Dos/DDos
[Network Security > DoS/DDoS]
A DoS/DDoS attack is a type of cyberattack designed to disrupt and render services or devices unusable. In this dialog, you can configure various filters to help protect both the device itself and other network devices from DoS attacks.
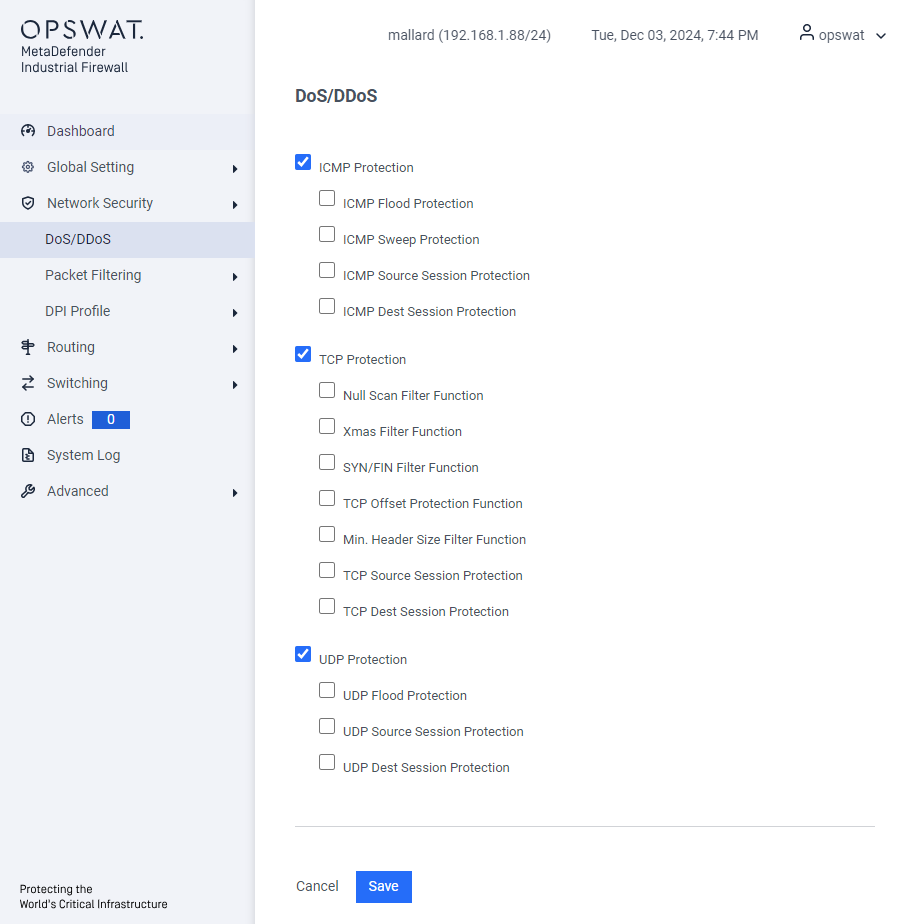
ICMP Protection:
- ICMP Flood Protection: Prevent overwhelming the network with a high volume of ICMP packets.
- ICMP Sweep Protection: Detect and block attempts to map out active devices on a network by sending ICMP requests to multiple IP addresses.
- ICMP Source Session Protection: Limit the number of ICMP requests from a single source
- ICMP Dest Session Protection: Limit the number of ICMP requests directed at a single destination
TCP Protection:
- Null Scan Filter Function: Blocks null scan attacks by filtering packets with no flags set.
- Xmas Filter Function: Prevents Xmas scan attacks by blocking packets with FIN, URG, and PSH flags set.
- SYN/FIN Filter Function: Detects and blocks SYN/FIN scan attacks.
- TCP Offset Protection Function: Ensures TCP packets have valid offsets to prevent manipulation.
- Min. Header Size Filter Function: Blocks packets below the minimum TCP header size to prevent attacks with malformed packets.
- TCP Source Session Protection: Limits the number of concurrent TCP connections from a single source IP address.
- TCP Dest Session Protection: Limits the number of concurrent TCP connections to a single destination IP address.
UDP Protection:
- UDP Flood Protection: Detects and blocks excessive UDP packets sent to a network.
- UDP Source Session Protection: Limits the number of concurrent UDP connections from a single source IP address.
- UDP Dest Session Protection: Limits the number of concurrent UDP connections to a single destination IP address.
DDOS - Rate Limiting Adjustment Explanation
Routing Mode
[Network Security > Packet Filtering > Routing Mode]
In this menu, you can configure the settings for the Routing Mode packet filter. This packet filter contains rules that the device sequentially applies to the data stream on its router interfaces. The Routing Mode packet filter performs stateful evaluation of the data stream, selectively filtering out undesired data packets.
When a data packet meets the criteria of one or more rules, the device executes the action specified by the first matching rule and disregards any subsequent rules. If no rules match the data packet, the device applies the default rule, which is set to “Block” by default. You can modify this default rule in the Configuration > Setting > Policy.
