Metadefender Core displays detailed information on scan nodes and the status of engine updates including anti-malware engines, archive engines, etc.
Certificates
On this page, path to certificates and private keys for signing scan batches or HTTPS configuration can be given.
- Certificate should be in a Base64-encoded X.509 certificate file (.crt, .cer) format.
- Private key should be a privacy-enhanced electronic mail file (.pem) format and it should not be locked by password.
Adding certificate-key pair to the inventory
- Go to Inventory→Certificates page
- Click on Add new certificate button
- Fill the Add new certificate form by giving a name, a path to certificate file and a path to the corresponding key file
- Click Add button
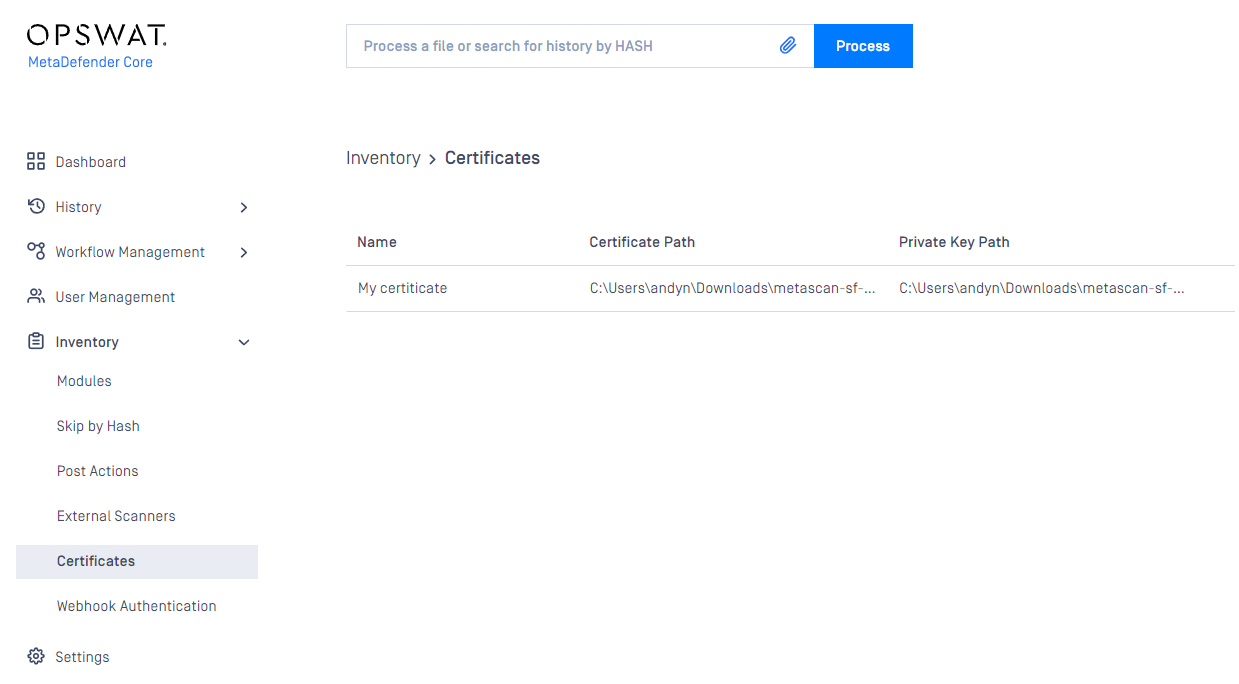
Checking the details of a certificate
By clicking the line of the certificate, the "Certificate viewer" pops up and shows the details of the certificate.
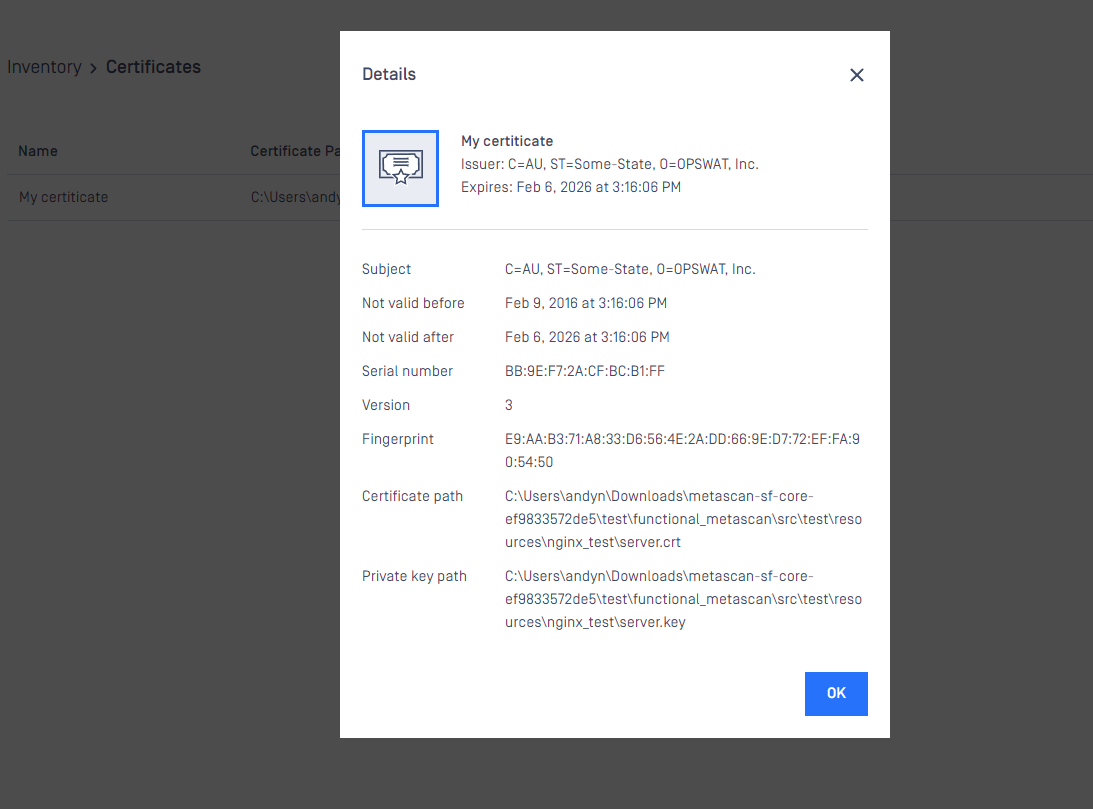
Modifying the name or the paths of a certification
Hover the mouse cursor over the line that is to be modified and click on the pen picto. The Modify certificate modal pops up and the fields can be edited.
