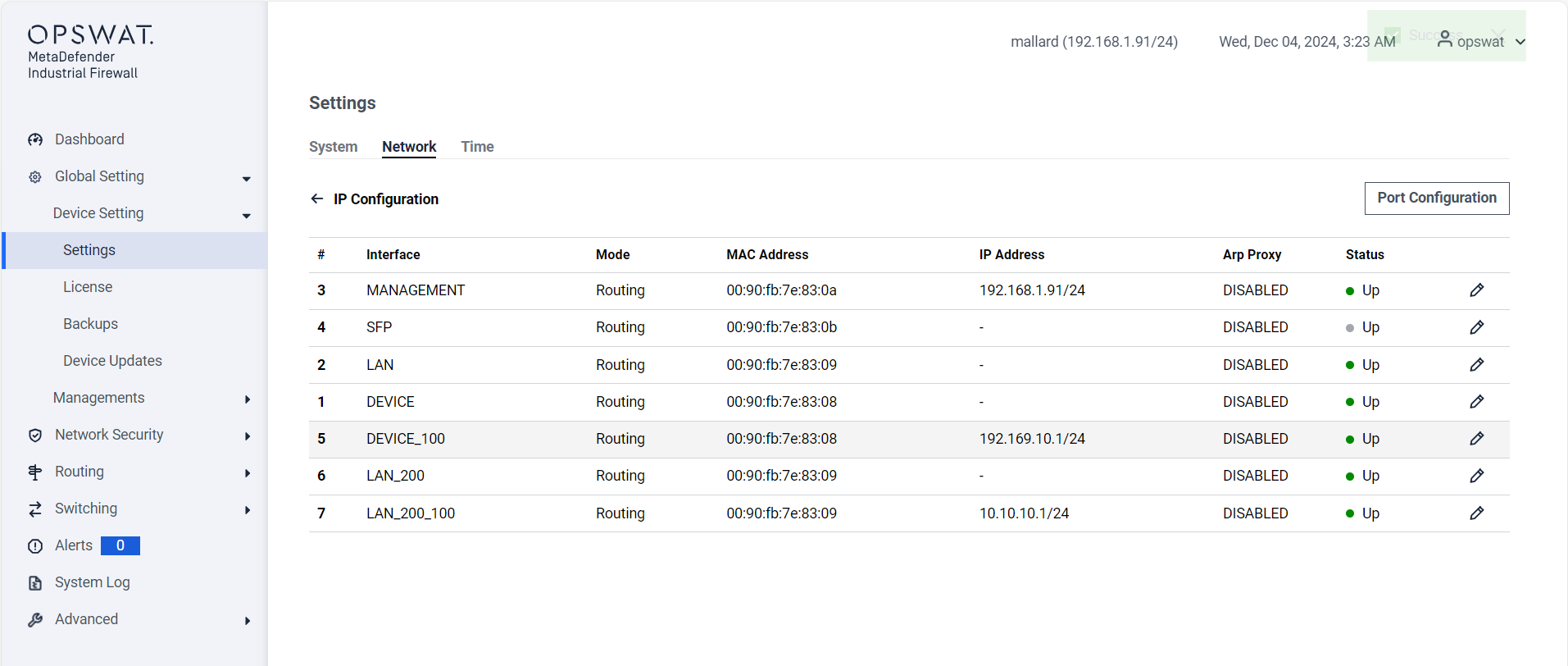
Apply Q-in-Q Rules
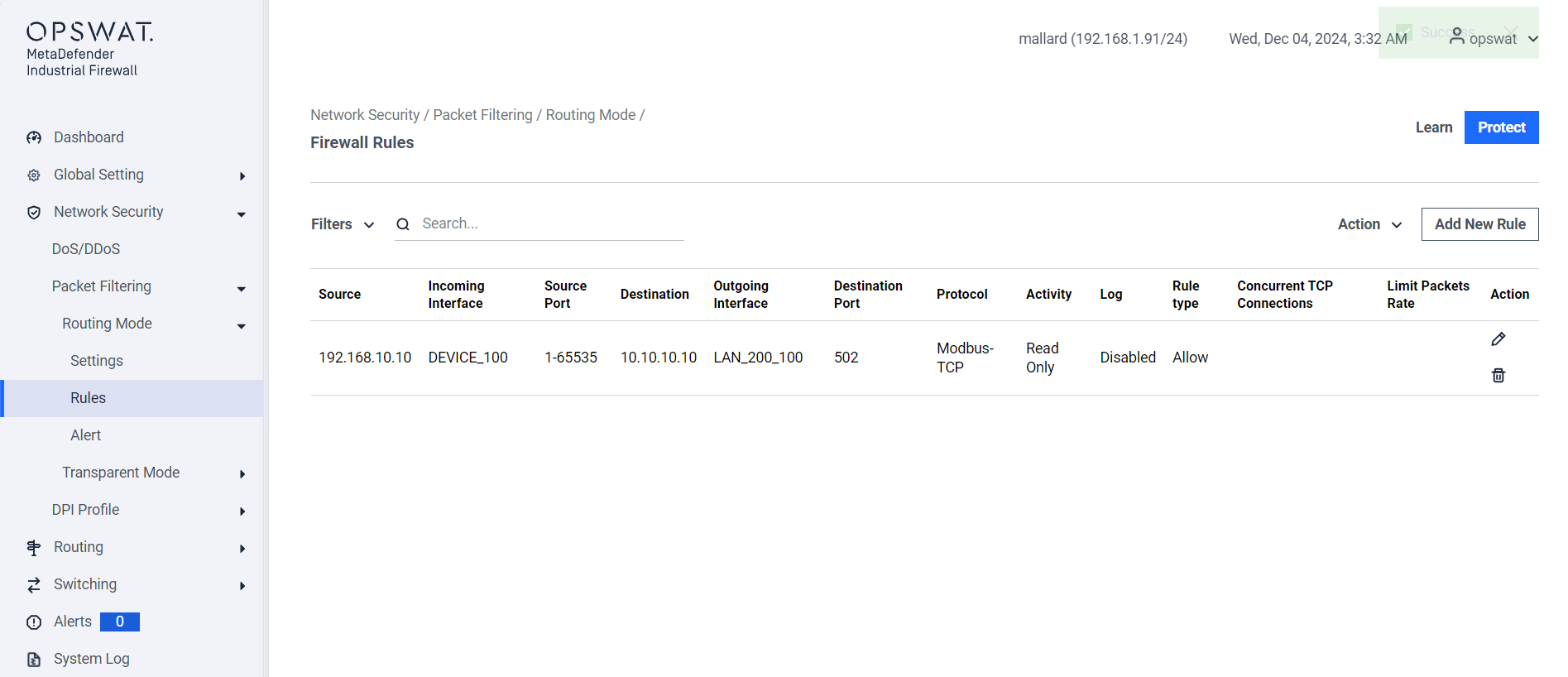
Benefit
- Traffic Segmentation: Keeps customer VLANs isolated while sharing infrastructure.
- Scalability: Supports a larger number of VLANs with minimal configuration changes.
- Security: Ensures customer data integrity and isolation.