Settings
[Network Security > Packet Filtering > Routing Mode > Settings]
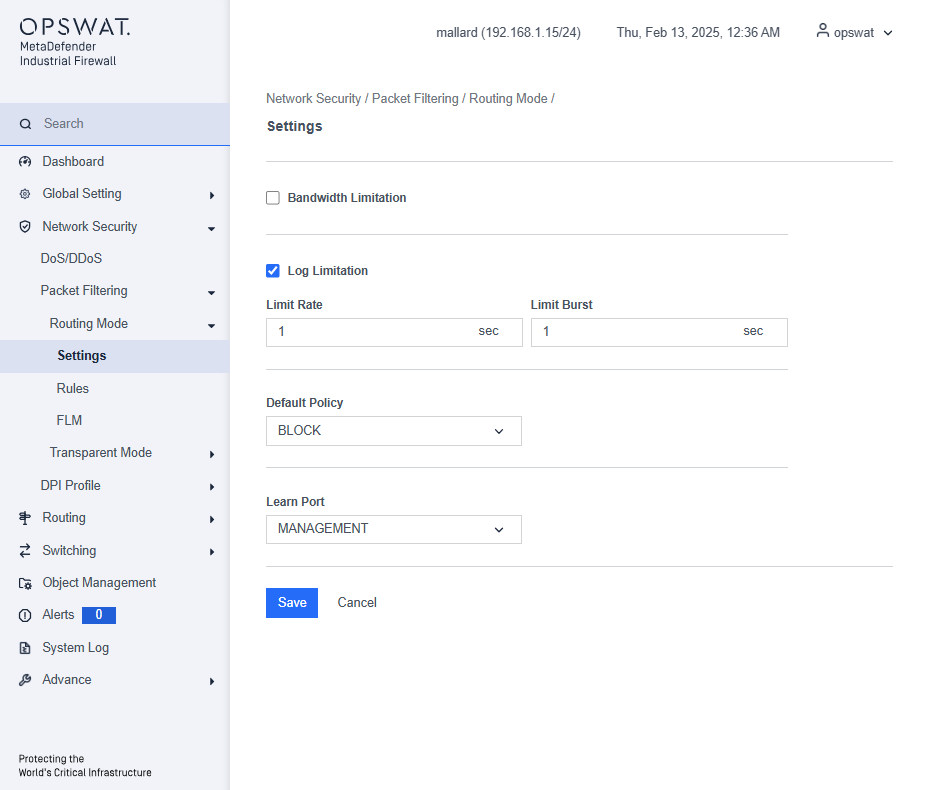
Bandwidth Limitation: Limit the maximum bandwidth in Routing mode.
Log Limitation: Restrict the logging of each firewall rule based on the specified rate limit and burst limit.
Default Policy: The default policy for routing mode is set to “Block.” This can be changed to “Allow” if needed.
Learn Port: Choose the port for learning the traffic.
[Network Security > DoS/DDoS > Routing Mode > Settings]
This page lets you create a firewall rule.
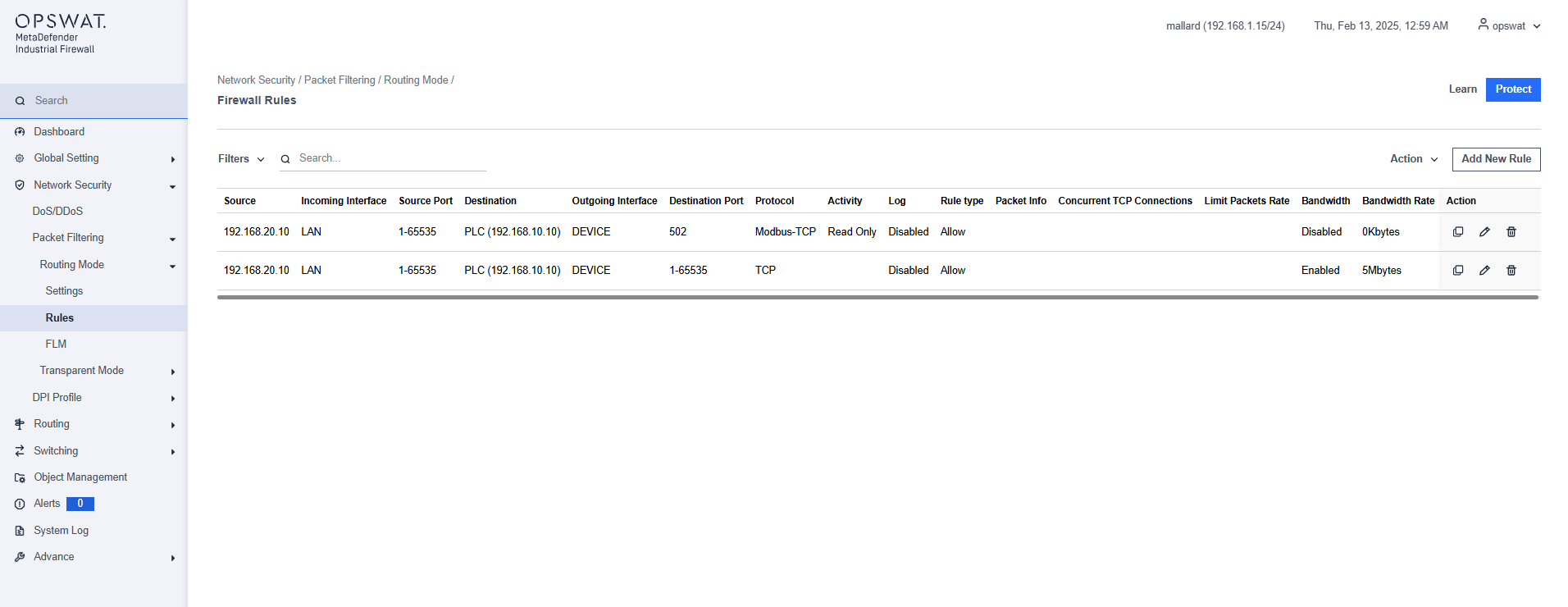
Filter:
- Protocol: Select the protocol to apply filtering rules
- Protected IPs: Specify the IP addresses configured in the Alert settings.