The certificate file and the key file should be readable by the user who owns the ometascan process.
Webhook Authentication
While leveraging webhook on MetaDefender Core, the callback connection stays at un-secured by default. To harden the security, MetaDefender Core supports a mutual authentication mode between the server (MetaDefender Core) and client (where the callback is sent to), and prevents the man-in-the-middle attack (scan results could be possibly altered unauthorizedly).
How this security feature works
- Admin user to request MetaDefender Core to generate a private-public key pair (the private key is encrypted within the product, and could not be seen or readable by anyone)
- Admin user to download and keep that public key in their secret vault on the client side (where the callback is sent to).
- Admin user to configure MetaDefender Core to use the private key in a desired workflow rule, for each scan request:
- MetaDefender Core to calculate the signature of scan result using the selected private key.
- MetaDefender Core to include the calculated signature into the callback response header before sending back to client.
- Client side (where the callback is sent to) to use the stored public key to:
- Decrypt the signature included in the callback response header.
- Calculate SHA256 hash checksum from the callback reponse body (which is the entire scan result).
- Compare the calculated SHA256 hash checksum to the hash value decrypted from the callback response header.
MetaDefender Core also supports admin users to configure the user role for whom allowed to see and modify webhook authentication settings.
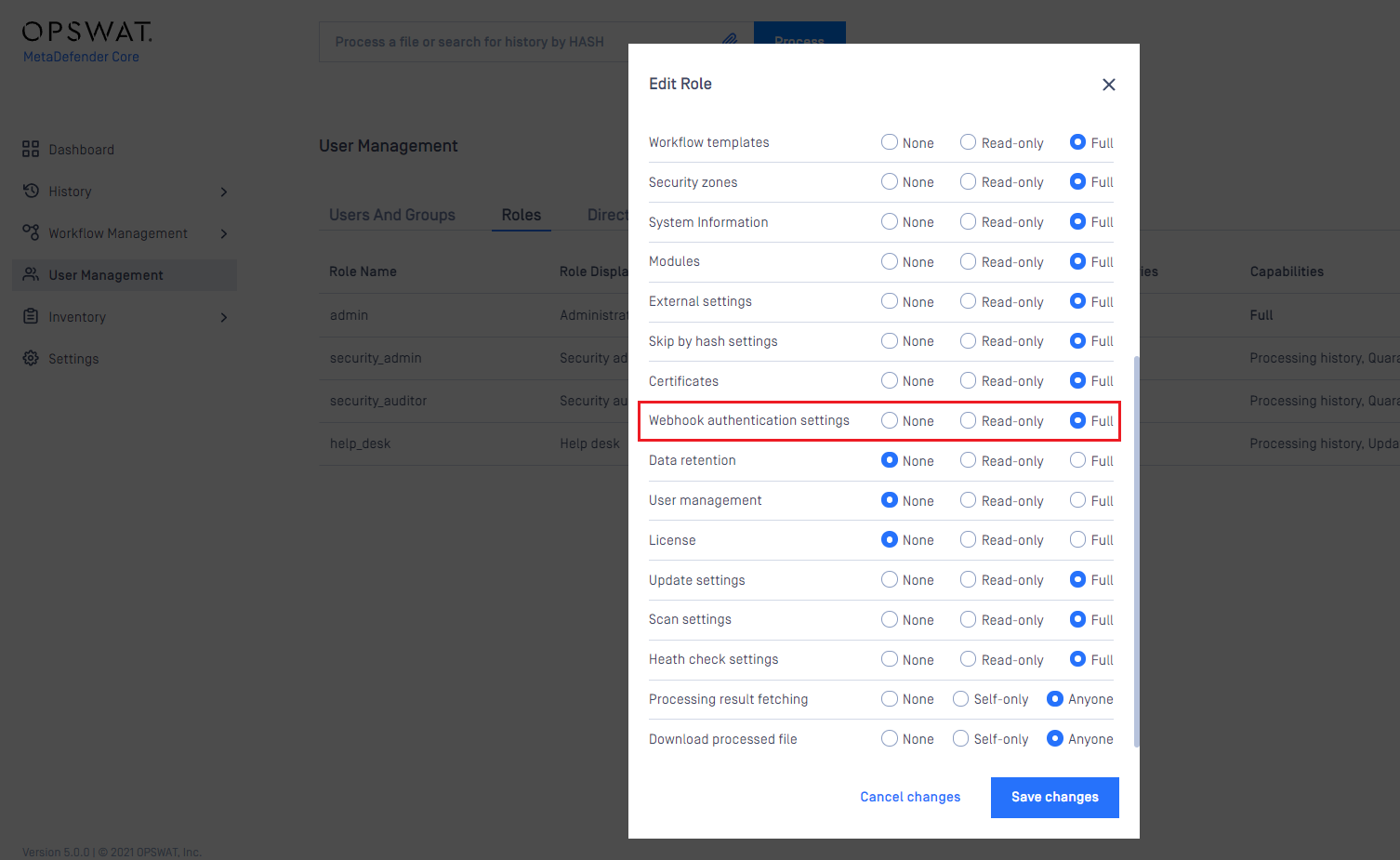
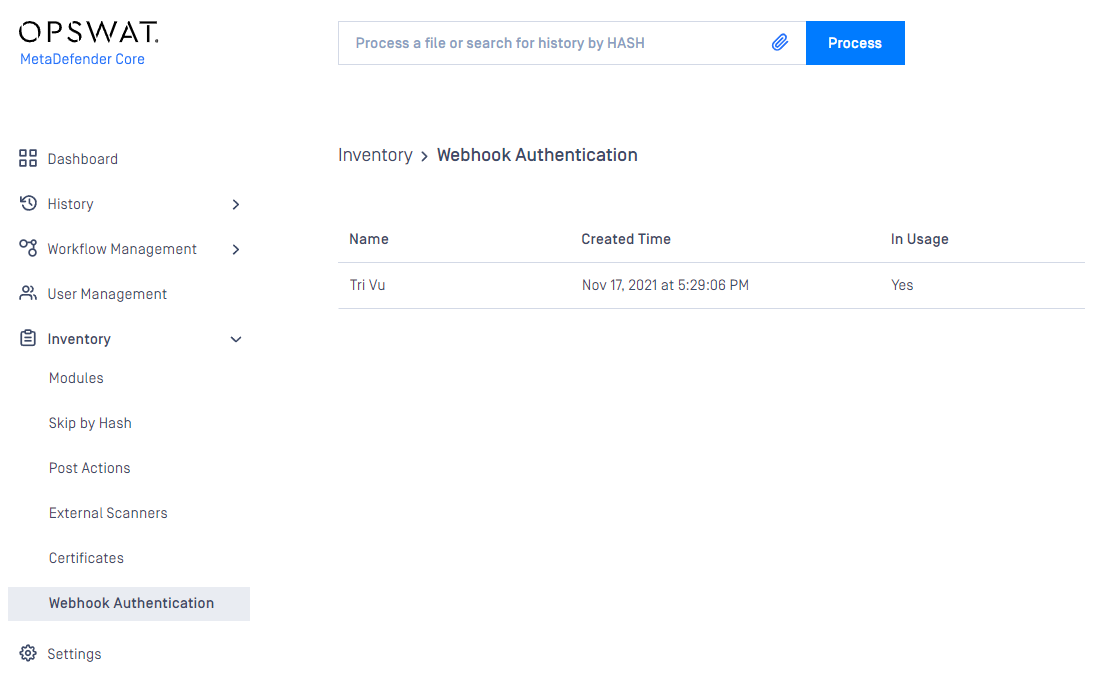
Create a new certificate-key pair for webhook authentication
- Go to Inventory→Webhook Authentication page
- Click on Add certificate button
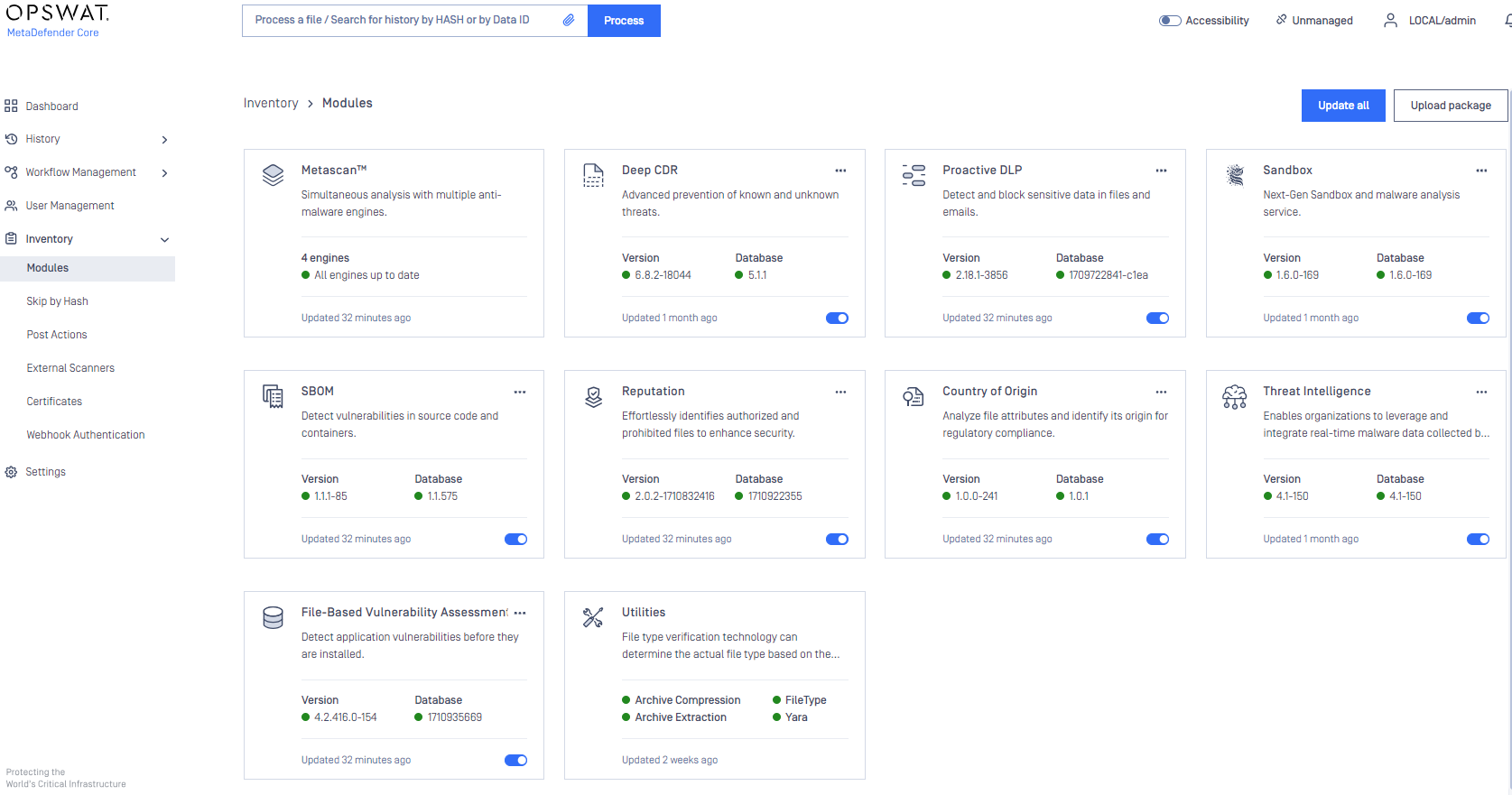
Modules
Engine type details
Under the Modules menu all the installed engines are listed with their details such as
Type of engine. Possible types are
- Anti-malware engine
- Archive engine
- Proactive DLP engine
- Deep CDR engine
- Adaptive Sandbox engine
- Software Bill of Materials engine
- Filetype detection engine