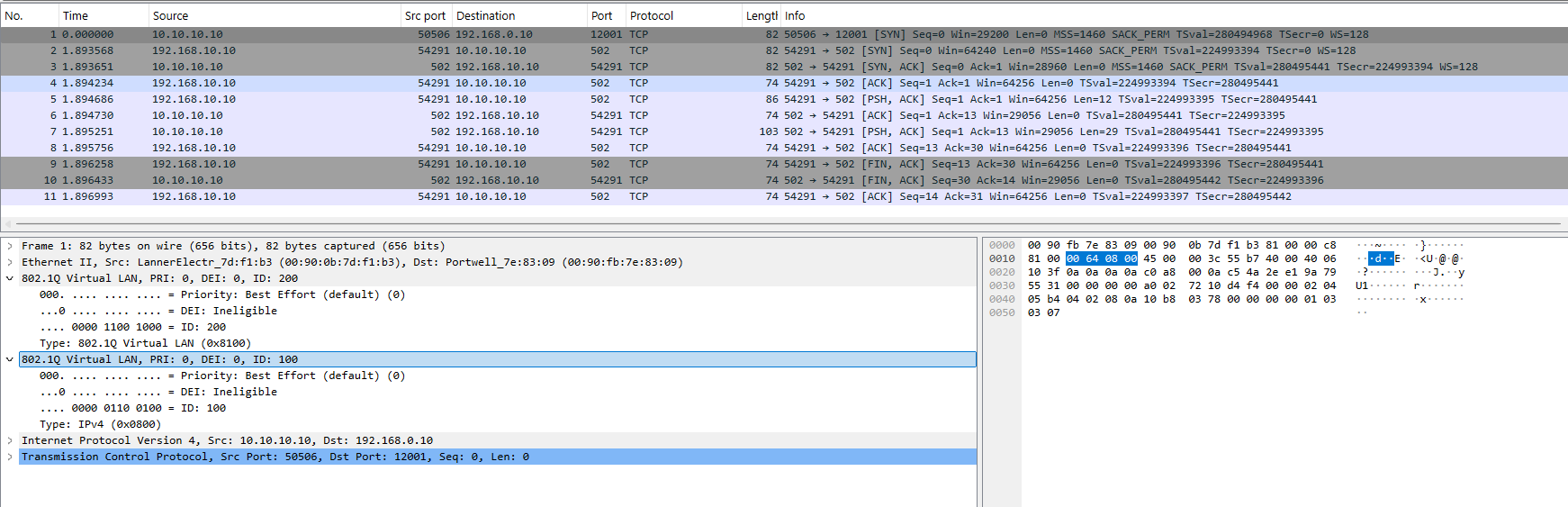
PCAP Analyze
Traffic that is captured from 192.168.10.10
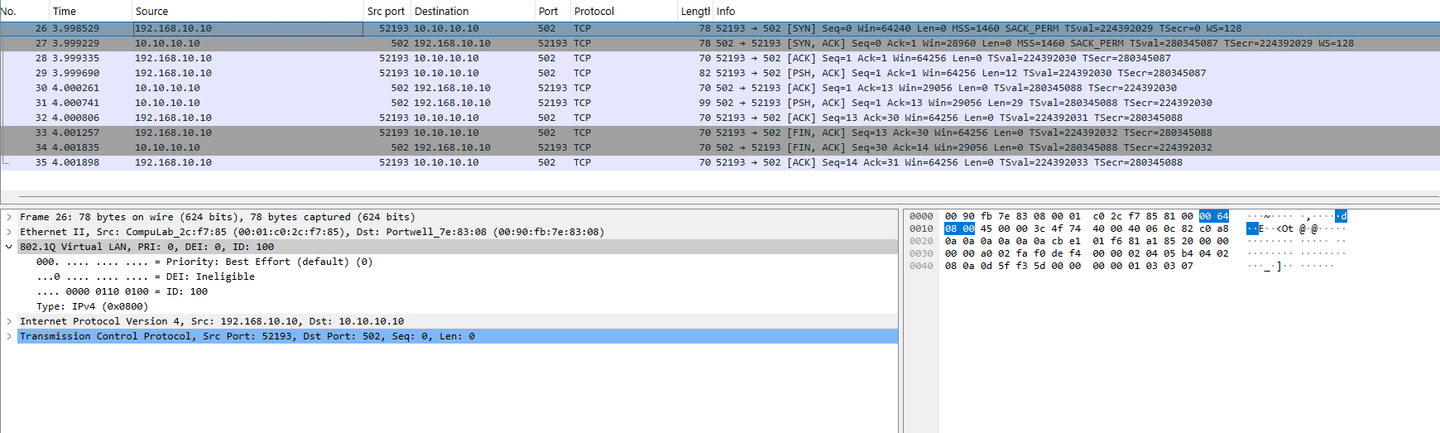
Traffic that is captured from 10.10.10.10
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on
Was this page helpful?
Next to read:
Transparent Mode and Bridge User CasesDiscard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message