Search: Perform a quick search by IP address, port, or protocol name.
Action:
- Clear All: Remove all existing rules.
- Import: Import the rules from a file.
- Export: Export the current rule to a file.
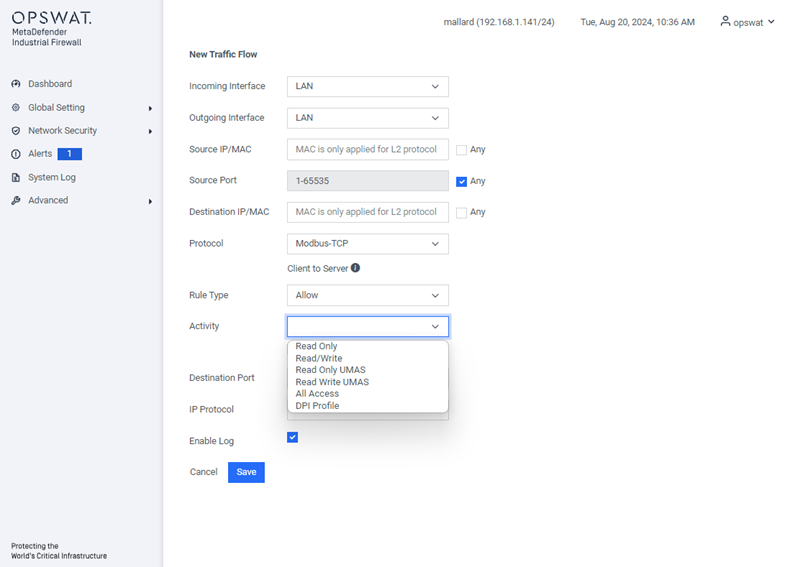
Add New Rule:
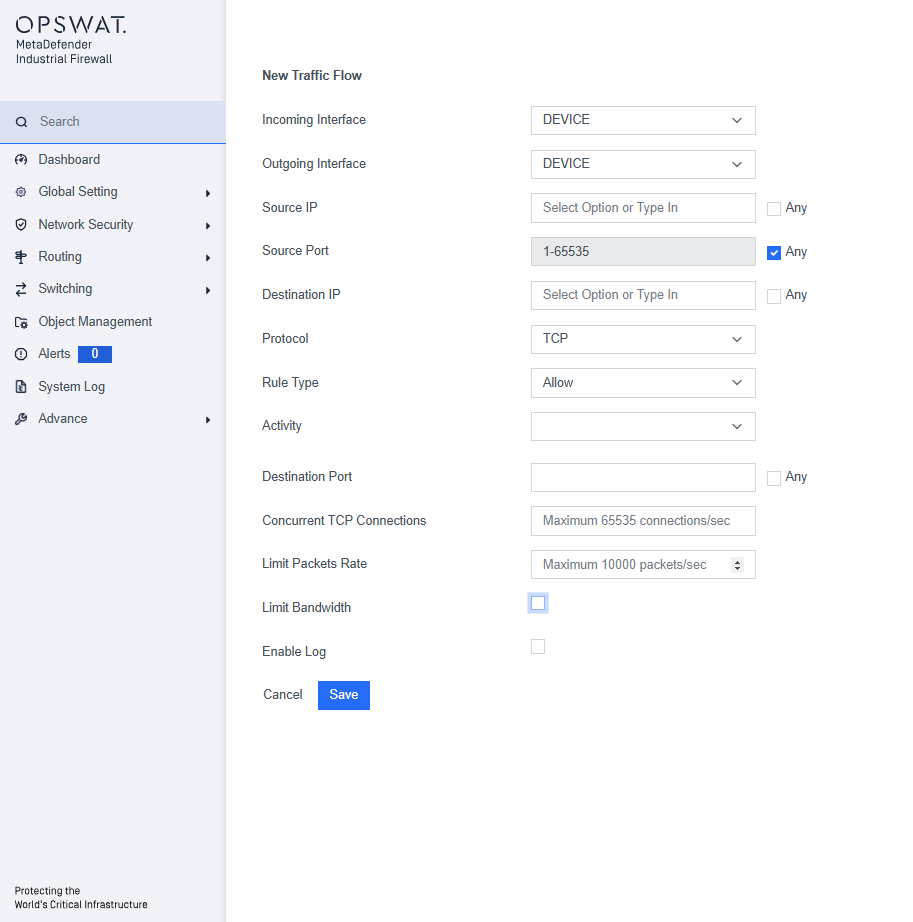
- Incoming Interface: The network interface through which the communication is received.