- Reputation engine
- Country of Origin engine
- Utility engine
- Vulnerability detection engine
Elapsed time since last update
Proportion of active and non-active engines of a particular type
Engine version
Version of database the engine is currently using
Engine status (Active/Non-Active)
Engines can be disabled (and re-enabled afterwards) by clicking on the switch at the end of the line that belongs to that particular engine. When an engine is disabled neither the engine nor the corresponding database package is updated and it will be removed from every node.
Pin & Unpin engines (for auto-update prevention)
Engine and its database can be pinned to prevent it from being applied new updates when you allow auto update on Core.
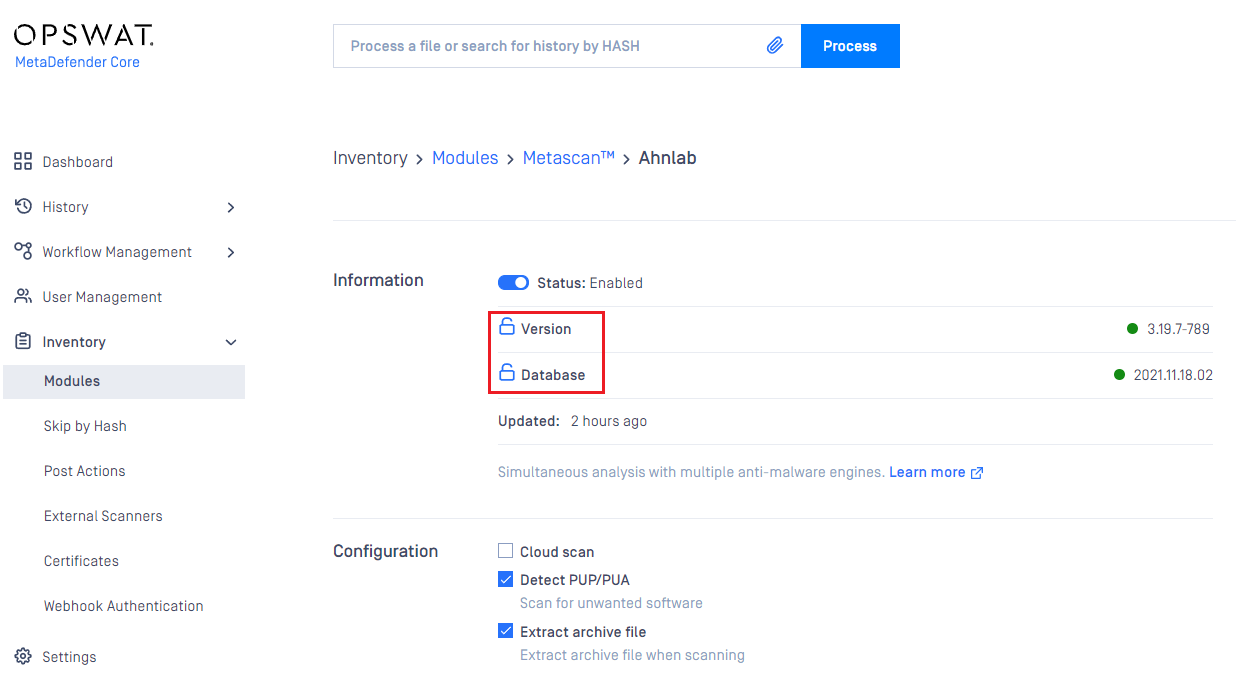
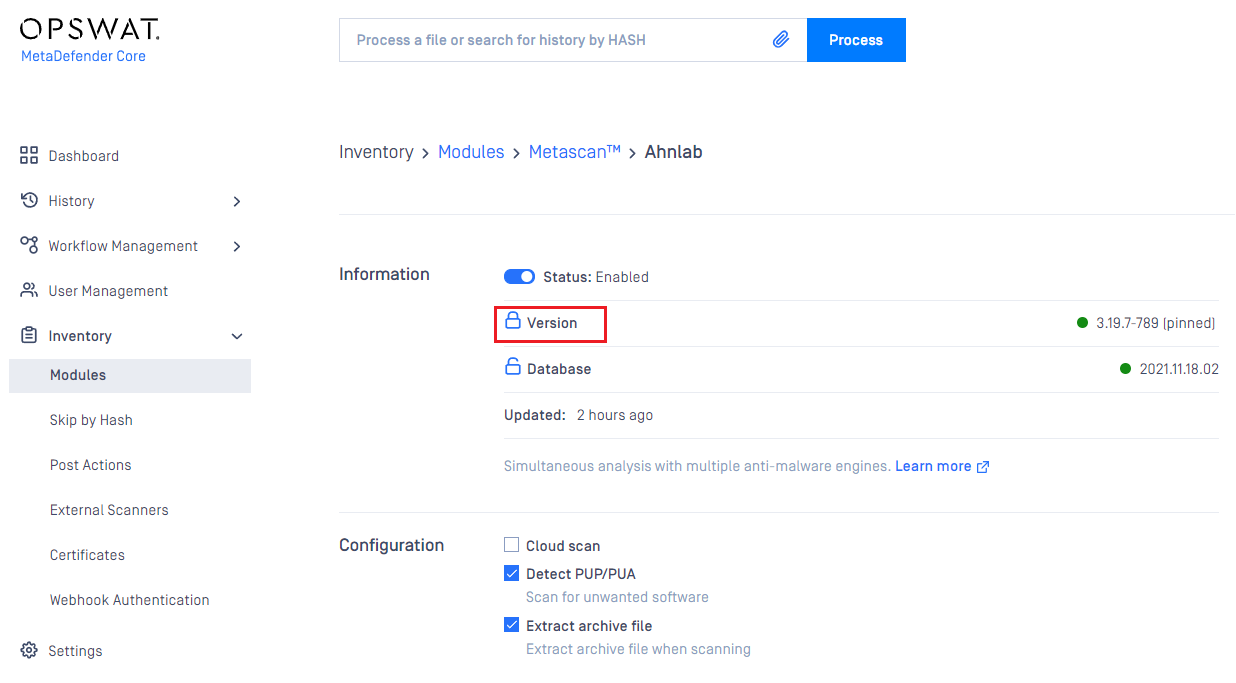
- You can pin engine and database individually on same engine
- When pinned, that means no auto update can be applied on that part (engine / database), even when user triggers "Update All" button
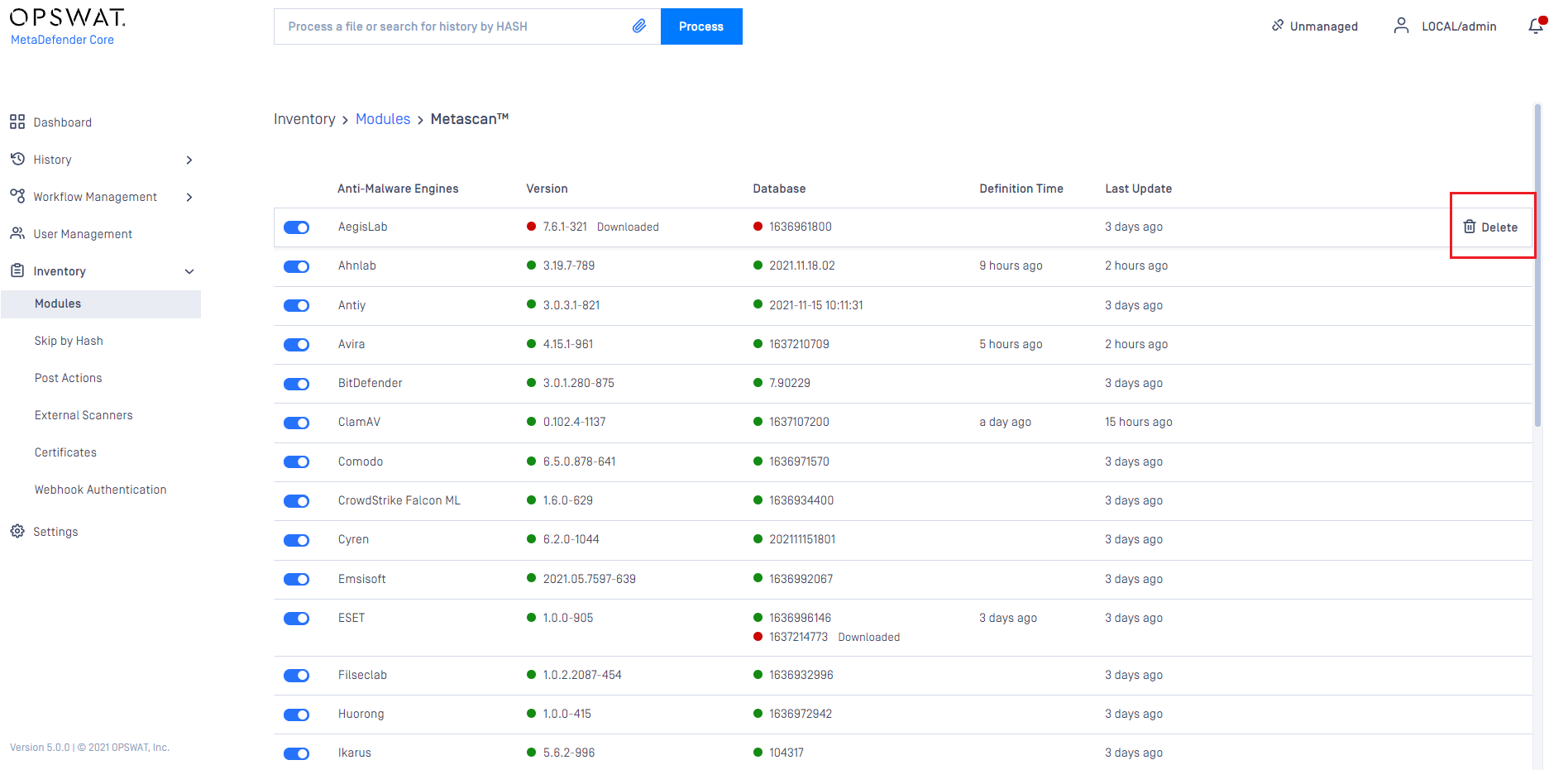
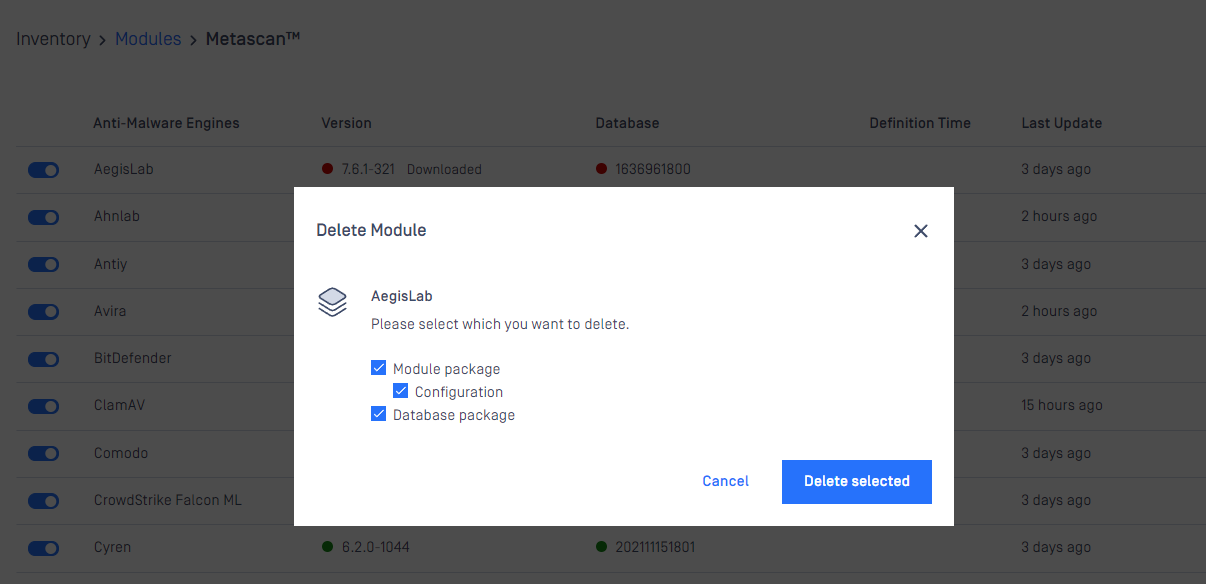
Remove engines (to start over engine download and deployment)
At some points, when engines become problematic and comes to the state of permanent failed, then you may need to remove engine.
Manual updates
To manually trigger update of scan engine and database packages, click on the Update now button.
To provide engine or database packages on your own, select the Upload package option.