- Outgoing Interface: The network interface through which the communication is sent.
- Source IP/MAC: The IP or MAC address (only applied for L2 protocol) of the device initiating the communication.
- Source Port: The port number used by the source device to send the communication.
- Destination IP/MAC: The IP or MAC address (only applied for L2 protocol) of the device receiving the communication.
- Protocol: The set of rules governing data formatting, transmission, and reception, allowing devices to communicate (e.g., Modbus, TCP). The available protocols depend on the license. Refer to “License” for more details.
- Rule type: Specifies whether to allow or block the communication.
- Activity: Activities that you see are determined by the protocol and are the types of access that can be allowed on this flow.
- Destination Port: The port number on the destination device, which may be pre-determined by the protocol.
- Concurrent TCP Connections: The number of simultaneous TCP connections allowed.
- Limit Packets Rate: The rate limit for packets to control traffic flow.
- Limit Bandwidth: Restrict the bandwidth for this rule.
- Enable Log: Option to log the activity for this rule.
FLM
[Network Security > Packet Filtering > Routing Mode > FLM]
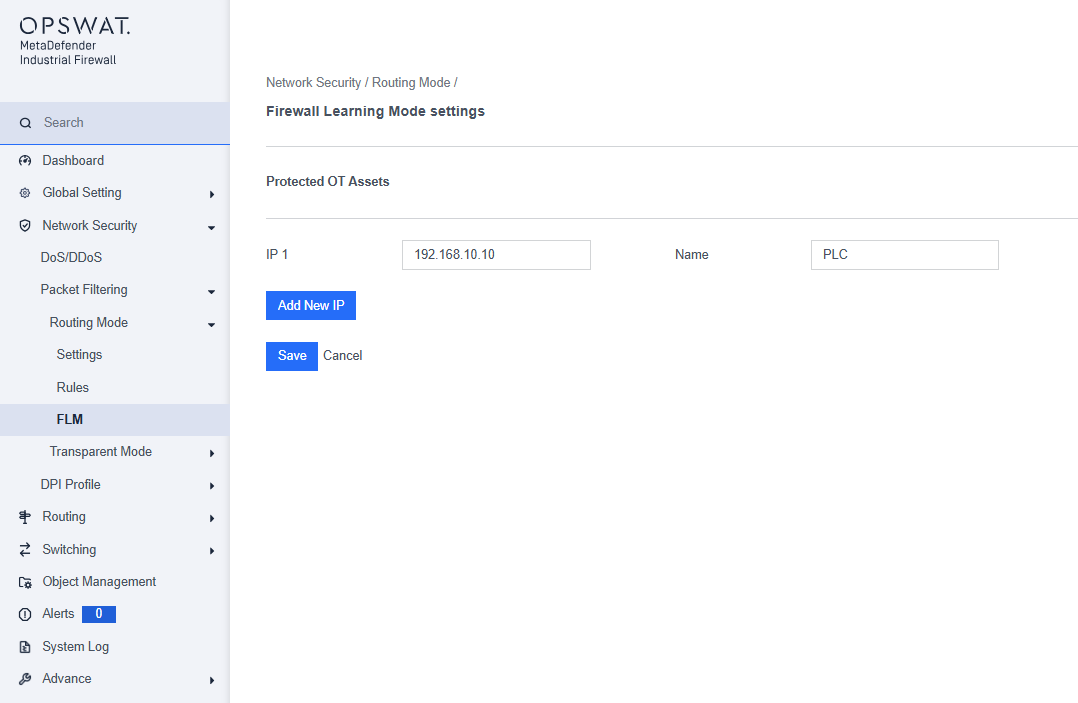
This page allows you to specify the destination IP or MAC (Layer 2) addresses for automatic network traffic learning. It also triggers event notifications for any traffic blocked with these destination IP or MAC addresses.
Transparent Mode
This mode is used when configuring the LAN and DEVICE interfaces to operate in Transparent Mode.
Settings
[Network Security > Transparent Mode > Settings]
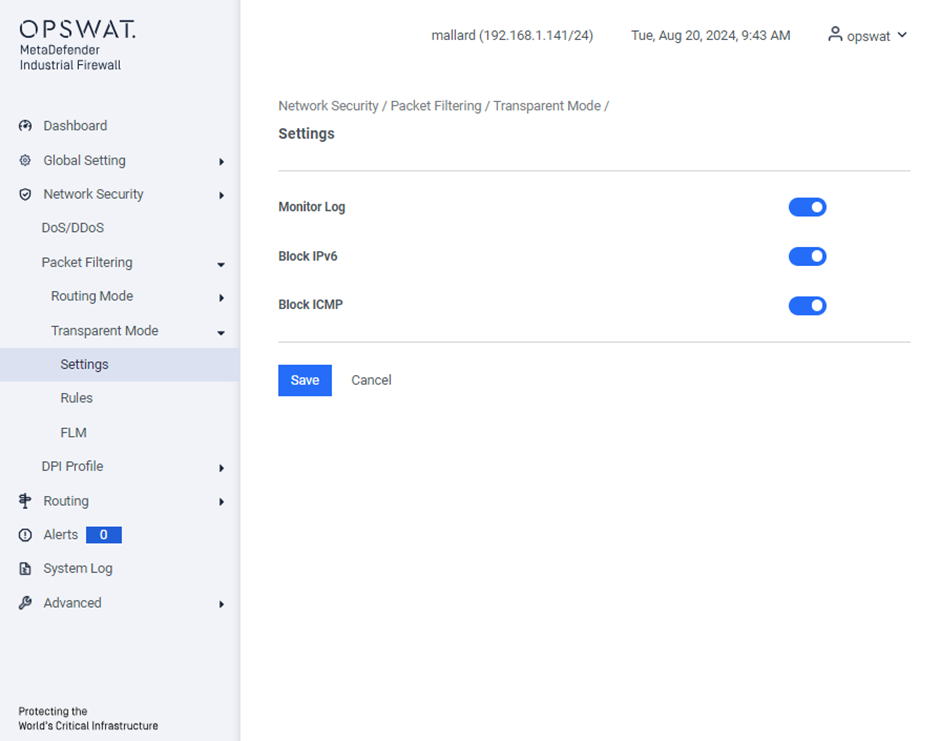
Monitor Log: Enable this option to log all traffic, whether it is allowed or blocked.
Block IPv6: Enable this option to block all IPv6 traffic.
Block ICMP: Enable this option to block ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) traffic.
Rules
[Network Security > Transparent Mode > Rules]
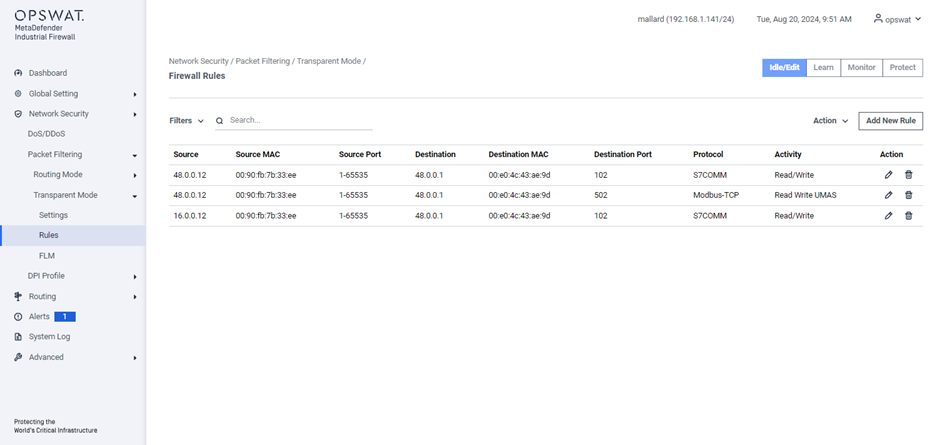
- Protocol: Select the protocol to apply filtering rules.
- Protected IPs: Specify the IP addresses configured in the Alert settings.
Search: Perform a quick search by IP address, port, or protocol name.
Action:
- Clear All: Remove all existing rules.
- Import: Import the rules from a file.
- Export: Export the current rule to a file.
Add New Rule:
- Source IP/MAC: IP/MAC address that sent the communication.
- Destination IP /MAC : IP/MAC address of the device receiving the communication.
- Protocol: Rules that dictate how to format, transmit, and receive data that let devices communicate. For example, Modbus or TCP. The available protocols are determined by the MetaDefender Industrial Firewall license. Refer to “Error! Reference source not found.” for more information.
- Activity: Activities that you see are determined by the protocol and are the types of access that can be allowed on this flow.