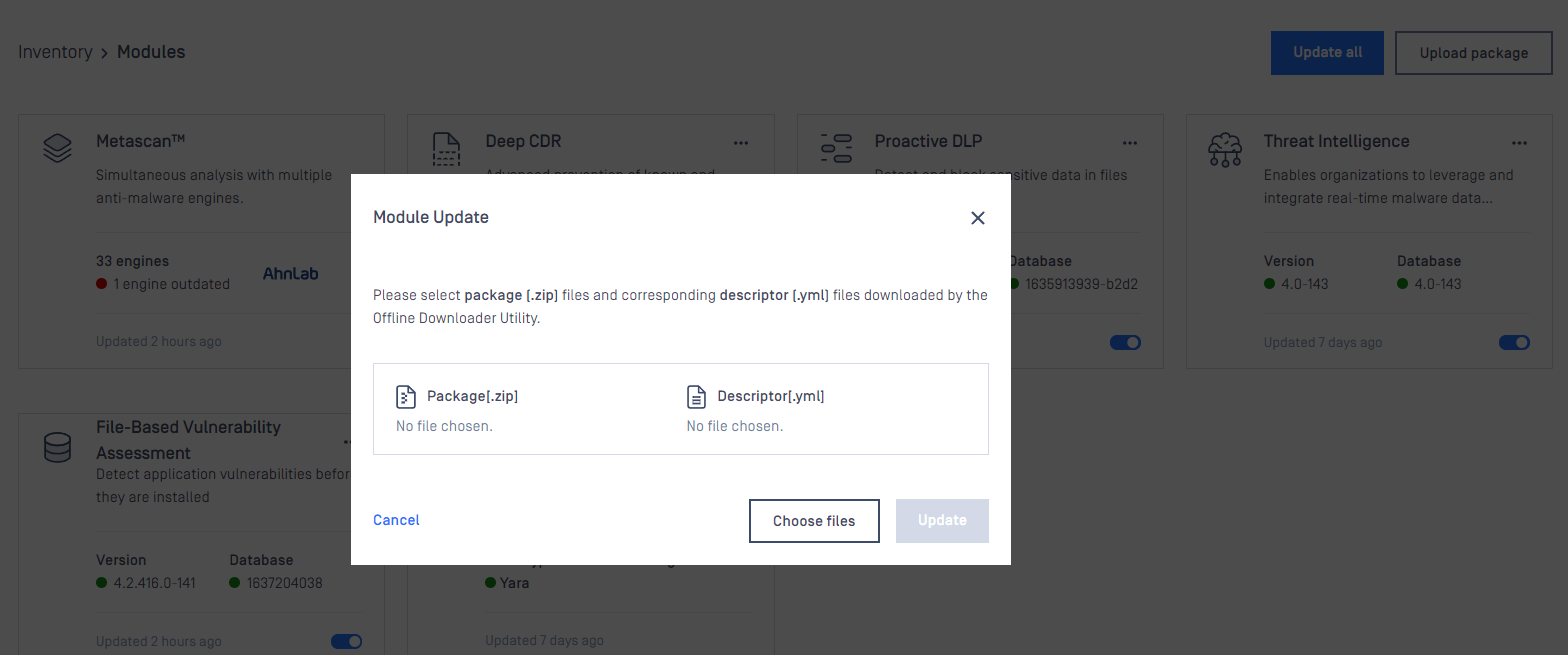
Upload packages
The package should be a ZIP and the descriptor YML file, which can be downloaded with the Update Downloader. Multiple files can be selected.
Engine or database versions that have ever been used on a system won't be accepted as updates.
Configuring engine advanced settings
Some engines advanced settings can be configured.
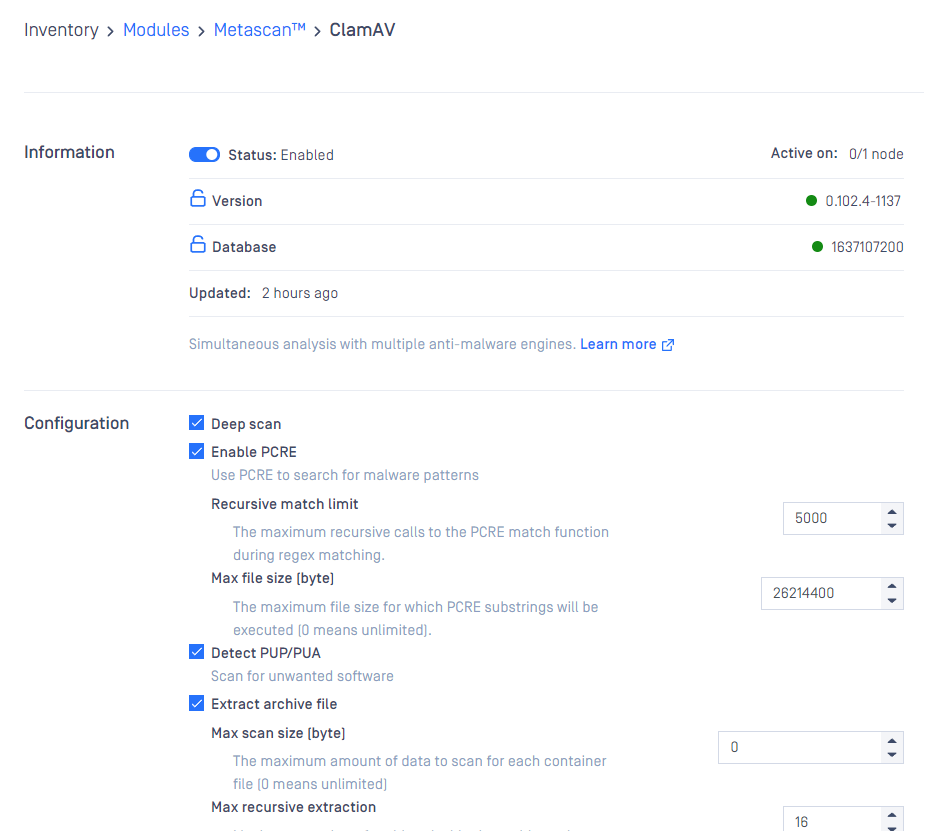
Choose your desired configurations and click Save Settings, then Close.
Skip by hash
This page contains three lists which belong to similar but different features. Note that rules listed in these there features are globally applied, not per workflow.
Skip engines
On this page, users can define rules on what files should be skipped by what engines. That is, a file with the given hash will not be processed by the listed engines.