- Destination Port: The default port that you see can be determined by the protocol
FLM
[Network Security > Packet Filtering > Transparent Mode > FLM]
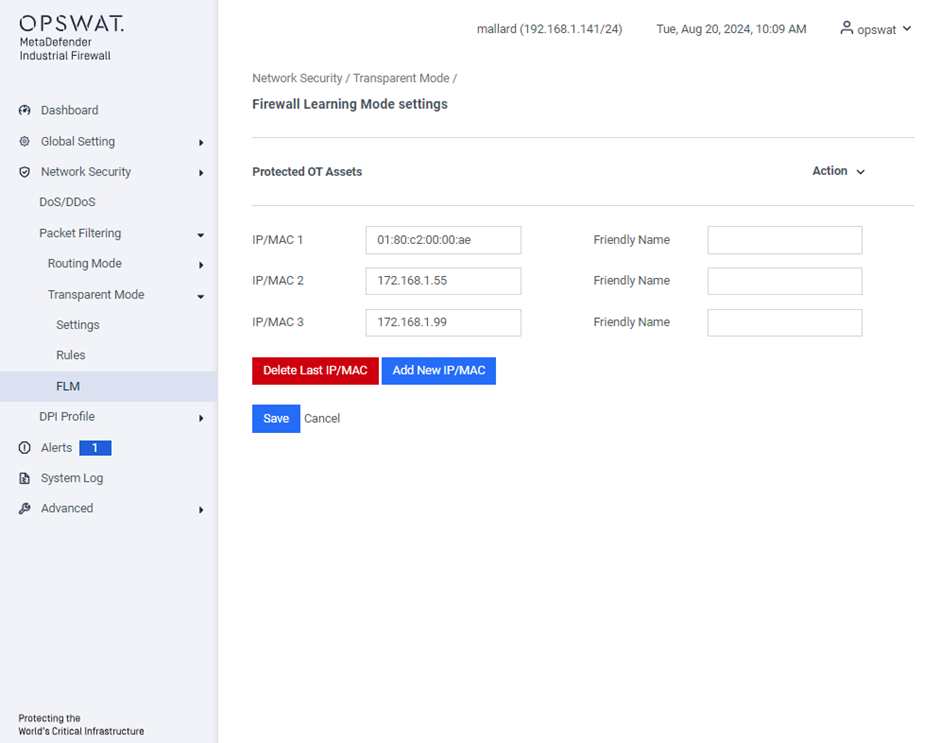
This page allows you to specify the destination IP or MAC (Layer 2) addresses for automatic network traffic learning. It also triggers event notifications for any traffic blocked with these destination IP or MAC addresses.
Configure Modbus Registers
You can configure a new or existing traffic flow to specific MODBUS registers and generate policies that only allow the specific learned registers or register ranges.
For a new traffic flow, click Add New Rule button:
- Protocol: MODBUS
- Activity: Read Only or Read/Write
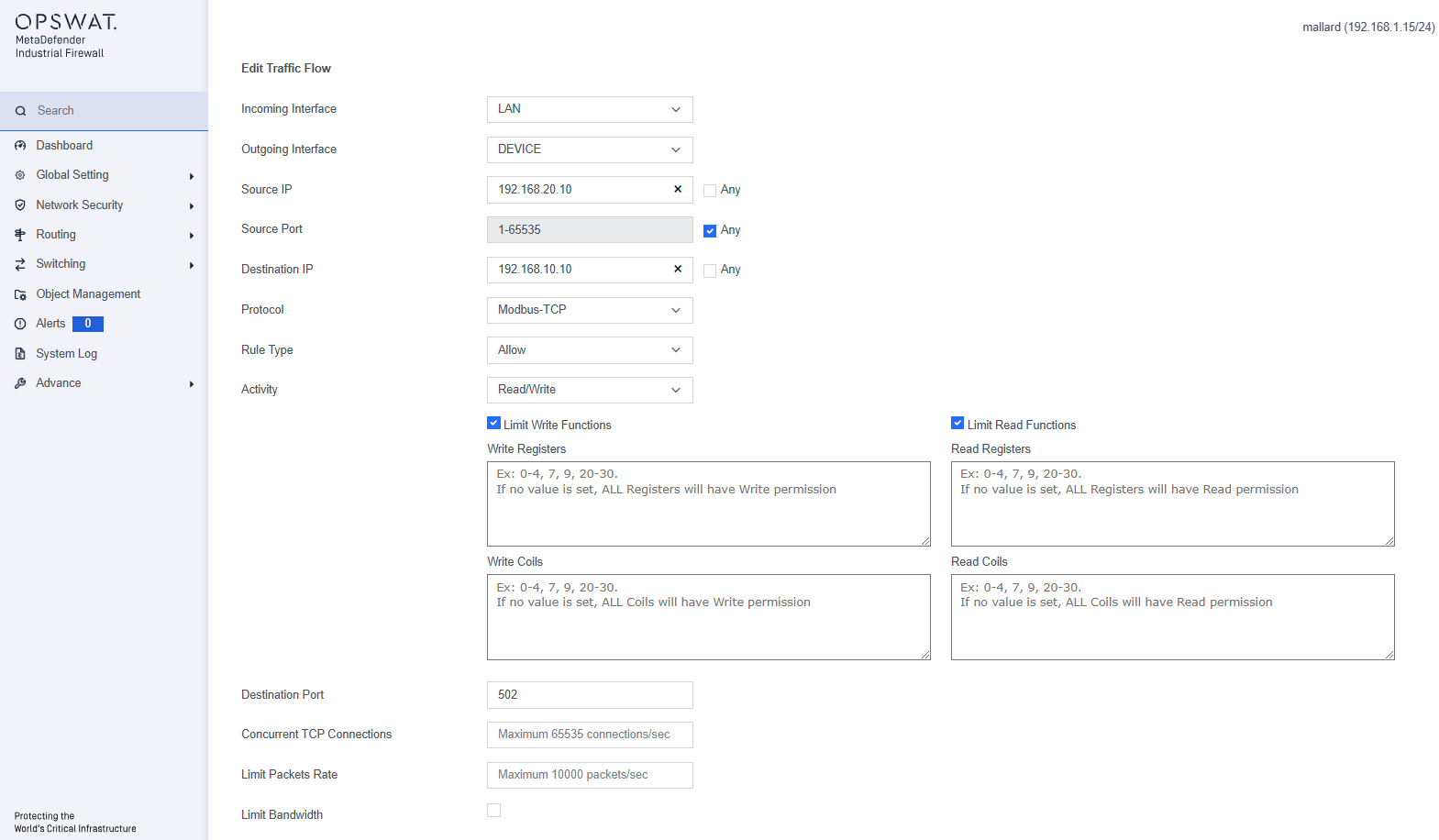
Additional boxes display to configure the MODBUS registers:
- Limit Read Functions Registers: Click to read only specified registers. You must click this box to display the Read Registers box.
- Write Registers: MODBUS registers that the policy will restrict writes to. Specify the registers as a comma-delimited list of individual values or ranges (e.g., 1,2,3,6-10).
- Read Registers: MODBUS registers that the policy will restrict reads to. Specify the registers as a comma-delimited list of individual values or ranges.
DPI Profile
[Network Security > DPI Profile]
The DPI (Deep Packet Inspection) function allows you to monitor and filter data packets, helping to protect your network from undesirable content such as spam or viruses. It inspects data packets for unwanted characteristics and protocol violations by examining both the header and the payload.
In this page, you can create the DPI profile. The device will block any data packets that do not match with the specified profiles.
The menu contains the following protocols:
- Modbus
- DNP3
- MQTT
- PROFINET-PTCP
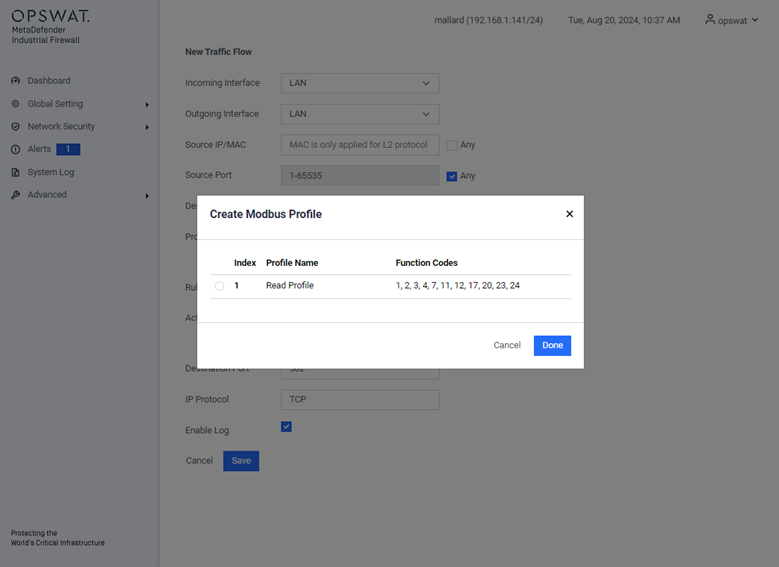
Example Creating Modbus Profile