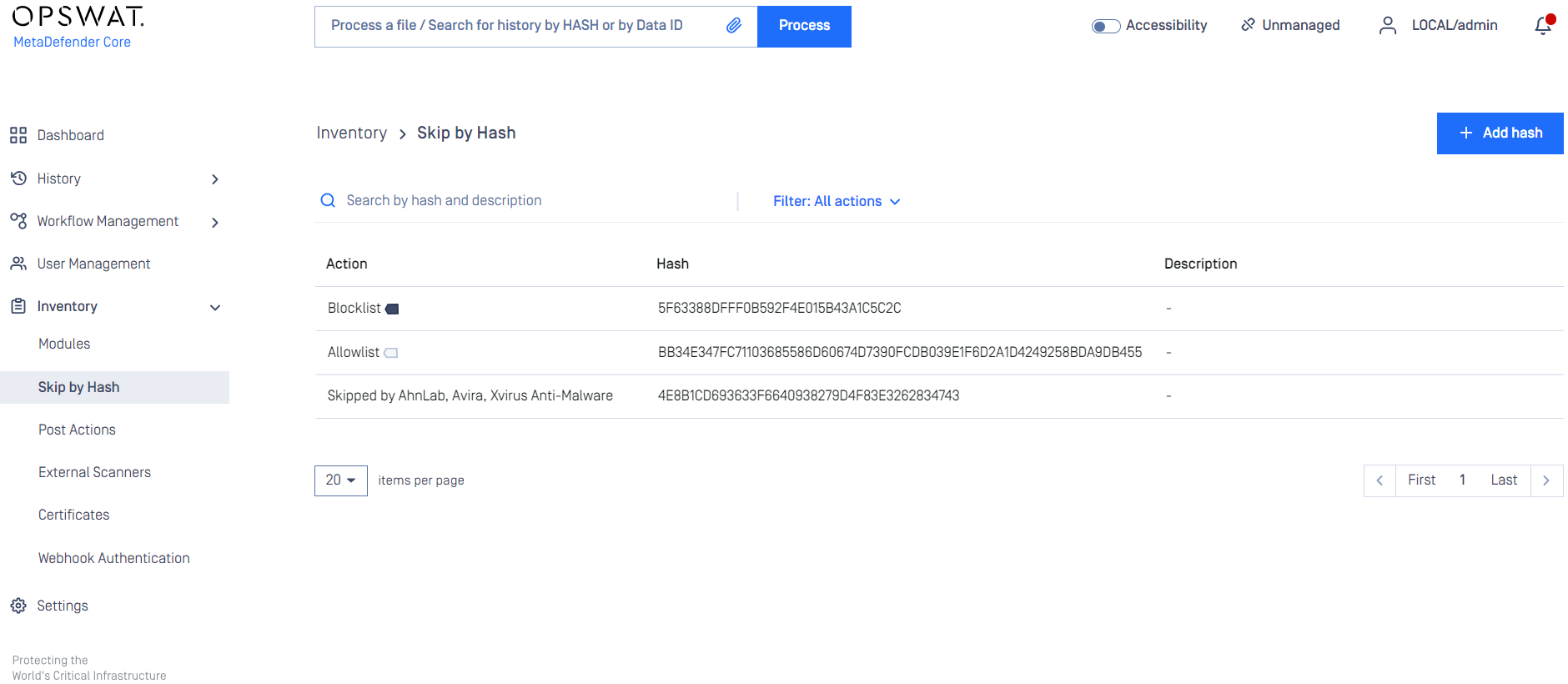
Adding a hash to the Skip engines list
On the Skip by Hash page click the "Add hash" button on the top right. "Add hash" page appears. Hash and at least one engine are mandatory to give, comment is optional. Hash can be either MD5, SHA1 or SHA256. After giving the necessary information and choosing the "Skip engines" action, click on the Add button.
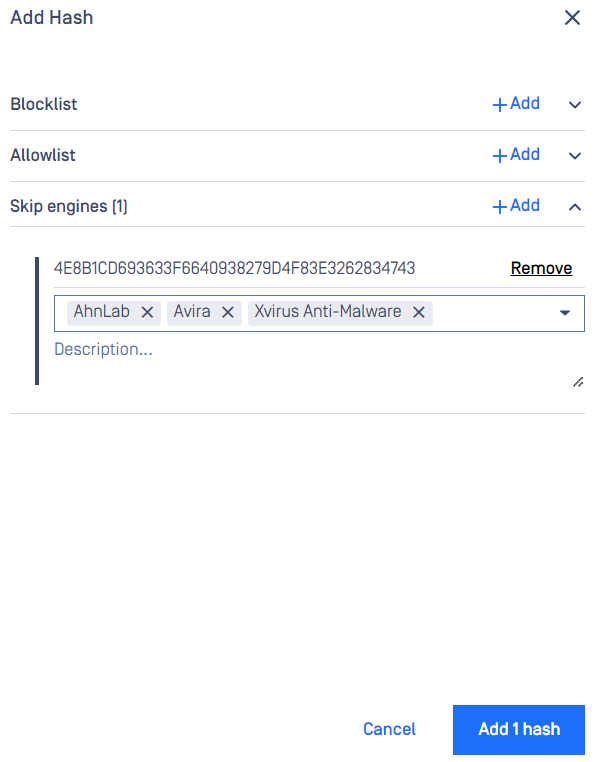
Allowlist
Files whose hashes listed here will be globally allowlisted, so they won't be processed in any workflow and will be allowed.
Blocklist
Files whose hashes listed here will be globally blocklisted, so they won't be processed in any workflow and will be blocked.