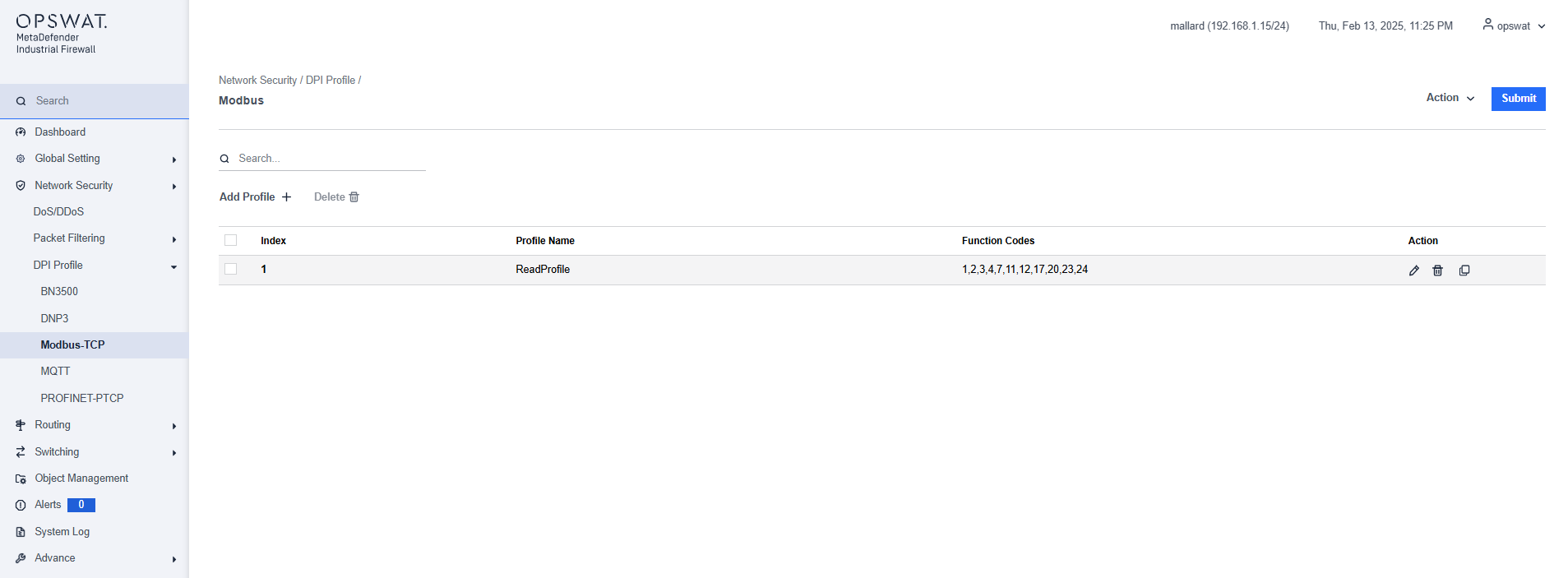
This page allows you to define Modbus TCP-specific profiles. These profiles specify function codes and register or coil addresses. The function codes in the Modbus TCP protocol determine the purpose of the data transfer. The device will block any data packets that violate the specified profiles. If an error is detected, the device can terminate the data connection upon user request. To assist you in defining function codes, predefined function code lists and a function code generator are provided.
- Add Profile: Create a new profile.
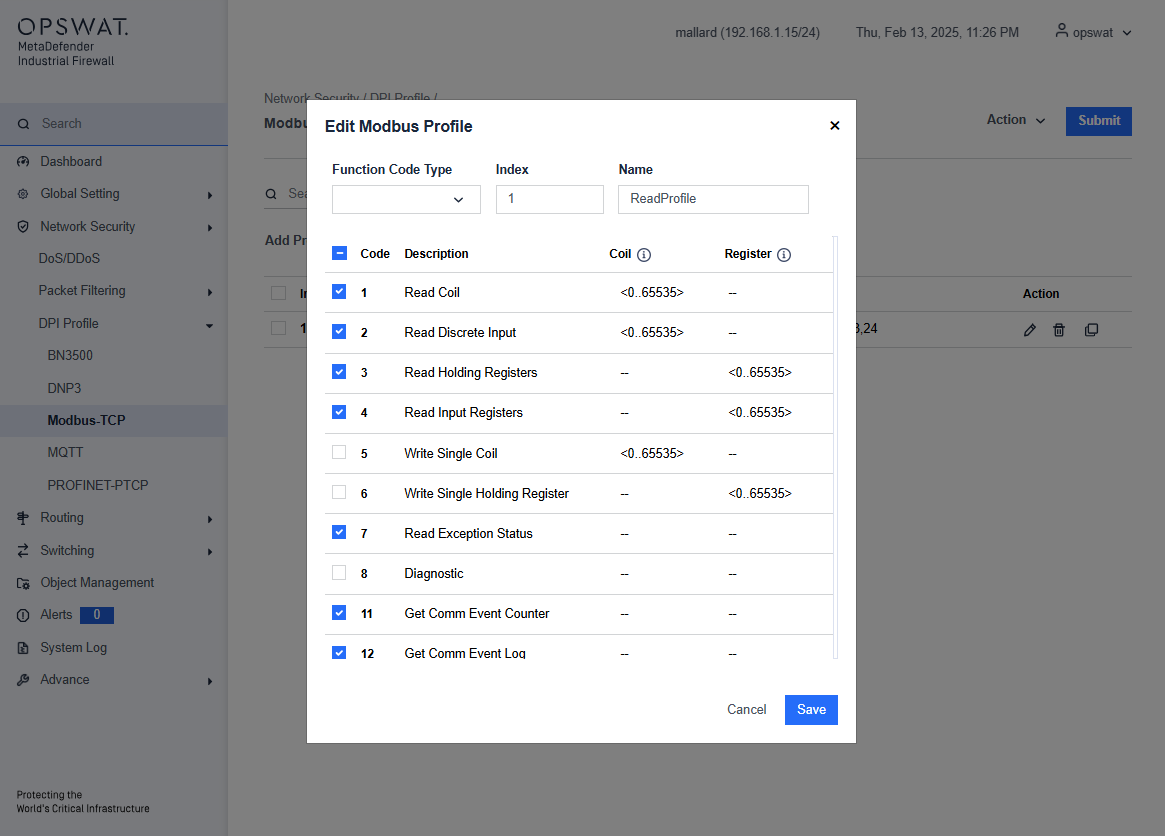
Action:
- Modify the selected profile.
- Remove the profile.
- Duplicate the profile.
Submit: Click this button to save all changes to the profiles.
After creating a profile, it will be available for selection when adding a new rule. You can select the DPI Profile, where the newly created profile will be displayed for use.